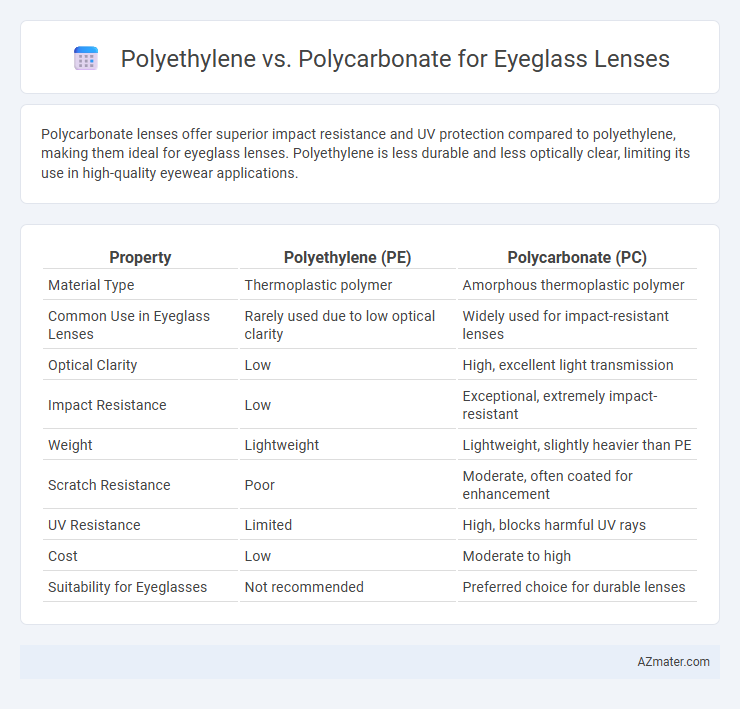
Polycarbonate lenses offer superior impact resistance and UV protection compared to polyethylene, making them ideal for eyeglass lenses. Polyethylene is less durable and less optically clear, limiting its use in high-quality eyewear applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene (PE) | Polycarbonate (PC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Amorphous thermoplastic polymer |
| Common Use in Eyeglass Lenses | Rarely used due to low optical clarity | Widely used for impact-resistant lenses |
| Optical Clarity | Low | High, excellent light transmission |
| Impact Resistance | Low | Exceptional, extremely impact-resistant |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight, slightly heavier than PE |
| Scratch Resistance | Poor | Moderate, often coated for enhancement |
| UV Resistance | Limited | High, blocks harmful UV rays |
| Cost | Low | Moderate to high |
| Suitability for Eyeglasses | Not recommended | Preferred choice for durable lenses |
Introduction to Eyeglass Lens Materials
Polyethylene and polycarbonate are two distinct materials used in eyeglass lenses, each offering unique optical and physical properties. Polycarbonate lenses are known for their high impact resistance, lightweight nature, and superior UV protection, making them ideal for safety glasses and active lifestyles. Polyethylene, although less common in eyeglass lenses, provides excellent chemical resistance and flexibility but generally lacks the optical clarity and scratch resistance of polycarbonate.
What is Polyethylene?
Polyethylene is a lightweight, durable thermoplastic polymer commonly used in various applications, including eyeglass lenses, due to its excellent impact resistance and flexibility. It offers a lower cost alternative compared to polycarbonate but generally lacks the same level of optical clarity and scratch resistance. While polyethylene lenses provide adequate protection and comfort, they may not be as effective for high-performance eyewear demanding superior durability and visual precision.
What is Polycarbonate?
Polycarbonate is a durable, impact-resistant thermoplastic commonly used for eyeglass lenses due to its lightweight and high optical clarity. It offers superior shatter resistance compared to traditional plastic lenses and provides built-in UV protection, making it ideal for safety and children's eyewear. Polycarbonate lenses also have excellent scratch resistance coatings and can be easily molded into thin, curved designs for enhanced comfort and aesthetics.
Optical Clarity: Polyethylene vs Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate lenses offer superior optical clarity compared to polyethylene, with higher light transmission and less distortion, making them ideal for precise vision correction. Polyethylene lenses often exhibit lower clarity due to their inherent material structure, resulting in increased haze and reduced sharpness. The advanced molecular composition of polycarbonate also enhances impact resistance without compromising visual performance, which polyethylene lacks.
Impact Resistance Comparison
Polycarbonate eyeglass lenses offer significantly higher impact resistance compared to polyethylene, making them more suitable for safety and sports eyewear. Polycarbonate can absorb substantial shock without cracking or shattering, whereas polyethylene lenses tend to have lower durability and are more prone to deformation under impact. The superior toughness of polycarbonate lenses enhances user protection, particularly in environments with high risk of lens damage.
Weight and Comfort Differences
Polyethylene eyeglass lenses are significantly lighter than polycarbonate lenses, enhancing wearer comfort during extended use by reducing pressure on the nose and ears. Polycarbonate lenses offer higher impact resistance and better optical clarity but tend to be heavier, which may cause discomfort over long periods. Weight differences typically range from 0.85 g/cm3 for polyethylene to 1.2 g/cm3 for polycarbonate, influencing the overall lens feel and user satisfaction.
UV Protection and Safety
Polycarbonate lenses offer superior UV protection by blocking 100% of harmful UVA and UVB rays, making them an excellent choice for eyeglass wearers concerned about eye health. Polyethylene lenses provide basic UV protection but generally fall short of the comprehensive barrier polycarbonate lenses deliver. In terms of safety, polycarbonate lenses are impact-resistant and highly durable, reducing the risk of eye injury during accidents, whereas polyethylene lenses are less robust and more prone to cracking or shattering.
Cost and Availability
Polyethylene lenses are generally more affordable due to lower production costs, making them a budget-friendly option for eyewear. Polycarbonate lenses, while slightly more expensive, offer greater availability in prescription and impact-resistant variants, making them a popular choice for durable eyeglasses. The widespread availability of polycarbonate also reflects its dominance in the safety eyewear market, despite the price difference.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
Polycarbonate eyeglass lenses offer superior impact resistance and durability, making them ideal for active lifestyles and safety glasses. Polyethylene lenses, while lightweight and flexible, generally have lower scratch resistance and can degrade faster under prolonged exposure to UV light. For long-lasting clarity and robust protection against scratches, polycarbonate is the preferred material compared to polyethylene.
Choosing the Right Lens Material
Polycarbonate eyeglass lenses offer superior impact resistance and UV protection, making them ideal for active lifestyles and children's eyewear. Polyethylene lenses are less common but provide lightweight and cost-effective options with moderate durability. Selecting the right lens material depends on balancing factors such as safety needs, optical clarity, weight, and budget.
Infographic: Polyethylene vs Polycarbonate for Eyeglass lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com