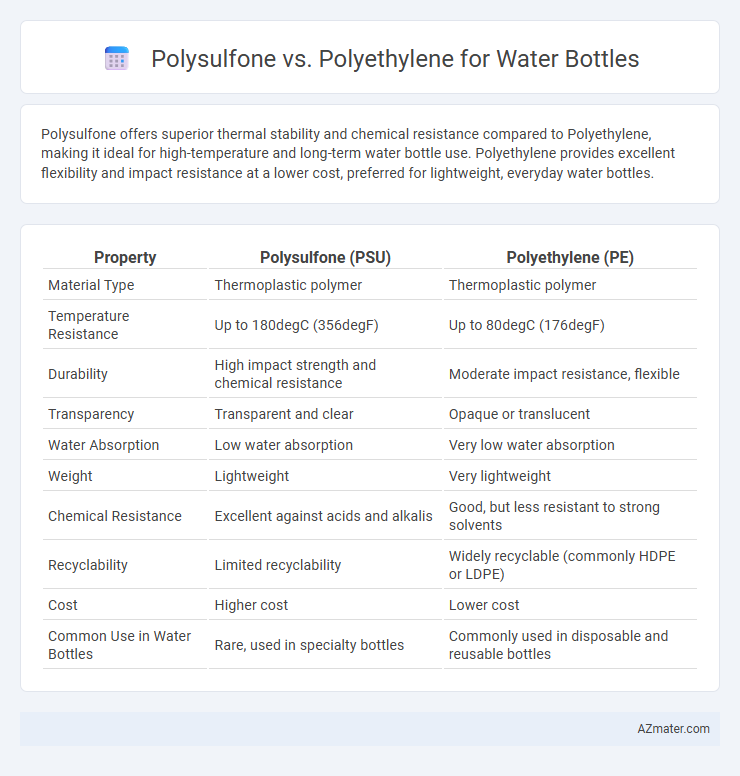
Polysulfone offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to Polyethylene, making it ideal for high-temperature and long-term water bottle use. Polyethylene provides excellent flexibility and impact resistance at a lower cost, preferred for lightweight, everyday water bottles.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfone (PSU) | Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 180degC (356degF) | Up to 80degC (176degF) |
| Durability | High impact strength and chemical resistance | Moderate impact resistance, flexible |
| Transparency | Transparent and clear | Opaque or translucent |
| Water Absorption | Low water absorption | Very low water absorption |
| Weight | Lightweight | Very lightweight |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against acids and alkalis | Good, but less resistant to strong solvents |
| Recyclability | Limited recyclability | Widely recyclable (commonly HDPE or LDPE) |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Common Use in Water Bottles | Rare, used in specialty bottles | Commonly used in disposable and reusable bottles |
Introduction to Polysulfone and Polyethylene
Polysulfone is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional heat resistance, chemical stability, and durability, making it suitable for reusable water bottles that require long-term performance and safety. Polyethylene, particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE), is widely used in water bottles due to its lightweight nature, impact resistance, and affordability, offering a cost-effective option for single-use or short-term use containers. Both materials provide distinct advantages, with polysulfone catering to high-temperature and heavy-use scenarios, while polyethylene excels in flexibility and economic production.
Material Composition and Structure
Polysulfone water bottles feature a rigid, aromatic polymer structure with high thermal stability and chemical resistance, making them suitable for hot and harsh environments. Polyethylene bottles consist of long chains of ethylene monomers, offering flexibility, impact resistance, and excellent moisture barrier properties. The molecular difference results in polysulfone providing superior durability and heat resistance, while polyethylene emphasizes lightweight and low-cost production.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polysulfone water bottles exhibit superior mechanical strength with high tensile and impact resistance compared to polyethylene, making them ideal for rugged use and high-pressure environments. Their exceptional thermal stability and resistance to chemical degradation contribute to long-term durability without cracking or warping. Polyethylene, while more flexible and lightweight, generally offers lower strength and shorter lifespan under stress, limiting its application for heavy-duty or high-temperature conditions.
Temperature Resistance and Stability
Polysulfone exhibits superior temperature resistance, maintaining structural integrity in temperatures up to 150degC, making it ideal for hot liquids and sterilization processes. Polyethylene, particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE), performs well at lower temperatures but softens around 80-100degC, limiting its use with hot liquids. Polysulfone also offers better chemical stability and longevity under thermal stress, enhancing performance for reusable water bottles.
Chemical Resistance and Safety
Polysulfone offers superior chemical resistance compared to polyethylene, withstanding strong acids and bases without degrading, making it ideal for water bottles exposed to harsh cleaning agents or environmental chemicals. Polyethylene, while generally safe and inert for food and beverage use, shows lower resistance to certain solvents and high temperatures, which can lead to leaching or material breakdown over time. Both materials are BPA-free and FDA-approved for food contact, but polysulfone's enhanced durability and stability provide greater long-term safety for reusable water bottles under rigorous chemical exposures.
Weight and Portability
Polysulfone water bottles are significantly lighter than polyethylene ones, enhancing portability for outdoor activities and daily use. Polysulfone offers a higher strength-to-weight ratio, making it an excellent choice for those seeking durable yet lightweight hydration solutions. Polyethylene bottles tend to be bulkier and heavier, which may reduce ease of transport and convenience.
Taste and Odor Impartation
Polysulfone water bottles exhibit excellent resistance to taste and odor impartation due to their high chemical stability and non-porous surface, ensuring water remains fresh and untainted. Polyethylene bottles, especially low-density polyethylene (LDPE), can sometimes absorb and retain flavors or odors from previous contents, leading to potential taste alterations over time. Choosing polysulfone minimizes the risk of off-flavors, making it a superior material for maintaining pure water taste in reusable bottles.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polysulfone water bottles exhibit higher durability and thermal resistance but pose challenges in recycling due to their complex polymer structure and limited industrial recycling facilities. Polyethylene, particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE), offers superior recyclability with established recycling streams and lower environmental impact during disposal. The environmental footprint of polyethylene is generally lower, as it breaks down more efficiently and can be repurposed into various products, reducing plastic waste accumulation.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Polysulfone water bottles generally cost more than polyethylene bottles due to their superior heat resistance and durability, making them suitable for long-term use. Polyethylene bottles dominate the market with widespread availability and lower production costs, often used for single-use or budget-friendly options. The price difference reflects polysulfone's advanced material properties, while polyethylene benefits from mass production and extensive supply chains.
Choosing the Best Material for Water Bottles
Polysulfone offers superior heat resistance, durability, and chemical stability compared to polyethylene, making it ideal for reusable water bottles subjected to high temperatures and frequent cleaning. Polyethylene is lightweight, cost-effective, and provides excellent impact resistance but lacks high-temperature tolerance and long-term durability. Choosing the best material depends on usage needs: polysulfone suits long-term, heavy-duty use, while polyethylene is preferred for budget-friendly, everyday, low-heat applications.
Infographic: Polysulfone vs Polyethylene for Water Bottle
 azmater.com
azmater.com