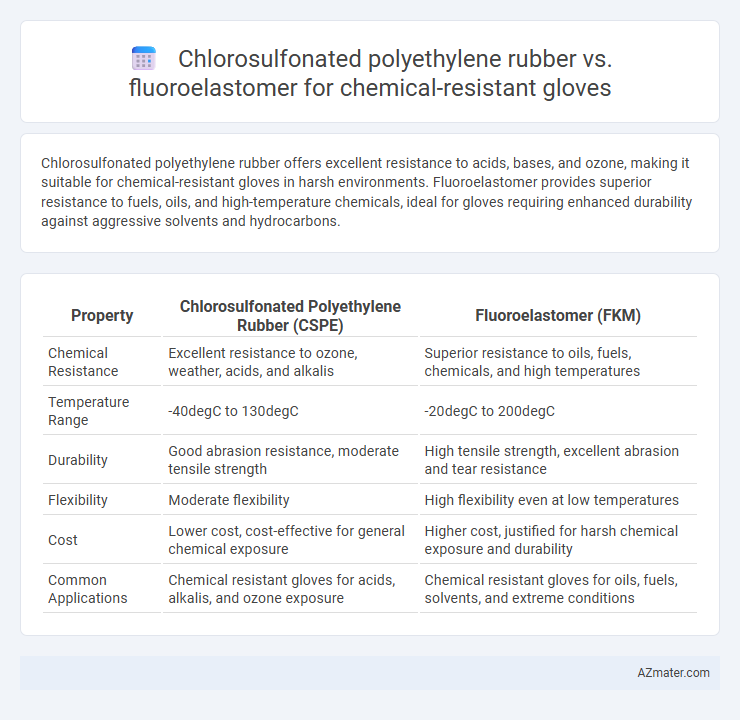
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber offers excellent resistance to acids, bases, and ozone, making it suitable for chemical-resistant gloves in harsh environments. Fluoroelastomer provides superior resistance to fuels, oils, and high-temperature chemicals, ideal for gloves requiring enhanced durability against aggressive solvents and hydrocarbons.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene Rubber (CSPE) | Fluoroelastomer (FKM) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to ozone, weather, acids, and alkalis | Superior resistance to oils, fuels, chemicals, and high temperatures |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 130degC | -20degC to 200degC |
| Durability | Good abrasion resistance, moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength, excellent abrasion and tear resistance |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | High flexibility even at low temperatures |
| Cost | Lower cost, cost-effective for general chemical exposure | Higher cost, justified for harsh chemical exposure and durability |
| Common Applications | Chemical resistant gloves for acids, alkalis, and ozone exposure | Chemical resistant gloves for oils, fuels, solvents, and extreme conditions |
Introduction to Chemical Resistant Gloves
Chemical resistant gloves are essential personal protective equipment designed to shield hands from hazardous chemicals, oils, and solvents encountered in industrial and laboratory environments. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber offers excellent resistance to oils, acids, and oxidizing agents with superior durability and weather resistance. Fluoroelastomer gloves provide outstanding chemical resistance against a wide range of solvents, fuels, and hydrocarbons, making them ideal for high-performance applications where exposure to aggressive chemicals is frequent.
Overview of Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene Rubber (CSM)
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent resistance to chemicals, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for chemical-resistant glove applications. CSM offers strong abrasion resistance and maintains flexibility over a wide temperature range, enhancing durability during prolonged use in harsh environments. Compared to fluoroelastomers, CSM provides superior resistance to acids, alkalis, and oxidizing agents while being more cost-effective for general chemical protection.
Overview of Fluoroelastomer (FKM)
Fluoroelastomer (FKM) offers exceptional chemical resistance, particularly against a broad spectrum of oils, fuels, and solvents, making it ideal for chemical-resistant gloves in harsh environments. Its high thermal stability up to 200degC and excellent resistance to oxidation and weathering exceed the capabilities of chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber. FKM's superior barrier properties and durability provide enhanced protection, reducing degradation and extending glove lifespan in demanding chemical handling applications.
Chemical Resistance Comparison: CSM vs FKM
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) offers excellent resistance to ozone, weathering, and aqueous chemicals but has limited resistance to aromatic and chlorinated solvents. Fluoroelastomer (FKM) provides superior chemical resistance against a broad range of aggressive chemicals, including hydrocarbons, oils, acids, and solvents, making it ideal for harsh industrial environments. In chemical-resistant glove applications, FKM generally outperforms CSM in durability and protection against a wider spectrum of chemicals, particularly in environments with exposure to fuels and aggressive organic solvents.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers excellent abrasion resistance and superior tensile strength, making it highly durable for chemical-resistant gloves exposed to mechanical stress. Fluoroelastomers (FKM) provide outstanding chemical resistance to a wide range of acids, oils, and solvents, while maintaining good flex and compression set resistance, ensuring long-term elasticity. Gloves made from CSM typically withstand harsher physical wear and tear, whereas FKM gloves excel in environments with aggressive chemicals and high temperatures, offering a balance between mechanical robustness and chemical durability.
Temperature Resistance: Performance in Extreme Conditions
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) exhibits excellent temperature resistance, maintaining flexibility and chemical resistance in a range from -40degC to 130degC, making it suitable for moderate to high-temperature applications. Fluoroelastomer (FKM) surpasses CSM with superior thermal stability, performing effectively between -25degC and 200degC, which allows it to withstand extreme heat without degradation. For chemical-resistant gloves, FKM is the preferred choice in environments with extreme temperature fluctuations and harsh chemical exposure due to its enhanced thermal resilience and durability.
Cost Analysis: CSM vs FKM Gloves
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) gloves typically offer a more cost-effective solution for chemical resistance compared to fluoroelastomer (FKM) gloves, with CSM gloves priced 20-40% lower depending on thickness and manufacturer. While FKM gloves provide superior resistance to a broader range of aggressive chemicals and higher temperature stability, the initial investment and ongoing cost make CSM gloves preferable for general chemical applications. Total cost of ownership for CSM gloves often remains lower due to competitive pricing and adequate performance in many industrial chemical handling environments.
Suitability for Specific Chemical Environments
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) exhibits excellent resistance to ozone, weathering, and a broad range of chemicals such as acids, alkalis, and alcohols, making it suitable for gloves used in harsh industrial environments involving these substances. Fluoroelastomers (FKM) provide superior chemical resistance to hydrocarbons, oils, fuels, and high-temperature solvents, ideal for gloves in applications requiring protection against petroleum-based chemicals and aggressive solvents. Choosing between CSM and FKM involves considering the specific chemical exposure; CSM is preferred for acidic or alkaline conditions, while FKM excels in environments with strong oils, fuels, and elevated temperatures.
Regulatory and Industry Standards Compliance
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSPE) gloves comply with standards such as ASTM D6413 for chemical resistance and meet EPA regulations for environmental safety, making them suitable for handling solvents and acids. Fluoroelastomer gloves consistently achieve higher compliance with stringent industry standards like ISO 374-1 for chemical protective gloves and NFPA 1999 for emergency medical services, especially for use with aggressive chemicals and oils. Both materials adhere to OSHA requirements, but fluoroelastomer offers superior resistance profiles under regulatory testing protocols, ensuring broader coverage in high-risk chemical environments.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Glove Material
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber offers excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and oils, making it suitable for general chemical handling applications. Fluoroelastomer gloves provide superior protection against aggressive solvents, fuels, and high-temperature chemicals, ideal for specialized industrial uses requiring enhanced chemical resistance. Selecting the right glove material depends on the specific chemical exposure, temperature conditions, and durability requirements to ensure optimal safety and performance.
Infographic: Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber vs Fluoroelastomer for Chemical resistant glove
 azmater.com
azmater.com