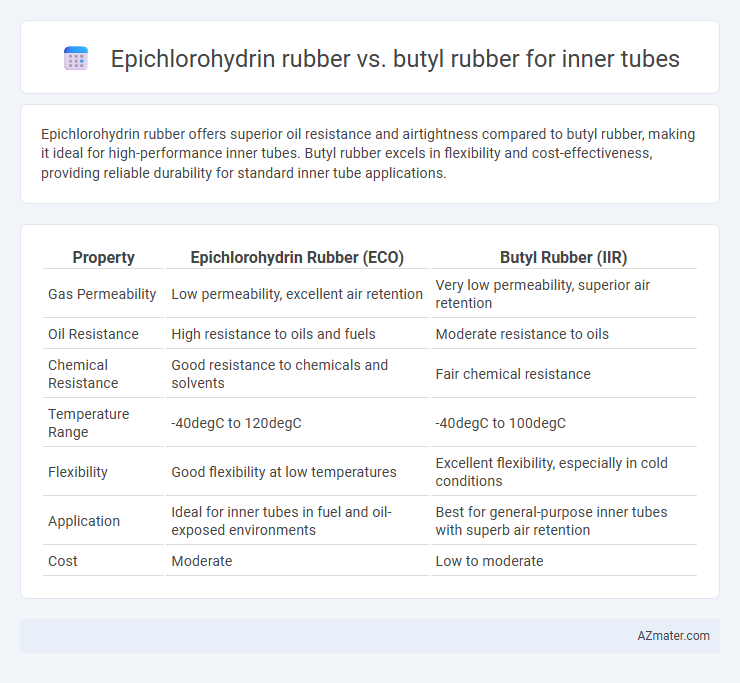
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior oil resistance and airtightness compared to butyl rubber, making it ideal for high-performance inner tubes. Butyl rubber excels in flexibility and cost-effectiveness, providing reliable durability for standard inner tube applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO) | Butyl Rubber (IIR) |
|---|---|---|
| Gas Permeability | Low permeability, excellent air retention | Very low permeability, superior air retention |
| Oil Resistance | High resistance to oils and fuels | Moderate resistance to oils |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to chemicals and solvents | Fair chemical resistance |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -40degC to 100degC |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility at low temperatures | Excellent flexibility, especially in cold conditions |
| Application | Ideal for inner tubes in fuel and oil-exposed environments | Best for general-purpose inner tubes with superb air retention |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to moderate |
Introduction to Inner Tube Materials
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior oil and chemical resistance along with excellent low-temperature flexibility, making it ideal for inner tubes exposed to harsh environments. Butyl rubber is widely used due to its outstanding air impermeability, good heat resistance, and strong vibration damping properties, enhancing inner tube durability and ride comfort. Selecting between these materials depends on specific application requirements such as exposure to chemicals or the need for superior airtightness in tires.
Overview of Epichlorohydrin Rubber
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and ozone, making it highly suitable for inner tube applications where chemical exposure is prominent. Compared to butyl rubber, ECO exhibits superior gas impermeability and better resistance to temperature variations, enhancing inner tube durability and performance. Its unique molecular structure provides enhanced elasticity and resilience, contributing to longer service life in demanding environments.
Properties of Butyl Rubber
Butyl rubber exhibits superior air impermeability and excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and chemicals compared to epichlorohydrin rubber, making it ideal for inner tubes that require long-lasting inflation and durability. Its low gas permeability significantly reduces air loss, enhancing tire performance and safety over time. Furthermore, butyl rubber's excellent flexibility and abrasion resistance contribute to its widespread use in high-quality inner tubes across various automotive and bicycle applications.
Air Retention Comparative Analysis
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior air retention in inner tubes due to its low permeability to gases, making it highly resistant to air leakage over time compared to butyl rubber. Butyl rubber, while offering good overall durability and chemical resistance, typically shows higher air permeability, resulting in faster deflation rates under similar conditions. The enhanced gas barrier properties of epichlorohydrin rubber contribute to extended inner tube life and reduced maintenance frequency in demanding applications.
Heat and Weather Resistance
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior heat and weather resistance compared to butyl rubber, maintaining flexibility and strength under high temperatures and prolonged UV exposure. Butyl rubber offers excellent air impermeability and chemical resistance but tends to degrade faster when exposed to harsh weather conditions and elevated temperatures. For inner tubes requiring durability in extreme climates, epichlorohydrin rubber provides enhanced longevity and performance due to its robust thermal stability and resistance to ozone and oxidation.
Flexibility and Low-Temperature Performance
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior flexibility and enhanced low-temperature performance for inner tubes compared to butyl rubber, maintaining elasticity and resistance to cracking in cold conditions. Butyl rubber excels in air impermeability but tends to stiffen and lose flexibility at lower temperatures, making it less effective for cold-weather applications. The chemical structure of epichlorohydrin rubber provides better cold resistance, ensuring reliable performance in a broader temperature range.
Chemical and Ozone Resistance
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance due to its chlorinated molecular structure, effectively resisting oils, fuels, and a wide range of chemicals, making it ideal for inner tubes exposed to harsh environments. Butyl rubber is renowned for exceptional ozone and weather resistance, maintaining flexibility and preventing cracking over prolonged exposure to atmospheric ozone. Both materials offer robust durability; however, epichlorohydrin rubber excels in chemical resistance while butyl rubber provides enhanced protection against ozone degradation in inner tube applications.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers moderate cost efficiency due to its enhanced weather resistance and oil resistance, making it suitable for specialized inner tubes exposed to harsh conditions but often comes at a higher price point compared to butyl rubber. Butyl rubber provides superior cost efficiency with widespread availability and excellent airtightness, making it the preferred material for most inner tubes in the automotive and bicycle industries. The broad supply chain and lower production costs of butyl rubber contribute to its dominance in the inner tube market, while epichlorohydrin rubber is reserved for niche applications requiring specific chemical resistance.
Application Suitability for Inner Tubes
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and ozone, making it highly suitable for inner tubes used in automotive and industrial vehicles where chemical exposure is common. Butyl rubber offers superior air impermeability and exceptional flexibility, enhancing inner tube durability and maintaining tire pressure over extended periods, especially in passenger vehicles and bicycles. The choice between Epichlorohydrin and Butyl rubber inner tubes depends on operational environments; Epichlorohydrin suits harsh chemical exposure, whereas Butyl excels in air retention and flexibility under varying road conditions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Inner Tube Material
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior oil and ozone resistance with excellent flexibility, making it ideal for heavy-duty inner tube applications exposed to harsh environments. Butyl rubber provides outstanding air retention and excellent impermeability, ensuring longer-lasting inflation and reliability for standard inner tubes. Choosing the optimal inner tube material depends on specific performance needs, where epichlorohydrin excels in chemical resistance and butyl dominates in air retention and durability.
Infographic: Epichlorohydrin rubber vs Butyl rubber for Inner tube
 azmater.com
azmater.com