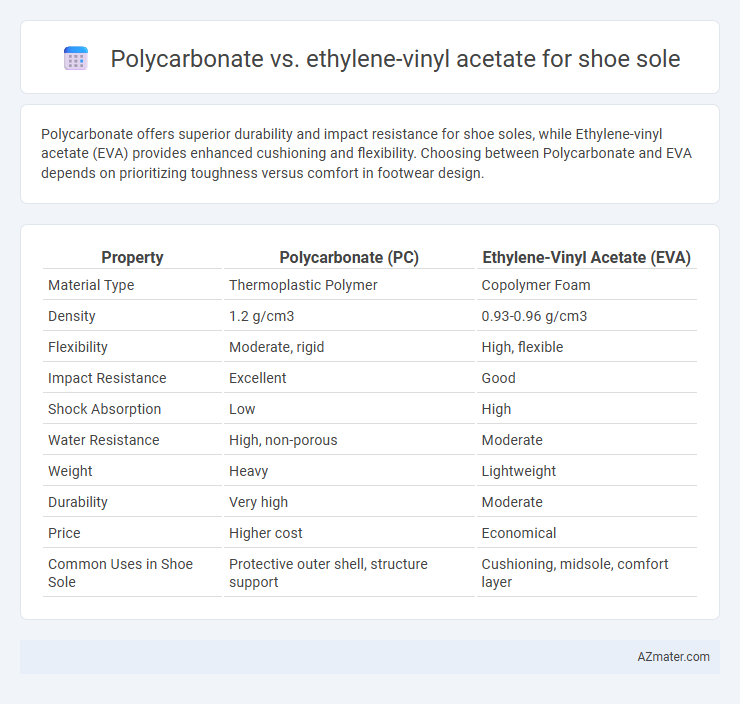
Polycarbonate offers superior durability and impact resistance for shoe soles, while Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) provides enhanced cushioning and flexibility. Choosing between Polycarbonate and EVA depends on prioritizing toughness versus comfort in footwear design.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polycarbonate (PC) | Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polymer | Copolymer Foam |
| Density | 1.2 g/cm3 | 0.93-0.96 g/cm3 |
| Flexibility | Moderate, rigid | High, flexible |
| Impact Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Shock Absorption | Low | High |
| Water Resistance | High, non-porous | Moderate |
| Weight | Heavy | Lightweight |
| Durability | Very high | Moderate |
| Price | Higher cost | Economical |
| Common Uses in Shoe Sole | Protective outer shell, structure support | Cushioning, midsole, comfort layer |
Introduction to Polycarbonate and Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate
Polycarbonate is a durable thermoplastic polymer known for its high impact resistance, transparency, and lightweight properties, making it ideal for robust shoe sole applications that require flexibility and strength. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) is a soft, flexible polymer characterized by excellent cushioning, shock absorption, and low-density attributes, commonly used in athletic and casual shoe soles for enhanced comfort. Both materials offer distinct advantages in footwear, with polycarbonate providing structural support and EVA ensuring superior flexibility and comfort.
Material Composition and Properties
Polycarbonate shoe soles are composed of a durable thermoplastic polymer known for high impact resistance, transparency, and rigidity, making them suitable for stability and long-lasting wear. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) soles consist of a flexible, lightweight copolymer formed by ethylene and vinyl acetate, offering excellent cushioning, shock absorption, and elasticity. The differences in material composition between rigid polycarbonate and soft EVA directly influence the sole's performance, with polycarbonate providing structural support and EVA enhancing comfort and flexibility.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Polycarbonate offers superior durability and wear resistance compared to ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) due to its high-impact strength and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for long-lasting shoe soles in demanding environments. EVA provides excellent cushioning and flexibility but tends to degrade faster under continuous friction and heavy use. For applications requiring robust wear performance, polycarbonate outperforms EVA by maintaining structural integrity and resisting deformation over time.
Comfort and Cushioning Analysis
Polycarbonate soles offer high durability and structural support but typically lack the flexibility and shock absorption found in ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) soles. EVA is renowned for its excellent cushioning properties, providing superior comfort by effectively absorbing impact and reducing foot fatigue during prolonged wear. The lightweight nature of EVA further enhances comfort, making it a preferred choice for athletic and casual shoe soles where flexibility and cushioning are critical.
Flexibility and Performance
Polycarbonate offers high durability and impact resistance but is comparatively rigid, making it less flexible for shoe sole applications. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) provides superior flexibility and cushioning, enhancing comfort and shock absorption during movement. The choice depends on performance needs: rigid support with durability favors polycarbonate, while flexibility and lightweight comfort prioritize EVA.
Weight Comparison for Shoe Soles
Polycarbonate shoe soles are generally heavier due to their dense molecular structure, providing enhanced durability and impact resistance, while ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) soles are significantly lighter and more flexible, offering superior shock absorption and comfort. EVA's low density and cushioning properties make it ideal for lightweight footwear applications aimed at reducing foot fatigue during extended wear. Choosing between polycarbonate and EVA soles hinges on balancing the trade-off between weight and performance requirements specific to the shoe's intended use.
Slip Resistance and Traction
Polycarbonate offers excellent slip resistance and traction due to its rigid structure and high surface hardness, making it suitable for shoe soles in industrial and safety footwear. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) provides moderate traction with superior flexibility and cushioning, ideal for athletic and casual shoes but less effective on slippery surfaces. The choice between polycarbonate and EVA depends on the desired balance between durability, slip resistance, and comfort in footwear performance.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polycarbonate shoe soles offer durability but pose significant environmental challenges due to their non-biodegradable nature and complex recycling processes, often requiring specialized facilities. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) soles are lighter and more flexible, with a relatively lower environmental footprint, yet they also present recycling difficulties because of limited industrial recycling options. Advances in bio-based EVA and improved recycling technologies aim to mitigate environmental impact, making EVA a more sustainable choice compared to polycarbonate for footwear applications.
Cost Considerations for Manufacturers
Polycarbonate offers superior durability and impact resistance for shoe soles but comes at a higher manufacturing cost compared to ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), which is more affordable and widely used due to its lightweight and cushioning properties. EVA provides cost efficiency with easier processing and lower raw material expenses, making it a preferred choice for budget-conscious manufacturers. Balancing performance requirements with cost considerations, manufacturers often select EVA for mass-market footwear while reserving polycarbonate for premium or specialty shoe soles where enhanced strength justifies the increased investment.
Best Applications in Footwear Industry
Polycarbonate offers exceptional impact resistance, durability, and clarity, making it ideal for transparent or high-performance shoe soles such as protective footwear and fashion sneakers. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) provides lightweight cushioning, flexibility, and excellent shock absorption, commonly used in athletic shoes, running sneakers, and casual footwear for enhanced comfort. EVA's superior softness and resilience are preferred for midsoles, while polycarbonate excels in outsoles requiring rigidity and abrasion resistance.
Infographic: Polycarbonate vs Ethylene-vinyl acetate for Shoe sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com