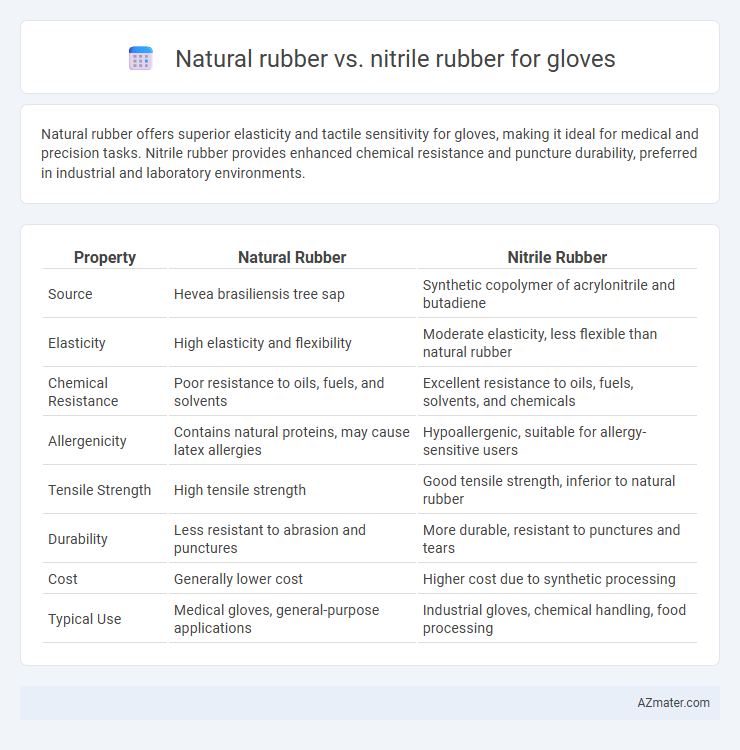
Natural rubber offers superior elasticity and tactile sensitivity for gloves, making it ideal for medical and precision tasks. Nitrile rubber provides enhanced chemical resistance and puncture durability, preferred in industrial and laboratory environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Natural Rubber | Nitrile Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Hevea brasiliensis tree sap | Synthetic copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene |
| Elasticity | High elasticity and flexibility | Moderate elasticity, less flexible than natural rubber |
| Chemical Resistance | Poor resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, solvents, and chemicals |
| Allergenicity | Contains natural proteins, may cause latex allergies | Hypoallergenic, suitable for allergy-sensitive users |
| Tensile Strength | High tensile strength | Good tensile strength, inferior to natural rubber |
| Durability | Less resistant to abrasion and punctures | More durable, resistant to punctures and tears |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to synthetic processing |
| Typical Use | Medical gloves, general-purpose applications | Industrial gloves, chemical handling, food processing |
Overview of Natural Rubber and Nitrile Rubber
Natural rubber, derived from the latex of rubber trees, is prized for its exceptional elasticity, comfort, and tactile sensitivity, making it ideal for gloves used in medical and industrial applications. Nitrile rubber, a synthetic compound made from acrylonitrile and butadiene, offers superior chemical resistance, puncture resistance, and durability, suited for environments with exposure to oils, solvents, and hazardous substances. The distinct material properties of natural rubber and nitrile rubber define their specific uses in glove manufacturing, balancing flexibility against chemical protection.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Natural rubber, primarily composed of cis-1,4-polyisoprene, features a highly elastic polymer chain that offers excellent flexibility and tensile strength in gloves. Nitrile rubber consists of copolymers of acrylonitrile and butadiene, with varying acrylonitrile content affecting its chemical resistance and elasticity. The polar nitrile groups provide nitrile gloves superior resistance to oils, solvents, and puncture compared to the non-polar structure of natural rubber gloves.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Natural rubber gloves are produced through latex dipping, where harvested latex from rubber trees is processed and coagulated to form a flexible film, involving steps such as centrifugation and compounding to enhance elasticity and tensile strength. Nitrile rubber gloves utilize synthetic acrylonitrile and butadiene monomers that undergo emulsion polymerization, followed by a dipping process in a nitrile latex, resulting in gloves with superior chemical resistance and puncture durability. The manufacturing of nitrile gloves often includes additional vulcanization and leaching stages to improve glove performance and reduce residual chemicals, differing significantly from the primarily biologically sourced natural rubber glove production.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Natural rubber gloves exhibit excellent elasticity and tensile strength, providing superior fit and tactile sensitivity, but they tend to degrade faster when exposed to oils, solvents, and chemicals. Nitrile rubber gloves offer enhanced durability with superior resistance to punctures, abrasions, and chemical exposure, making them ideal for industrial and medical applications requiring extended wear and protection. In terms of strength, nitrile gloves generally outperform natural rubber gloves in maintaining integrity under harsh conditions and prolonged use.
Barrier Protection Abilities
Natural rubber gloves provide excellent elasticity and tactile sensitivity, making them highly effective for barrier protection against biological hazards and certain chemicals. Nitrile rubber gloves offer superior chemical resistance, puncture resistance, and are hypoallergenic, which enhances their protective performance against oils, solvents, and hazardous substances. The choice between natural rubber and nitrile gloves depends on the specific exposure risks, with nitrile preferred in environments requiring high chemical resistance and natural rubber favored for durability and comfort in biological protection.
Comfort and Fit for Users
Natural rubber gloves offer superior elasticity and tactile sensitivity, ensuring a snug fit that enhances user comfort during prolonged wear. Nitrile rubber gloves provide excellent fit retention and resistance to punctures, making them ideal for users requiring durability without sacrificing comfort. Both materials accommodate a wide range of hand sizes, but natural rubber typically delivers a softer, more flexible feel that conforms closely to the skin.
Allergic Reactions and Skin Sensitivity
Natural rubber gloves contain latex proteins that can trigger allergic reactions in sensitive individuals, leading to symptoms such as itching, redness, and swelling. Nitrile rubber gloves are synthetic and latex-free, significantly reducing the risk of allergic responses while offering similar durability and chemical resistance. For those with skin sensitivity or latex allergies, nitrile gloves provide a safer alternative without compromising protection.
Cost and Availability
Natural rubber gloves generally cost less due to the abundant availability of latex sourced from rubber trees, primarily in Southeast Asia. Nitrile rubber gloves are more expensive as they rely on synthetic production processes involving petrochemicals, resulting in variable pricing influenced by oil markets. Availability of natural rubber gloves can be subject to fluctuations caused by climate and harvesting cycles, whereas nitrile gloves offer more consistent supply through industrial manufacturing.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Natural rubber gloves are derived from renewable latex harvested from rubber trees, offering biodegradability and a lower carbon footprint compared to synthetic alternatives. Nitrile rubber gloves are petroleum-based, resulting in higher environmental impact due to fossil fuel extraction and slower decomposition rates. Sustainable practices favor natural rubber for reduced ecological damage, although innovations in nitrile recycling are enhancing its sustainability profile.
Choosing the Right Glove Material
Natural rubber gloves provide superior elasticity and tactile sensitivity, making them ideal for medical and laboratory applications requiring precise touch. Nitrile rubber gloves offer enhanced chemical resistance and durability, suitable for handling oils, solvents, and hazardous materials in industrial and automotive settings. Selecting the right glove material depends on balancing protection needs, allergy considerations, and the specific environmental exposure associated with the task.
Infographic: Natural rubber vs Nitrile rubber for Glove
 azmater.com
azmater.com