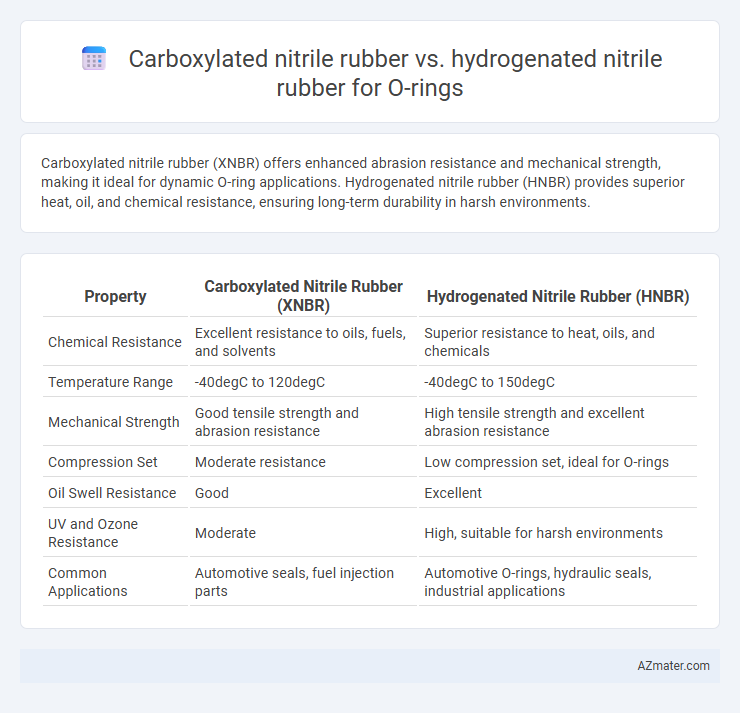
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers enhanced abrasion resistance and mechanical strength, making it ideal for dynamic O-ring applications. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior heat, oil, and chemical resistance, ensuring long-term durability in harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR) | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents | Superior resistance to heat, oils, and chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -40degC to 150degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Good tensile strength and abrasion resistance | High tensile strength and excellent abrasion resistance |
| Compression Set | Moderate resistance | Low compression set, ideal for O-rings |
| Oil Swell Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| UV and Ozone Resistance | Moderate | High, suitable for harsh environments |
| Common Applications | Automotive seals, fuel injection parts | Automotive O-rings, hydraulic seals, industrial applications |
Introduction to Nitrile Rubber O-Rings
Nitrile rubber O-rings, commonly used in sealing applications, offer excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals. Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) enhances abrasion resistance and mechanical strength through carboxyl group cross-linking, making it suitable for dynamic sealing under harsh conditions. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior heat, ozone, and chemical resistance due to hydrogenation of the nitrile structure, ideal for high-temperature and aggressive environments.
Overview of Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR)
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) is a high-performance elastomer known for its exceptional tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and enhanced chemical resistance compared to standard nitrile rubber. XNBR contains carboxyl groups that improve its cross-linking density, resulting in superior mechanical properties and resilience in harsh environments, making it ideal for O-ring applications subjected to dynamic stress and aggressive fluids. Its resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents, combined with good low-temperature flexibility, distinguishes it from hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR), which offers higher thermal stability but comparatively lower abrasion resistance.
Overview of Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR)
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) is a high-performance elastomer known for its exceptional resistance to heat, ozone, and chemical degradation, making it ideal for O-ring applications in harsh environments. Compared to Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR), HNBR offers superior mechanical strength and improved aging properties, particularly in automotive and industrial sealing solutions. HNBR's enhanced stability at temperatures up to 150degC and its excellent oil and fuel resistance contribute significantly to the longevity and reliability of O-rings.
Material Composition and Chemical Structure
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) features carboxyl groups added to the conventional nitrile rubber polymer, enhancing its polarity and improving oil, fuel, and chemical resistance in O-ring applications. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) undergoes selective hydrogenation of carbon-carbon double bonds in nitrile rubber, resulting in a saturated polymer backbone with superior heat, ozone, and oxidative resistance. The presence of carboxyl groups in XNBR improves abrasion resistance and tensile strength, whereas the saturated structure of HNBR offers enhanced durability under extreme temperatures and aggressive chemical environments.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR), making it ideal for high-wear O-ring applications. HNBR provides enhanced elasticity, excellent compression set resistance, and greater thermal stability, which improves sealing performance in high-temperature environments. Both materials exhibit strong chemical resistance, but HNBR outperforms XNBR in oil and fuel exposure, extending O-ring service life in aggressive conditions.
Temperature Resistance and Environmental Suitability
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior low-temperature flexibility down to -40degC but has limited heat resistance up to around 120degC, making it suitable for applications requiring moderate thermal stability and enhanced oil resistance. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) withstands higher temperatures up to 150degC and exhibits excellent resistance to ozone, chemicals, and environmental degradation, ideal for demanding automotive and industrial O-ring seals. Choosing between XNBR and HNBR depends on specific temperature exposure and environmental conditions, with HNBR favored for high-heat and harsh environments due to its enhanced durability and aging resistance.
Chemical Compatibility and Performance
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers enhanced oil and fuel resistance with improved abrasion resistance, making it suitable for O-rings exposed to petroleum-based fluids and slightly polar chemicals. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and ozone resistance, performing well in high-temperature applications and aggressive chemicals such as ozone, acids, and alkalis. While XNBR excels in applications requiring dynamic flexibility and chemical swell resistance, HNBR outperforms in durability and chemical compatibility under harsh environmental conditions.
Application Areas for XNBR and HNBR O-Rings
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) O-rings are widely used in automotive fuel systems, hydraulic equipment, and industrial applications requiring strong oil, fuel, and chemical resistance combined with improved abrasion resistance. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) O-rings excel in high-temperature environments, aerospace, and oil and gas industries due to their superior thermal stability, resistance to ozone, oxidation, and mechanical properties under extreme conditions. Both materials serve critical sealing roles but differ significantly in performance based on temperature range and chemical exposure in applications.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) generally offers lower material costs compared to hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR), making it a budget-friendly choice for standard O-ring applications with moderate chemical and temperature resistance. HNBR commands a higher price due to its superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and durability, often justifying the investment in critical or high-performance sealing environments. Availability for XNBR is widespread across multiple manufacturers, while HNBR, though available globally, may face supply constraints or extended lead times depending on specific grades and demand fluctuations in industries like automotive and oil & gas.
How to Choose Between XNBR and HNBR for O-Rings
Choosing between carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) and hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) for O-rings depends on the specific application environment and performance requirements. XNBR offers enhanced abrasion resistance and tensile strength due to its carboxyl groups, making it ideal for applications involving mechanical wear and dynamic seals. HNBR provides superior heat, chemical, and ozone resistance with excellent compression set properties, making it suitable for high-temperature and chemically aggressive environments.
Infographic: Carboxylated nitrile rubber vs Hydrogenated nitrile rubber for O-ring
 azmater.com
azmater.com