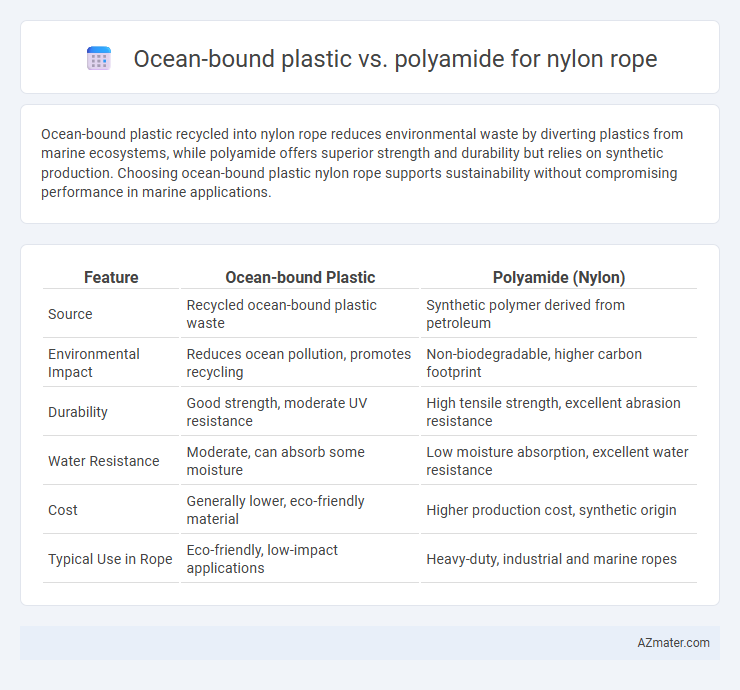
Ocean-bound plastic recycled into nylon rope reduces environmental waste by diverting plastics from marine ecosystems, while polyamide offers superior strength and durability but relies on synthetic production. Choosing ocean-bound plastic nylon rope supports sustainability without compromising performance in marine applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ocean-bound Plastic | Polyamide (Nylon) |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Recycled ocean-bound plastic waste | Synthetic polymer derived from petroleum |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces ocean pollution, promotes recycling | Non-biodegradable, higher carbon footprint |
| Durability | Good strength, moderate UV resistance | High tensile strength, excellent abrasion resistance |
| Water Resistance | Moderate, can absorb some moisture | Low moisture absorption, excellent water resistance |
| Cost | Generally lower, eco-friendly material | Higher production cost, synthetic origin |
| Typical Use in Rope | Eco-friendly, low-impact applications | Heavy-duty, industrial and marine ropes |
Introduction to Rope Materials: Ocean-Bound Plastic vs Polyamide
Ocean-bound plastic, sourced from coastal waste, offers an eco-friendly alternative in nylon rope manufacturing by reducing marine pollution and promoting sustainability. Polyamide, a synthetic polymer commonly used in traditional nylon ropes, provides high tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and elasticity ideal for demanding applications. Comparing both materials highlights the environmental benefits of ocean-bound plastic while affirming polyamide's proven performance in durability and reliability for rope production.
What is Ocean-Bound Plastic?
Ocean-bound plastic refers to plastic waste collected from coastal areas within 50 kilometers of the shoreline before it enters the ocean, preventing marine pollution. It is recycled and repurposed into materials like polyamide fibers used in producing sustainable nylon ropes. Using ocean-bound plastic for nylon rope helps reduce plastic pollution while maintaining the strength, durability, and flexibility characteristic of traditional polyamide.
Understanding Polyamide in Nylon Ropes
Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, is a synthetic polymer renowned for its high tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and elasticity, making it ideal for durable nylon ropes. Ocean-bound plastic, often recycled polyethylene or polypropylene, offers an eco-friendly alternative but typically lacks the mechanical properties of pure polyamide fibers. Understanding the superior performance of polyamide in nylon ropes is crucial for applications requiring strength, longevity, and resilience in marine environments.
Environmental Impact: Ocean-Bound Plastic vs Polyamide
Ocean-bound plastic rope significantly reduces environmental impact by repurposing waste materials destined for marine pollution, cutting down on plastic debris infiltration into oceans and lowering carbon emissions through recycling processes. In contrast, polyamide rope production relies heavily on fossil fuels and releases greenhouse gases, contributing to ocean acidification and habitat degradation. Utilizing ocean-bound plastic supports circular economies and decreases reliance on virgin petrochemicals, offering a more sustainable solution for nylon rope manufacturing.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Ocean-bound plastic ropes offer environmental benefits by reducing marine pollution but generally have lower tensile strength and durability compared to polyamide (nylon) ropes. Polyamide nylon rope exhibits superior resistance to abrasion, UV degradation, and chemical exposure, making it ideal for heavy-duty and outdoor applications. Strength metrics show nylon ropes achieving breaking strengths up to 80 MPa, while ocean-bound plastic fibers typically range below 50 MPa, highlighting nylon's advantage in demanding environments.
Cost Analysis: Ocean-Bound Plastic vs Polyamide Ropes
Ocean-bound plastic ropes generally offer a cost advantage due to the use of recycled materials, reducing raw material expenses compared to virgin polyamide ropes. Polyamide ropes typically have higher production costs owing to energy-intensive synthesis processes and the use of petrochemical feedstocks. Despite a higher upfront price, polyamide ropes provide superior strength and durability, which can influence long-term cost efficiency depending on the application.
Performance in Marine Environments
Ocean-bound plastic nylon rope offers excellent resistance to saltwater corrosion and UV degradation, making it ideal for marine environments. Polyamide ropes demonstrate high tensile strength and abrasion resistance but may absorb more water, potentially reducing durability over time. When comparing both, ocean-bound plastic nylon ropes provide enhanced sustainability while maintaining competitive performance in harsh sea conditions.
Recycling and End-of-Life Considerations
Ocean-bound plastic used in nylon rope production offers significant environmental benefits by diverting waste from marine ecosystems and reducing virgin material consumption. Polyamide ropes, traditionally derived from non-renewable petrochemicals, present more challenges in recycling due to contamination and complex chemical structures. Recycling ocean-bound plastic fibers enhances circularity, enabling easier end-of-life recovery and lowering the carbon footprint compared to conventional polyamide ropes.
Applications and Suitability for Different Industries
Ocean-bound plastic-derived nylon rope offers a sustainable alternative with comparable strength and durability for marine and outdoor applications, making it suitable for fishing, shipping, and environmental industries focused on reducing plastic waste. Polyamide nylon rope, known for its high abrasion resistance and elasticity, excels in industrial settings such as construction, safety harnesses, and sports equipment where performance under stress is critical. Both materials serve diverse industries, but ocean-bound plastic rope emphasizes eco-friendliness, while traditional polyamide ropes prioritize technical reliability and longevity.
Future Trends in Sustainable Rope Manufacturing
Ocean-bound plastic is increasingly used in sustainable rope manufacturing as it reduces marine pollution and conserves natural resources, aligning with global environmental goals. Polyamide, traditionally derived from petrochemicals, faces pressure to integrate recycled content and adopt bio-based alternatives to lower carbon footprints. Future trends emphasize hybrid ropes combining ocean-bound plastic fibers with bio-based polyamides, promoting durability while minimizing ecological impact.
Infographic: Ocean-bound plastic vs Polyamide for Nylon rope
 azmater.com
azmater.com