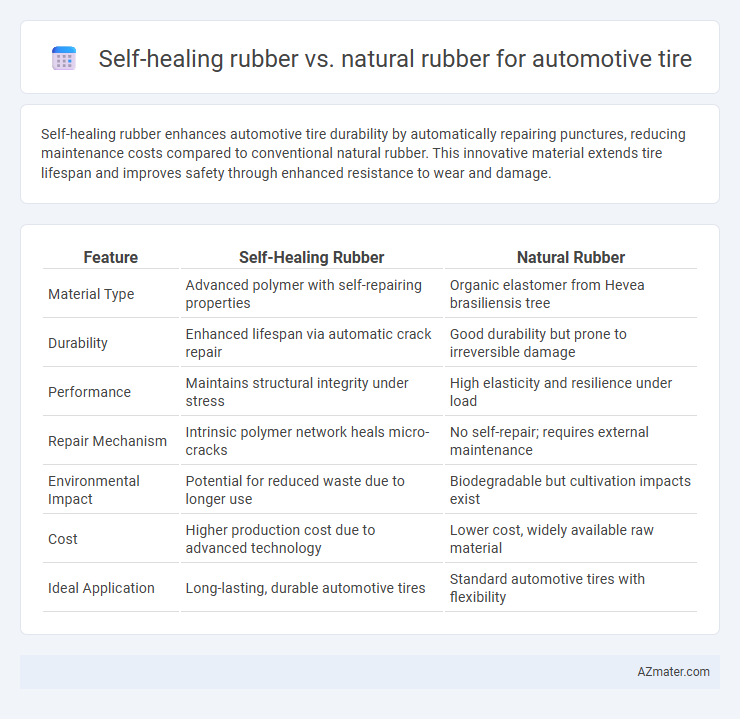
Self-healing rubber enhances automotive tire durability by automatically repairing punctures, reducing maintenance costs compared to conventional natural rubber. This innovative material extends tire lifespan and improves safety through enhanced resistance to wear and damage.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Self-Healing Rubber | Natural Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Advanced polymer with self-repairing properties | Organic elastomer from Hevea brasiliensis tree |
| Durability | Enhanced lifespan via automatic crack repair | Good durability but prone to irreversible damage |
| Performance | Maintains structural integrity under stress | High elasticity and resilience under load |
| Repair Mechanism | Intrinsic polymer network heals micro-cracks | No self-repair; requires external maintenance |
| Environmental Impact | Potential for reduced waste due to longer use | Biodegradable but cultivation impacts exist |
| Cost | Higher production cost due to advanced technology | Lower cost, widely available raw material |
| Ideal Application | Long-lasting, durable automotive tires | Standard automotive tires with flexibility |
Introduction: The Evolution of Automotive Tire Materials
Self-healing rubber offers innovative advantages over natural rubber by enhancing tire longevity and safety through its ability to autonomously repair micro-cracks caused by road wear. Natural rubber, derived from Hevea brasiliensis latex, has been a standard in tire manufacturing due to its excellent elasticity and durability but lacks self-repair capabilities. The evolution of automotive tire materials is marked by integrating advanced compounds like self-healing polymers that address durability limitations, reduce maintenance costs, and improve overall performance under varying driving conditions.
What Is Natural Rubber? Key Properties and Uses
Natural rubber, derived from latex sap of Hevea brasiliensis trees, exhibits high elasticity, resilience, and excellent tensile strength, making it a preferred material in automotive tires. Key properties such as superior abrasion resistance, flexibility at low temperatures, and good wear performance enable natural rubber to provide durability and traction for vehicle tires. Its widespread use in tire manufacturing is driven by the ability to maintain road grip, enhance driving safety, and support various tire components like sidewalls and tread compounds.
Understanding Self-Healing Rubber: Technology and Mechanism
Self-healing rubber in automotive tires utilizes advanced polymer networks embedded with reversible covalent bonds or microcapsules containing healing agents that activate upon damage, enabling the material to autonomously repair cracks and punctures. This technology enhances tire durability and safety by extending service life and reducing maintenance, distinguishing it from traditional natural rubber which lacks intrinsic self-repair capabilities. Understanding the underlying mechanism involves analyzing the dynamic chemical interactions and physical mobility within the polymer matrix that facilitate spontaneous healing without external intervention.
Performance Comparison: Durability and Longevity
Self-healing rubber exhibits enhanced durability compared to natural rubber due to its ability to autonomously repair micro-cracks, significantly extending tire lifespan and reducing maintenance frequency. Natural rubber, while known for excellent elasticity and grip, tends to degrade faster under repetitive stress and environmental factors, leading to reduced longevity. The integration of self-healing polymers in automotive tires results in superior wear resistance and improved performance stability, positioning it as a promising alternative to traditional natural rubber in tire manufacturing.
Puncture Resistance: Self-Healing vs Natural Rubber
Self-healing rubber significantly enhances puncture resistance in automotive tires by autonomously repairing micro-cracks and punctures, reducing the risk of sudden air loss and extending tire lifespan. Natural rubber, while offering excellent elasticity and durability, lacks intrinsic self-repair capabilities, making it more susceptible to persistent punctures and damage over time. Advanced formulations of self-healing rubber incorporate dynamic covalent bonds or microcapsules that activate upon damage, providing a superior safety advantage compared to traditional natural rubber tires.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Self-healing rubber in automotive tires significantly reduces environmental waste by extending tire lifespan and minimizing landfill accumulation compared to traditional natural rubber. Natural rubber production involves deforestation and high water consumption, whereas self-healing rubber incorporates synthetic polymers that enhance durability and reduce resource extraction. The increased sustainability of self-healing rubber supports circular economy principles by promoting tire reusability and lowering overall carbon footprint in the automotive industry.
Cost Analysis: Manufacturing and Market Price
Self-healing rubber offers potential cost savings in automotive tire manufacturing by reducing the need for frequent tire replacements and repairs due to its automatic damage recovery properties, though its initial production costs remain higher compared to natural rubber. Natural rubber, widely available and less expensive to produce, dominates the tire market due to established supply chains and lower raw material costs, resulting in more competitive market prices. However, advancements in self-healing rubber technology could drive down manufacturing expenses over time, potentially narrowing the price gap while offering improved tire lifespan and performance.
Practical Applications in the Automotive Industry
Self-healing rubber enhances tire longevity by autonomously repairing minor cuts and abrasions, reducing maintenance frequency and improving safety in automotive applications. Natural rubber, prized for its elasticity, resilience, and traction, remains the primary material in traditional tire manufacturing due to its proven performance under diverse driving conditions. Integrating self-healing polymers into tire compounds offers a practical advancement by extending tire lifespan, optimizing vehicle downtime, and contributing to sustainability within the automotive industry.
Future Trends: Innovations in Tire Materials
Self-healing rubber is emerging as a transformative material in automotive tire technology by autonomously repairing micro-cracks, enhancing tire longevity and safety compared to traditional natural rubber. Innovations in polymer chemistry and nanotechnology are accelerating the development of these advanced compounds, promising tires with superior durability and reduced environmental impact. Future trends emphasize integrating self-healing elastomers with smart sensors to enable real-time damage detection and proactive maintenance, revolutionizing tire performance and sustainability.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Rubber for Automotive Tires
Self-healing rubber offers enhanced durability and reduces maintenance costs due to its ability to repair minor damages, making it ideal for prolonging tire life in automotive applications. Natural rubber provides superior elasticity, traction, and performance in diverse driving conditions but lacks self-repair capabilities, leading to more frequent replacements. Selecting the optimal rubber depends on prioritizing either longevity and reduced downtime with self-healing properties or established performance and cost-effectiveness with natural rubber.
Infographic: Self-healing rubber vs Natural rubber for Automotive tire
 azmater.com
azmater.com