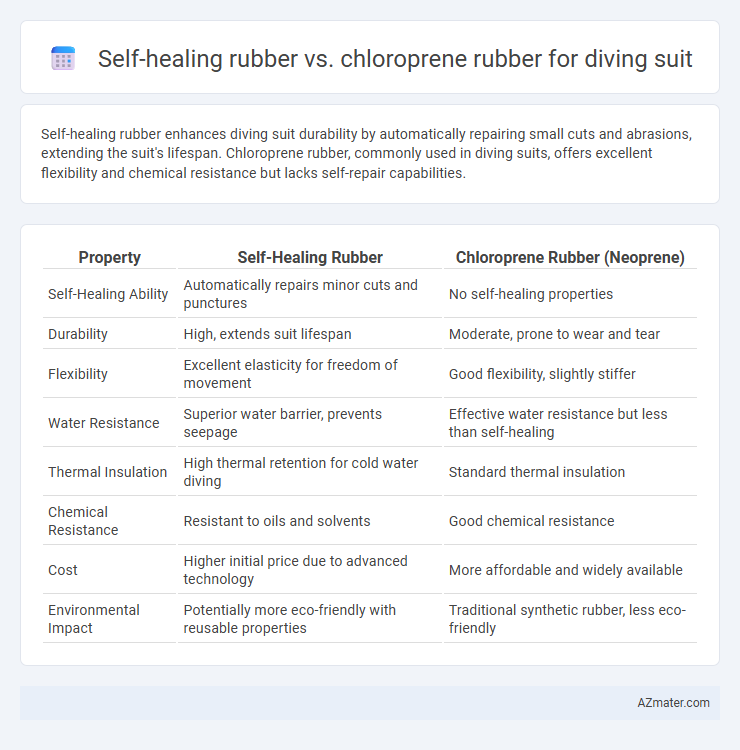
Self-healing rubber enhances diving suit durability by automatically repairing small cuts and abrasions, extending the suit's lifespan. Chloroprene rubber, commonly used in diving suits, offers excellent flexibility and chemical resistance but lacks self-repair capabilities.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Self-Healing Rubber | Chloroprene Rubber (Neoprene) |
|---|---|---|
| Self-Healing Ability | Automatically repairs minor cuts and punctures | No self-healing properties |
| Durability | High, extends suit lifespan | Moderate, prone to wear and tear |
| Flexibility | Excellent elasticity for freedom of movement | Good flexibility, slightly stiffer |
| Water Resistance | Superior water barrier, prevents seepage | Effective water resistance but less than self-healing |
| Thermal Insulation | High thermal retention for cold water diving | Standard thermal insulation |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to oils and solvents | Good chemical resistance |
| Cost | Higher initial price due to advanced technology | More affordable and widely available |
| Environmental Impact | Potentially more eco-friendly with reusable properties | Traditional synthetic rubber, less eco-friendly |
Introduction to Diving Suit Materials
Diving suits commonly use chloroprene rubber due to its excellent flexibility, thermal insulation, and resistance to water and chemicals, making it ideal for underwater conditions. Self-healing rubber, an emerging material, offers the advantage of repairing minor cuts and abrasions autonomously, potentially extending the suit's lifespan and durability in harsh marine environments. While chloroprene remains the industry standard, innovations in self-healing polymers could revolutionize diving suit materials by enhancing safety and reducing maintenance needs.
Overview of Self-Healing Rubber
Self-healing rubber is an innovative material that autonomously repairs minor cuts and punctures, significantly extending the durability of diving suits compared to traditional Chloroprene rubber, which lacks this capability. This advanced polymer incorporates dynamic covalent bonds or microcapsules filled with healing agents, enabling the restoration of structural integrity underwater. The enhanced longevity and reduced maintenance requirements make self-healing rubber a superior choice for high-performance diving applications.
Chloroprene Rubber: Properties and Applications
Chloroprene rubber, commonly known as neoprene, offers excellent resistance to water, oils, and temperature variations, making it the preferred material for diving suits. Its inherent flexibility, durability, and resistance to UV radiation and chemical degradation ensure prolonged performance underwater. Widely used in wetsuits, snorkeling gear, and diving gloves, chloroprene rubber provides thermal insulation and enhances comfort for divers in various aquatic environments.
Durability and Tear Resistance Comparison
Self-healing rubber exhibits superior durability and tear resistance compared to chloroprene rubber in diving suits, as its molecular structure enables automatic repair of micro-cracks, extending suit lifespan under harsh underwater conditions. Chloroprene rubber, while offering good elasticity and chemical resistance, tends to degrade faster when exposed to repeated stress and abrasive environments typical in diving activities. The enhanced tear resistance of self-healing rubber significantly reduces the risk of suit failure, providing divers with improved safety and cost-efficiency over time.
Flexibility and Comfort Underwater
Self-healing rubber enhances flexibility and comfort underwater by restoring its molecular structure after minor damage, ensuring consistent flexibility during dives. Chloroprene rubber, commonly used in diving suits, offers excellent elongation and resilience but lacks self-repair capabilities, potentially reducing comfort over time due to wear and tear. The self-healing property significantly improves durability and maintains suit elasticity, translating into better underwater movement and prolonged comfort for divers.
Self-Healing Mechanisms in Diving Suits
Self-healing rubber used in diving suits incorporates microcapsules or dynamic covalent bonds that autonomously repair punctures and abrasions, significantly extending the suit's durability underwater. Chloroprene rubber, commonly known as neoprene, offers excellent flexibility and thermal insulation but lacks intrinsic self-repair capabilities, necessitating manual patching for damage. Innovations in self-healing mechanisms enhance diving suit safety and longevity by reducing maintenance frequency and ensuring consistent material integrity in demanding marine environments.
Thermal Insulation Performance
Self-healing rubber offers enhanced thermal insulation performance compared to chloroprene rubber due to its ability to maintain material integrity and reduce micro-cracks that cause heat loss in diving suits. Chloroprene rubber, commonly used in wetsuits, provides reliable insulation but can degrade over time, leading to diminished heat retention. The self-healing properties improve durability and consistent thermal protection critical for prolonged underwater activities.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Self-healing rubber used in diving suits offers enhanced sustainability by reducing waste through its ability to repair minor damages, extending the material's lifespan compared to traditional chloroprene rubber. Chloroprene rubber, while durable and widely used in diving gear, poses environmental challenges due to the energy-intensive production process and potential release of hazardous chemicals during manufacturing and disposal. Selecting self-healing rubber contributes to a lower ecological footprint by minimizing replacement frequency and decreasing overall material consumption in underwater equipment.
Cost Effectiveness and Availability
Self-healing rubber offers improved durability and extended lifespan for diving suits, reducing replacement frequency and long-term costs despite higher initial prices. Chloroprene rubber, widely available and cost-effective, provides reliable performance and good chemical resistance, making it a standard choice in the diving industry. Evaluation of total cost-effectiveness favors self-healing rubber in demanding environments, while chloroprene suits budget-conscious buyers with easier accessibility.
Future Trends in Diving Suit Technology
Self-healing rubber offers significant advancements over traditional chloroprene rubber in diving suit technology by enhancing durability and reducing maintenance through its ability to autonomously repair minor punctures and abrasions. This innovation promotes extended suit lifespan and increased safety for divers operating in extreme underwater environments, aligning with the industry's push towards sustainable and high-performance materials. Future trends indicate a growing integration of self-healing polymers with smart sensors to provide real-time damage detection and adaptive thermal regulation in next-generation diving suits.
Infographic: Self-healing rubber vs Chloroprene rubber for Diving suit
 azmater.com
azmater.com