Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers high stiffness and low friction, making it suitable for durable foam seat components, while polyurethane provides superior cushioning and flexibility for enhanced comfort. Choosing between POM and polyurethane depends on whether structural integrity or comfort is the primary focus for foam seat applications.
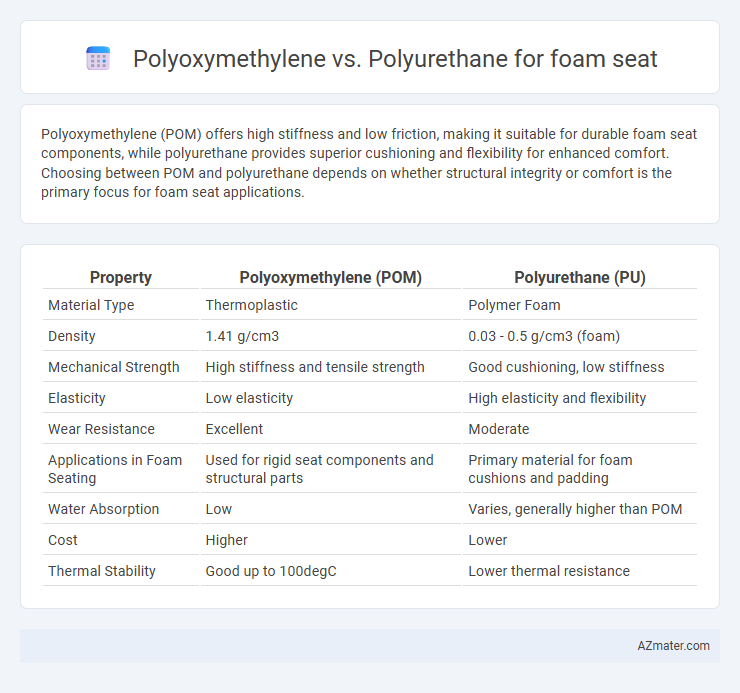
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyoxymethylene (POM) | Polyurethane (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic | Polymer Foam |
| Density | 1.41 g/cm3 | 0.03 - 0.5 g/cm3 (foam) |
| Mechanical Strength | High stiffness and tensile strength | Good cushioning, low stiffness |
| Elasticity | Low elasticity | High elasticity and flexibility |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
| Applications in Foam Seating | Used for rigid seat components and structural parts | Primary material for foam cushions and padding |
| Water Absorption | Low | Varies, generally higher than POM |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Thermal Stability | Good up to 100degC | Lower thermal resistance |
Introduction to Polyoxymethylene and Polyurethane
Polyoxymethylene (POM) is a high-performance engineering thermoplastic known for its excellent stiffness, low friction, and high wear resistance, making it suitable for durable components within foam seat structures. Polyurethane (PU), a versatile polymer, is widely used in foam seats due to its superior flexibility, cushioning properties, and abrasion resistance, providing comfort and resilience in seating applications. Comparing POM's rigidity and dimensional stability with PU's elastic and shock-absorbing characteristics highlights their distinct roles in foam seat design and performance.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Polyoxymethylene (POM) is a highly crystalline thermoplastic polymer composed of repeating formaldehyde units, characterized by strong acetal linkages that provide excellent stiffness and dimensional stability for foam seat applications. Polyurethane (PU), a versatile polymer formed from the reaction of polyols and diisocyanates, exhibits variable chemical structures ranging from flexible to rigid foams with urethane linkages that offer superior cushioning and impact absorption. The chemical structure of POM results in higher mechanical strength and abrasion resistance, while polyurethane's segmented copolymer composition grants enhanced elasticity and resilience tailored for ergonomic foam seating.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polyoxymethylene (POM) exhibits high stiffness, low friction, and excellent dimensional stability, making it suitable for load-bearing seat components requiring rigidity and wear resistance. Polyurethane (PU) foam offers superior elasticity, impact absorption, and cushioning properties, enhancing comfort and energy dissipation in foam seats. Mechanical performance comparison shows POM excels in tensile strength and hardness, while PU foam provides better flexibility and compressive resilience for dynamic seating applications.
Comfort and Ergonomics in Foam Seats
Polyurethane foam excels in comfort and ergonomics for foam seats due to its superior cushioning, flexibility, and ability to conform to body contours, promoting pressure distribution and reducing fatigue. Polyoxymethylene (POM) is less commonly used in foam seats but offers higher stiffness and dimensional stability, which may limit its comfort compared to polyurethane. The choice of polyurethane enhances ergonomic support and durability, making it the preferred material for foam seats focused on maximizing user comfort.
Durability and Longevity Assessment
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers high durability in foam seat applications due to its superior wear resistance and low friction properties, ensuring long-lasting structural integrity under repetitive stress. Polyurethane (PU) foam, while providing excellent cushioning and flexibility, typically exhibits faster degradation over time when exposed to compression and environmental factors such as UV light and moisture. For longevity, POM-based components maintain dimensional stability and resist mechanical fatigue better than PU foams, making them more suitable for high-use seating environments requiring extended lifespan.
Manufacturing Processes and Ease of Fabrication
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers high precision and ease in machining due to its crystalline structure, making it suitable for complex, durable seat components in foam seating. Polyurethane foam, formed through chemical reactions involving polyols and isocyanates, excels in molding and pouring processes, allowing customizable density and cushioning properties ideal for ergonomic seats. Manufacturing polyurethane foam is generally more flexible and faster, while polyoxymethylene requires specialized machining but provides superior structural integrity in seat frameworks.
Cost Analysis: Polyoxymethylene vs Polyurethane
Polyurethane foam seats typically offer a lower upfront cost compared to polyoxymethylene; however, polyurethane's durability and resistance to compression set may reduce long-term replacement expenses. Polyoxymethylene, known for its high stiffness and excellent dimensional stability, generally incurs higher initial costs but can provide superior longevity and structural support in seat applications. Evaluating total cost of ownership involves balancing polyurethane's affordability with polyoxymethylene's enhanced performance and lifespan benefits in foam seating solutions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyoxymethylene (POM) foams exhibit lower environmental impact due to their recyclability and reduced chemical additives compared to polyurethane (PU) foams, which often rely on petrochemical derivatives and contain harmful isocyanates. Polyurethane foams contribute to higher carbon emissions and pose challenges in biodegradability, while POM's chemical structure allows for more efficient recycling processes and less toxic degradation. Sustainability considerations favor POM for seat foams when assessing lifecycle emissions, recyclability potential, and the use of safer raw materials.
Common Applications in Foam Seating
Polyurethane foam is widely used in foam seating for its excellent cushioning, flexibility, and durability, commonly found in automotive seats, office chairs, and furniture padding. Polyoxymethylene (POM), although primarily recognized for its high strength and rigidity in mechanical parts, is less common in foam seating but may be employed in specialized seat components like internal structural supports or adjustment mechanisms. Polyurethane's superior comfort and resilience make it the preferred material in most foam seating applications.
Choosing the Right Material for Foam Seats
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior rigidity and dimensional stability for foam seat components, making it ideal for structural parts that require precision and durability. Polyurethane, with its excellent cushioning properties and high resilience, is preferred for the foam itself, providing comfort and impact absorption in seating applications. Selecting the right material involves balancing POM's strength and wear resistance against polyurethane's flexibility and softness to optimize both support and comfort in foam seats.
Infographic: Polyoxymethylene vs Polyurethane for Foam seat
 azmater.com
azmater.com