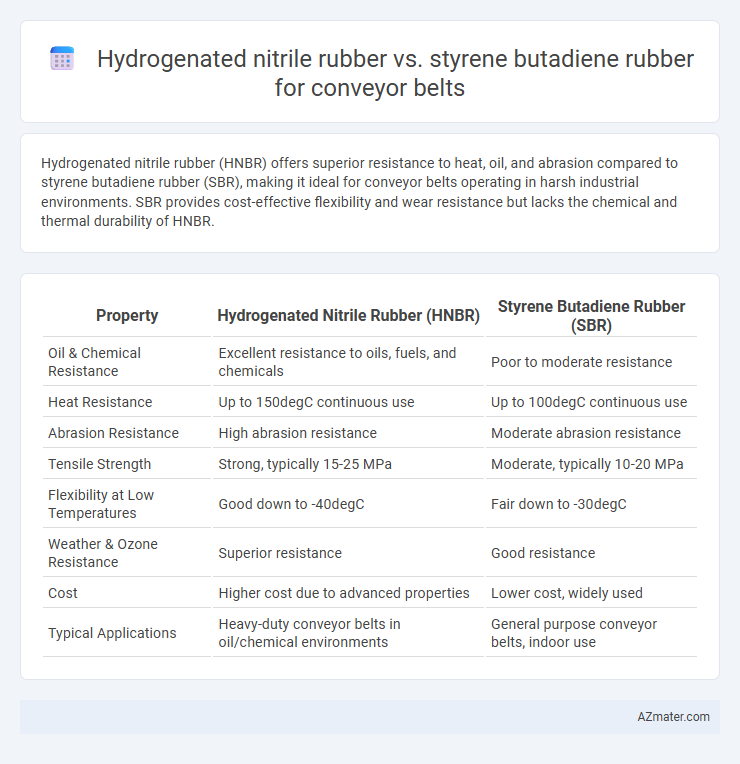
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to heat, oil, and abrasion compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making it ideal for conveyor belts operating in harsh industrial environments. SBR provides cost-effective flexibility and wear resistance but lacks the chemical and thermal durability of HNBR.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) | Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Oil & Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals | Poor to moderate resistance |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 150degC continuous use | Up to 100degC continuous use |
| Abrasion Resistance | High abrasion resistance | Moderate abrasion resistance |
| Tensile Strength | Strong, typically 15-25 MPa | Moderate, typically 10-20 MPa |
| Flexibility at Low Temperatures | Good down to -40degC | Fair down to -30degC |
| Weather & Ozone Resistance | Superior resistance | Good resistance |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Lower cost, widely used |
| Typical Applications | Heavy-duty conveyor belts in oil/chemical environments | General purpose conveyor belts, indoor use |
Introduction to Conveyor Belt Materials
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to heat, oil, and abrasion, making it ideal for conveyor belts in harsh industrial environments. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) provides good flexibility and cost-efficiency but lacks the high chemical and temperature resistance of HNBR. Selection of conveyor belt materials depends on the specific operational demands, with HNBR preferred for durability and longevity in aggressive conditions.
Overview of Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR)
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) is a high-performance elastomer known for its exceptional resistance to heat, oil, and abrasion, making it ideal for conveyor belt applications in harsh environments. Its enhanced hydrogenation process improves thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to conventional nitrile rubber, ensuring longer service life under continuous mechanical stress. HNBR's superior tensile strength and elasticity also provide excellent durability and flexibility, critical for maintaining conveyor belt integrity in demanding industrial settings.
Overview of Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) is a synthetic rubber known for its excellent abrasion resistance, high tensile strength, and good aging stability, making it a popular choice for conveyor belts in heavy-duty applications. Its polymer composition combines styrene and butadiene, providing enhanced flexibility and resistance to heat, oxidizing agents, and abrasion compared to many natural rubbers. SBR conveyor belts offer durability and reliable performance even in harsh industrial environments, outperforming hydrogenated nitrile rubber in terms of cost-efficiency and general wear resistance.
Key Physical Properties: HNBR vs SBR
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior heat resistance up to 150degC, excellent oil and chemical resistance, and higher tensile strength compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), which typically withstands temperatures only up to 100degC and exhibits moderate mechanical properties. HNBR's enhanced abrasion resistance and low compression set make it ideal for conveyor belts exposed to harsh environments and aggressive chemicals, while SBR is more cost-effective but less durable under extreme conditions. The choice between HNBR and SBR depends on operational demands, with HNBR providing longer service life and reliability in high-temperature and corrosive settings.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), especially against oils, fuels, and solvents, making it ideal for conveyor belts exposed to harsh industrial chemicals. HNBR's saturated polymer backbone enhances resistance to degradation by heat, ozone, and chemicals, whereas SBR is more prone to swelling and deterioration in the presence of hydrocarbons and oxidative agents. This chemical resistance advantage of HNBR extends the operational lifespan and reliability of conveyor belts in demanding chemical environments.
Temperature and Environmental Performance
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior heat resistance, maintaining structural integrity in temperatures up to 150degC, compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), which typically withstands around 100degC. HNBR exhibits excellent resistance to ozone, oils, and chemicals, enhancing its durability in harsh environmental conditions critical for conveyor belts. SBR, while cost-effective, degrades faster under environmental stressors such as UV exposure and oxidation, limiting its lifespan in demanding industrial applications.
Abrasion and Wear Resistance
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior abrasion and wear resistance compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making it ideal for conveyor belt applications subjected to harsh conditions. HNBR's enhanced molecular structure provides improved durability against mechanical stress, chemical exposure, and high temperatures, significantly extending conveyor belt lifespan. SBR, while cost-effective and flexible, tends to degrade faster under abrasive environments, leading to more frequent maintenance and replacements.
Cost and Availability Factors
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) typically incurs higher costs than styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) due to its enhanced chemical and thermal resistance, making it suitable for demanding conveyor belt environments. SBR offers broader availability and lower initial price, benefiting applications with moderate temperature and abrasion levels. Cost-effectiveness depends on the conveyor belt's exposure conditions, where HNBR's durability may reduce long-term expenses despite a higher upfront investment.
Industry Applications and Suitability
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to abrasion, heat, oils, and chemicals, making it highly suitable for conveyor belts used in harsh industrial environments such as automotive manufacturing, oil refineries, and mining operations. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), while cost-effective and providing good abrasion resistance, is better suited for lighter-duty conveyor belts in industries like packaging, food processing, and general material handling where exposure to extreme chemicals or high temperatures is minimal. The choice between HNBR and SBR depends on specific operational demands, with HNBR excelling in durability and chemical resistance for heavy industrial applications and SBR preferred for standard tasks with moderate wear and tear.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Conveyor Belts
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to abrasion, oils, and high temperatures, making it ideal for conveyor belts in demanding industrial environments. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) provides excellent flexibility and cost efficiency but has lower resistance to heat and chemicals compared to HNBR. Selecting the right rubber depends on the conveyor belt's operational conditions, with HNBR preferred for durability and chemical exposure, while SBR suits general-purpose applications.
Infographic: Hydrogenated nitrile rubber vs Styrene butadiene rubber for Conveyor belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com