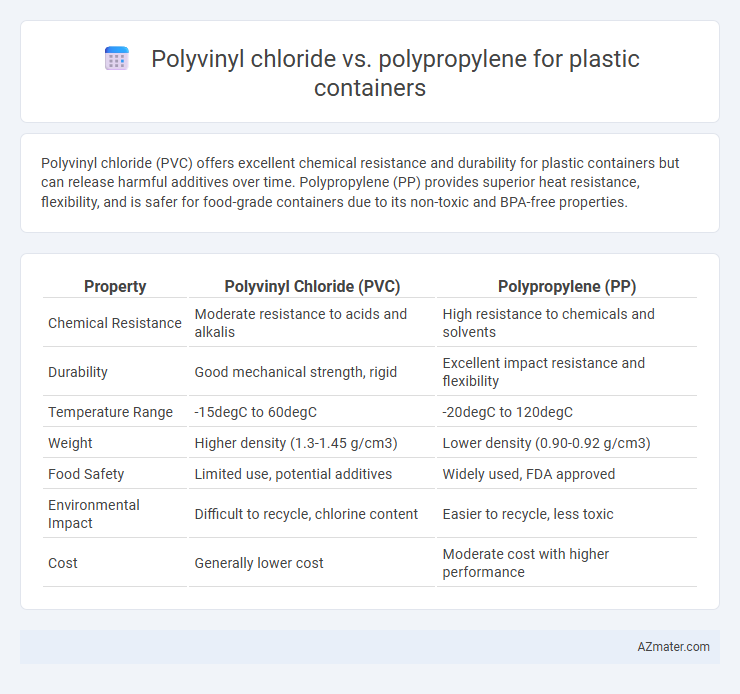
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers excellent chemical resistance and durability for plastic containers but can release harmful additives over time. Polypropylene (PP) provides superior heat resistance, flexibility, and is safer for food-grade containers due to its non-toxic and BPA-free properties.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance to acids and alkalis | High resistance to chemicals and solvents |
| Durability | Good mechanical strength, rigid | Excellent impact resistance and flexibility |
| Temperature Range | -15degC to 60degC | -20degC to 120degC |
| Weight | Higher density (1.3-1.45 g/cm3) | Lower density (0.90-0.92 g/cm3) |
| Food Safety | Limited use, potential additives | Widely used, FDA approved |
| Environmental Impact | Difficult to recycle, chlorine content | Easier to recycle, less toxic |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Moderate cost with higher performance |
Introduction to Plastic Containers
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polypropylene (PP) are widely used materials in the production of plastic containers, each offering distinct chemical and physical properties. PVC provides excellent durability, chemical resistance, and clarity, making it suitable for containers requiring transparency and toughness. Polypropylene, known for its high melting point, resistance to fatigue, and lightweight nature, is preferred for food storage containers that demand safety, flexibility, and recyclability.
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer known for its durability, chemical resistance, and versatility in manufacturing plastic containers. It offers excellent clarity and rigidity, making it ideal for packaging applications requiring strong barrier properties against moisture and oxygen. PVC containers are often used in food, pharmaceutical, and industrial sectors due to their affordability and ease of molding into various shapes.
Overview of Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic polymer widely used for plastic containers due to its excellent chemical resistance, high impact strength, and low density, making it lighter than polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Its superior thermal resistance allows PP containers to withstand higher temperatures without deforming, ideal for microwaveable and dishwasher-safe applications. Additionally, polypropylene's recyclability and resistance to fatigue from repeated use enhance its sustainability and durability compared to polyvinyl chloride in packaging solutions.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is composed of repeating vinyl chloride monomers (CH2=CHCl) featuring chlorine atoms that provide rigidity and chemical resistance, whereas polypropylene (PP) consists of propylene monomers (CH2=CHCH3) with a methyl group that imparts flexibility and impact resistance. PVC's polar chlorine atoms create a dense, semi-crystalline structure, making it less permeable and more durable against solvents, while PP's nonpolar methyl side groups result in a lighter, more crystalline arrangement with higher thermal resistance. The differing chemical structures influence their suitability for plastic containers: PVC offers superior barrier properties against gases and chemicals, whereas PP excels in heat tolerance and lower density for lightweight packaging.
Durability and Lifespan Differences
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers exceptional chemical resistance and rigidity, making it highly durable in harsh environments but tends to become brittle over time when exposed to UV light. Polypropylene (PP) provides superior impact resistance and flexibility, maintaining its structural integrity longer under repeated stress and temperature fluctuations. The lifespan of polypropylene containers generally exceeds that of PVC, especially in outdoor or high-impact applications due to its better resistance to environmental degradation.
Safety and Food-Grade Suitability
Polypropylene (PP) is widely preferred over Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) for plastic containers due to its superior safety profile and food-grade suitability, as PP is BPA-free, non-toxic, and resistant to chemical leaching. PVC contains additives like phthalates that can migrate into food, raising health concerns, especially under heat exposure. Regulatory agencies like the FDA approve polypropylene for direct food contact, ensuring it meets stringent safety standards for food storage and handling.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) poses significant environmental concerns due to the release of harmful chemicals, such as dioxins, during production and incineration, while its recycling process is complex and less efficient. Polypropylene (PP) offers a more environmentally friendly profile with lower toxicity, higher resistance to chemical leaching, and greater recyclability, making it a preferred choice for sustainable plastic containers. The recyclability rate of PP is higher in most municipal programs, reducing landfill waste and supporting circular economy initiatives.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers a lower material cost compared to polypropylene (PP), making it a budget-friendly option for plastic containers in large-scale production. PVC's ease of processing and ability to be rigid or flexible allows for versatile manufacturing methods such as extrusion and injection molding, while polypropylene requires higher temperatures and energy costs during molding. Despite higher initial costs, polypropylene provides superior chemical resistance and durability, potentially reducing long-term expenses versus PVC containers.
Typical Applications of PVC vs PP Containers
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) containers are commonly used for packaging chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and food products due to their excellent chemical resistance and clarity. Polypropylene (PP) containers excel in applications requiring high heat resistance and durability, such as microwave-safe food containers, laboratory containers, and industrial storage. PVC is favored for rigid and transparent containers, while PP is preferred for flexible, impact-resistant, and reusable packaging solutions.
Choosing the Right Material for Plastic Containers
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers excellent chemical resistance and durability, making it ideal for containers storing harsh chemicals or liquids prone to degradation. Polypropylene (PP) provides superior heat resistance and flexibility, suitable for food storage and applications requiring repeated use or microwave compatibility. Selecting between PVC and PP depends on the container's intended use, exposure conditions, and regulatory standards for safety and environmental impact.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride vs Polypropylene for Plastic container
 azmater.com
azmater.com