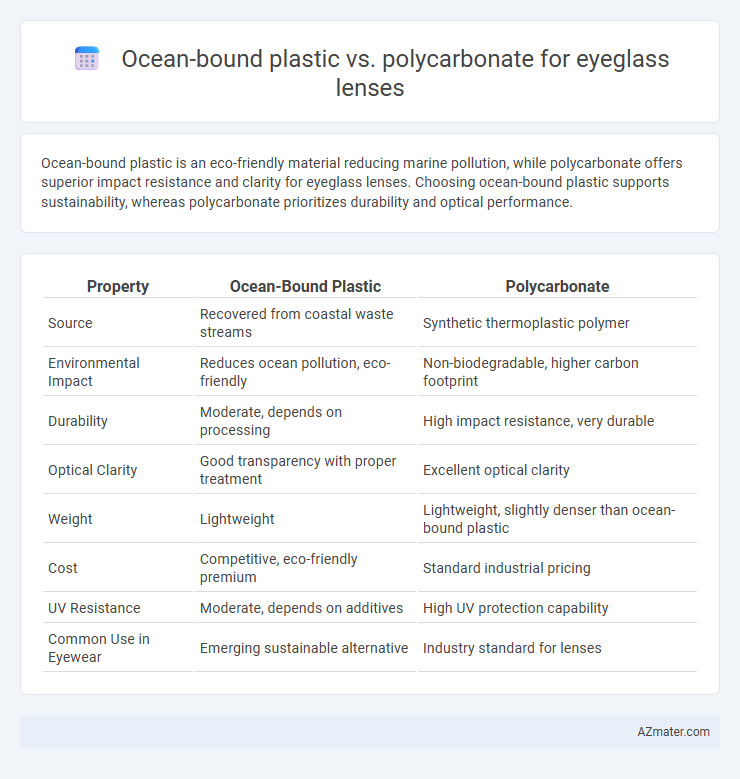
Ocean-bound plastic is an eco-friendly material reducing marine pollution, while polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and clarity for eyeglass lenses. Choosing ocean-bound plastic supports sustainability, whereas polycarbonate prioritizes durability and optical performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ocean-Bound Plastic | Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Recovered from coastal waste streams | Synthetic thermoplastic polymer |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces ocean pollution, eco-friendly | Non-biodegradable, higher carbon footprint |
| Durability | Moderate, depends on processing | High impact resistance, very durable |
| Optical Clarity | Good transparency with proper treatment | Excellent optical clarity |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight, slightly denser than ocean-bound plastic |
| Cost | Competitive, eco-friendly premium | Standard industrial pricing |
| UV Resistance | Moderate, depends on additives | High UV protection capability |
| Common Use in Eyewear | Emerging sustainable alternative | Industry standard for lenses |
Understanding Ocean-Bound Plastic for Eyeglass Lenses
Ocean-bound plastic for eyeglass lenses refers to recycled materials collected from coastal areas at high risk of ocean pollution, transforming waste into sustainable eyewear components that reduce environmental impact. Unlike traditional polycarbonate lenses, which are derived from petroleum-based sources and offer high durability and impact resistance, ocean-bound plastic lenses emphasize eco-friendliness while maintaining adequate optical clarity and performance. This innovative approach supports circular economy principles, minimizing plastic pollution in marine ecosystems through upcycling into functional, stylish lenses.
What is Polycarbonate and Its Role in Eyewear
Polycarbonate is a durable, impact-resistant thermoplastic widely used in eyeglass lenses due to its lightweight nature and high clarity. Unlike ocean-bound plastic, which is recycled from plastic waste collected near coastlines to reduce environmental pollution, polycarbonate is manufactured through a chemical process ensuring consistent optical quality and strength. Its role in eyewear is critical for providing shatterproof lenses with built-in UV protection, making it a preferred material for safety glasses and everyday eyewear.
Environmental Impact: Ocean-Bound Plastic vs Polycarbonate
Ocean-bound plastic lenses significantly reduce environmental harm by repurposing waste that would otherwise pollute marine ecosystems, lowering microplastic pollution and conserving ocean biodiversity. Polycarbonate lenses, while durable and lightweight, are derived from petroleum-based plastics that contribute to carbon emissions and persist in landfills for centuries. The sustainable choice of ocean-bound plastic lenses promotes circular economy principles and reduces the carbon footprint associated with traditional polycarbonate production.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Ocean-bound plastic eyeglass lenses offer moderate durability but typically fall short in strength compared to polycarbonate lenses, which are renowned for their impact resistance and high tensile strength. Polycarbonate materials provide superior fracture resistance, making them ideal for active lifestyles and safety eyewear, while ocean-bound plastics prioritize environmental sustainability over maximum durability. The strength advantage of polycarbonate ensures longer lens lifespan under stress, whereas ocean-bound plastic lenses contribute to reducing plastic pollution with slightly compromised durability.
Optical Clarity and Visual Performance
Ocean-bound plastic lenses offer impressive optical clarity with a natural resistance to glare and distortions, enhancing visual comfort in everyday use. Polycarbonate lenses, known for their impact resistance, provide excellent visual performance with high clarity but may have slightly lower scratch resistance compared to ocean-bound plastics. Both materials deliver reliable optics, yet ocean-bound plastic stands out for its eco-friendly composition without compromising lens clarity or sharpness.
Weight and Comfort for Daily Wear
Ocean-bound plastic eyeglass lenses offer a lightweight alternative with a density typically around 1.2 g/cm3, enhancing comfort for all-day wear by reducing pressure on the nose and ears. Polycarbonate lenses, with a slightly higher density near 1.20 g/cm3 but greater impact resistance, provide durability while maintaining comparable lightness. Both materials support ease of daily wear, though ocean-bound plastic prioritizes sustainability alongside comfort.
UV Protection and Safety Features
Ocean-bound plastic eyeglass lenses offer eco-friendly UV protection by incorporating recycled materials with UV-blocking coatings, reducing environmental impact while filtering harmful rays. Polycarbonate lenses provide superior UV protection inherently due to their molecular structure, blocking nearly 100% of UVA and UVB rays, and excel in safety features with high impact resistance and shatterproof qualities. Both materials enhance eye safety, but polycarbonate is preferred for high-impact activities, whereas ocean-bound plastic combines sustainability with adequate UV defense.
Cost Analysis: Ocean-Bound Plastic vs Polycarbonate Lenses
Ocean-bound plastic lenses often cost more than polycarbonate lenses due to higher material sourcing and processing expenses linked to recycling ocean-bound waste. Polycarbonate lenses benefit from established mass production methods, resulting in lower unit costs and more affordable pricing for consumers. However, ocean-bound plastic lenses may justify the premium price through environmental impact savings and sustainability value.
Sustainability Considerations in Eyewear Manufacturing
Ocean-bound plastic offers a sustainable alternative for eyeglass lenses by utilizing recycled materials that reduce marine pollution and lower carbon footprints in manufacturing processes. Polycarbonate lenses, while durable and impact-resistant, are derived from non-renewable fossil fuels and pose challenges in biodegradability and recycling efforts. Prioritizing ocean-bound plastic in eyewear production supports circular economy principles and aligns with increasing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products.
Future Prospects: Innovations in Eco-Friendly Eyeglass Lenses
Ocean-bound plastic offers a promising sustainable alternative for eyeglass lenses by reducing marine pollution and supporting circular economy initiatives. Polycarbonate remains a popular choice due to its lightweight, impact resistance, and optical clarity, but innovations are underway to blend eco-friendly materials with polycarbonate's durability. Future prospects highlight the development of hybrid lenses incorporating bio-based polymers derived from ocean-bound plastic, aiming to enhance environmental sustainability without compromising lens performance.
Infographic: Ocean-bound plastic vs Polycarbonate for Eyeglass lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com