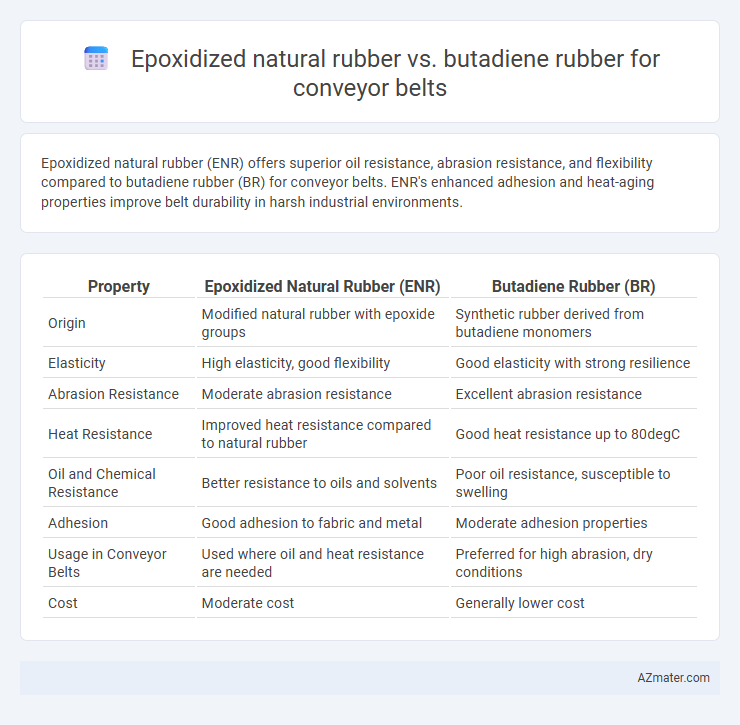
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior oil resistance, abrasion resistance, and flexibility compared to butadiene rubber (BR) for conveyor belts. ENR's enhanced adhesion and heat-aging properties improve belt durability in harsh industrial environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) | Butadiene Rubber (BR) |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Modified natural rubber with epoxide groups | Synthetic rubber derived from butadiene monomers |
| Elasticity | High elasticity, good flexibility | Good elasticity with strong resilience |
| Abrasion Resistance | Moderate abrasion resistance | Excellent abrasion resistance |
| Heat Resistance | Improved heat resistance compared to natural rubber | Good heat resistance up to 80degC |
| Oil and Chemical Resistance | Better resistance to oils and solvents | Poor oil resistance, susceptible to swelling |
| Adhesion | Good adhesion to fabric and metal | Moderate adhesion properties |
| Usage in Conveyor Belts | Used where oil and heat resistance are needed | Preferred for high abrasion, dry conditions |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Generally lower cost |
Introduction to Conveyor Belt Materials
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced oil resistance, heat stability, and improved mechanical properties compared to butadiene rubber, making it suitable for heavy-duty conveyor belts in harsh environments. Butadiene rubber provides excellent abrasion resistance, low-temperature flexibility, and good tensile strength, commonly used in conveyor belts for general industrial applications requiring durability and resilience. Selecting between ENR and butadiene rubber depends on specific operational demands, such as exposure to oils, chemicals, temperature variations, and mechanical stress on conveyor belt materials.
Overview of Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR)
Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) is a chemically modified form of natural rubber with improved oil resistance, abrasion resistance, and enhanced mechanical properties, making it suitable for conveyor belt applications in harsh environments. The epoxidation process introduces epoxy groups into the polymer chain, increasing polarity and compatibility with fillers and other polymers, which enhances strength and heat resistance compared to traditional natural rubber. ENR offers superior aging stability and better resistance to swelling in oils and chemicals than Butadiene Rubber (BR), providing longer service life and reliability in conveyor belts exposed to diverse industrial conditions.
Overview of Butadiene Rubber (BR)
Butadiene Rubber (BR) is a synthetic polymer known for its excellent abrasion resistance, high resilience, and good low-temperature flexibility, making it a preferred choice for conveyor belts in heavy-duty applications. Its high tensile strength and superior wear resistance contribute to the durability and longevity of conveyor belts handling rough or sharp materials. Compared to Epoxidized Natural Rubber, BR offers better resistance to mechanical stress and thermal aging, enhancing performance in demanding industrial environments.
Mechanical Properties: ENR vs BR
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits superior abrasion resistance and tensile strength compared to butadiene rubber (BR), making it highly suitable for conveyor belt applications. ENR's enhanced elasticity and improved resistance to heat and oil aging contribute to longer service life under mechanical stress, whereas BR offers better crack propagation resistance and resilience at low temperatures. The choice between ENR and BR depends on the conveyor belt environment, with ENR preferred for durability and BR for flexibility in extreme conditions.
Abrasion and Wear Resistance Comparison
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) demonstrates superior abrasion resistance compared to butadiene rubber (BR), making it more suitable for conveyor belt applications subjected to harsh wear conditions. ENR's enhanced polarity and crosslink density improve its wear resistance, reducing material degradation and extending belt lifespan. In contrast, butadiene rubber offers good elasticity but generally exhibits lower resistance to abrasion and wear under heavy mechanical stress.
Chemical Resistance: Performance in Harsh Environments
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to butadiene rubber (BR), making it more suitable for conveyor belts in harsh environments exposed to oils, fuels, and solvents. The epoxide groups in ENR enhance polarity and cross-linking density, improving resistance to swelling and degradation. Butadiene rubber, although offering excellent abrasion resistance, tends to degrade faster when exposed to aggressive chemicals, limiting its durability in such conditions.
Flexibility and Low-Temperature Performance
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits superior flexibility and enhanced low-temperature performance compared to butadiene rubber (BR) in conveyor belt applications, due to its higher polarity and improved filler interaction. ENR maintains elasticity and resists stiffness at sub-zero temperatures, ensuring consistent operational efficiency in cold environments. In contrast, butadiene rubber tends to harden and lose flexibility when exposed to low temperatures, limiting its effectiveness in cold-weather conveyor systems.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced oil resistance and abrasion properties but comes at a higher cost due to specialized processing and limited large-scale availability compared to butadiene rubber (BR). Butadiene rubber is more cost-effective and widely available globally, making it a preferred choice for conveyor belts where budget constraints and supply consistency are critical. ENR's limited production volume and higher raw material expenses can impact overall project budgeting despite its superior performance in specific applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior environmental benefits compared to butadiene rubber due to its biodegradability and renewable sourcing from natural latex, reducing reliance on fossil fuels. ENR's improved resistance to oxygen and ozone extends conveyor belt lifespan, minimizing waste and resource consumption in industrial applications. In contrast, butadiene rubber, derived from petrochemicals, has a higher carbon footprint and limited recyclability, raising concerns about long-term sustainability in conveyor belt manufacturing.
Application Suitability: Choosing the Best Rubber for Conveyor Belts
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior oil and heat resistance compared to butadiene rubber, making it highly suitable for conveyor belts in demanding industrial environments such as mining and chemical processing. Butadiene rubber excels in abrasion resistance and flexibility, which is advantageous for conveyor belts requiring high wear resistance and impact durability in material handling and bulk transport. Selection depends on specific operating conditions: use ENR for enhanced chemical and thermal resistance, and choose butadiene rubber for superior mechanical toughness and longevity.
Infographic: Epoxidized natural rubber vs Butadiene rubber for Conveyor belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com