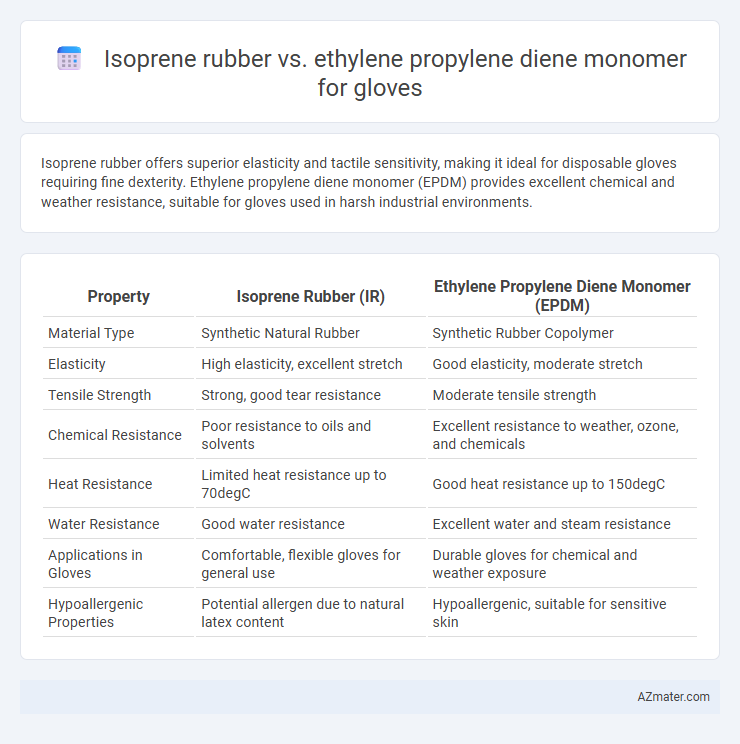
Isoprene rubber offers superior elasticity and tactile sensitivity, making it ideal for disposable gloves requiring fine dexterity. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) provides excellent chemical and weather resistance, suitable for gloves used in harsh industrial environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Isoprene Rubber (IR) | Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic Natural Rubber | Synthetic Rubber Copolymer |
| Elasticity | High elasticity, excellent stretch | Good elasticity, moderate stretch |
| Tensile Strength | Strong, good tear resistance | Moderate tensile strength |
| Chemical Resistance | Poor resistance to oils and solvents | Excellent resistance to weather, ozone, and chemicals |
| Heat Resistance | Limited heat resistance up to 70degC | Good heat resistance up to 150degC |
| Water Resistance | Good water resistance | Excellent water and steam resistance |
| Applications in Gloves | Comfortable, flexible gloves for general use | Durable gloves for chemical and weather exposure |
| Hypoallergenic Properties | Potential allergen due to natural latex content | Hypoallergenic, suitable for sensitive skin |
Introduction to Isoprene Rubber and EPDM
Isoprene rubber (IR) is a synthetic elastomer renowned for its excellent tensile strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance, commonly used in glove manufacturing for its natural rubber-like properties. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) offers superior weather, ozone, and chemical resistance, making it suitable for gloves used in harsh industrial environments. Both materials provide distinct advantages; IR excels in comfort and flexibility, while EPDM withstands prolonged exposure to heat and corrosive substances.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Isoprene rubber (IR) is a natural polymer composed of repeating units of cis-1,4-polyisoprene, characterized by high unsaturation in its chemical structure, which imparts excellent elasticity and tensile strength to gloves. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) features a saturated backbone of ethylene and propylene units combined with a diene monomer that introduces controlled unsaturation, enhancing chemical and weather resistance. The higher degree of unsaturation in isoprene rubber provides superior flexibility and sensitivity, whereas EPDM's saturated structure offers better resistance to heat, ozone, and aging in glove applications.
Physical Properties Differences
Isoprene rubber offers superior tensile strength and elasticity compared to Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM), making it ideal for gloves requiring high flexibility and durability. EPDM exhibits excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering but has lower tensile strength and elongation than Isoprene rubber, which impacts glove performance in dynamic or mechanical stress conditions. The hydrophobic nature of EPDM also results in reduced grip and tactility compared to the more natural feel and softness of Isoprene rubber gloves.
Glove Manufacturing Process: Isoprene vs EPDM
Isoprene rubber offers superior elasticity and tactile sensitivity, making it highly suitable for precision glove manufacturing, whereas EPDM provides enhanced chemical and weather resistance, ideal for gloves used in harsh environments. The glove manufacturing process for isoprene involves intricate polymerization and vulcanization techniques to achieve fine texture and durability, while EPDM manufacturing requires careful control of curing agents to maintain its robustness and flexibility. Choice between isoprene and EPDM in glove production depends on balancing comfort, protection, and application-specific requirements.
Comfort and Fit: User Experience
Isoprene rubber gloves offer superior comfort and fit due to their natural latex-like elasticity and softness, providing excellent tactile sensitivity and flexibility ideal for prolonged use. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) gloves, while highly durable and resistant to chemicals, tend to be less flexible and may feel stiffer, potentially reducing comfort and dexterity for extended wear. Users requiring enhanced sensitivity and snug fit often prefer isoprene rubber gloves over EPDM for tasks demanding precision and comfort.
Durability and Tear Resistance
Isoprene rubber gloves offer excellent elasticity and comfort but have lower durability and tear resistance compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) gloves. EPDM gloves excel in tear resistance and maintain durability under harsh chemical and environmental conditions, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. The molecular structure of EPDM provides superior resistance to ozone, heat, and aging, enhancing glove lifespan significantly over isoprene options.
Chemical and Environmental Resistance
Isoprene rubber offers excellent flexibility and tactile sensitivity but has limited chemical resistance, particularly against oils and solvents, making it less suitable for gloves exposed to harsh chemicals. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) exhibits superior resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and oxidizing agents, as well as excellent weathering and ozone resistance, enhancing glove durability in demanding environments. EPDM's outstanding environmental resistance makes it the preferred choice for gloves used in industrial and outdoor applications where exposure to chemicals and extreme conditions is common.
Cost and Availability in the Glove Market
Isoprene rubber offers moderate cost and is widely used in medical gloves due to its natural latex properties, though supply can be affected by natural rubber market fluctuations. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) is generally less expensive and more readily available, as it is synthetic and not reliant on natural resources, making it a cost-effective alternative in high-volume glove production. Market availability of EPDM gloves is more stable with lower price volatility compared to isoprene rubber gloves, which depend heavily on agricultural output and global demand.
Typical Applications and Industry Preferences
Isoprene rubber excels in medical and surgical gloves due to its superior elasticity, biocompatibility, and tactile sensitivity, making it a preferred choice in healthcare industries. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) gloves are favored in industrial and chemical handling applications for their outstanding resistance to heat, ozone, and a broad range of chemicals. Industry preferences diverge with healthcare sectors prioritizing isoprene for its hypoallergenic properties, while manufacturing and automotive sectors opt for EPDM for durability and chemical resistance.
Summary: Choosing the Right Material for Gloves
Isoprene rubber offers excellent elasticity, softness, and natural latex-like properties, making it suitable for gloves requiring high sensitivity and comfort, especially in medical and laboratory settings. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) provides superior chemical resistance, durability, and weathering properties, ideal for gloves used in industrial environments with exposure to harsh chemicals and outdoor conditions. Selecting between Isoprene rubber and EPDM depends on the glove's intended use, balancing sensitivity and comfort against chemical resistance and durability.
Infographic: Isoprene rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene monomer for Glove
 azmater.com
azmater.com