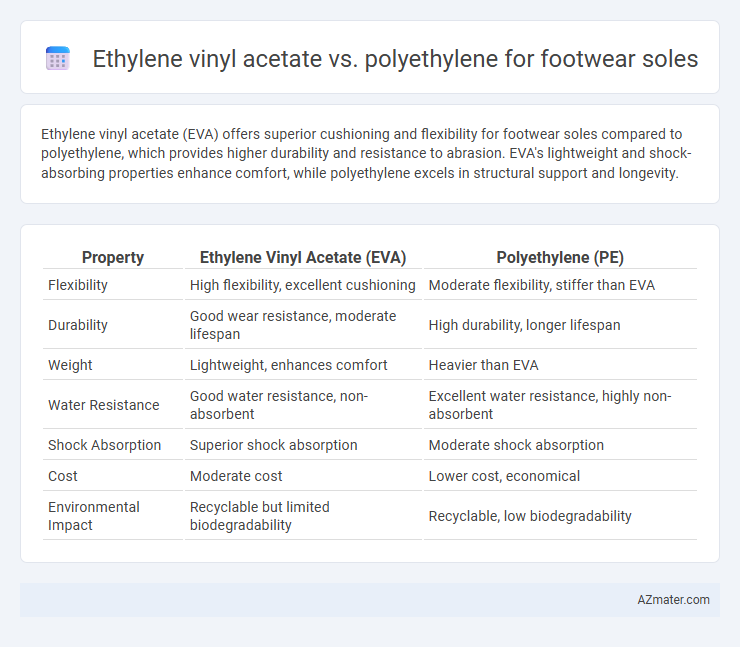
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior cushioning and flexibility for footwear soles compared to polyethylene, which provides higher durability and resistance to abrasion. EVA's lightweight and shock-absorbing properties enhance comfort, while polyethylene excels in structural support and longevity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) | Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High flexibility, excellent cushioning | Moderate flexibility, stiffer than EVA |
| Durability | Good wear resistance, moderate lifespan | High durability, longer lifespan |
| Weight | Lightweight, enhances comfort | Heavier than EVA |
| Water Resistance | Good water resistance, non-absorbent | Excellent water resistance, highly non-absorbent |
| Shock Absorption | Superior shock absorption | Moderate shock absorption |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Lower cost, economical |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable but limited biodegradability | Recyclable, low biodegradability |
Introduction to EVA and Polyethylene in Footwear Soles
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) is a lightweight, flexible polymer widely used in footwear soles due to its excellent cushioning, shock absorption, and resistance to cracking. Polyethylene, a durable and cost-effective thermoplastic, offers high wear resistance and rigidity, making it suitable for more robust footwear designs but with less flexibility compared to EVA. The choice between EVA and polyethylene depends on the desired balance of comfort, durability, and performance in footwear applications.
Material Composition and Properties
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) is a copolymer made from ethylene and vinyl acetate, characterized by its lightweight, flexibility, and excellent cushioning properties, making it ideal for footwear soles that require shock absorption and comfort. Polyethylene (PE), a polymer composed solely of ethylene monomers, offers superior durability, chemical resistance, and stiffness but lacks the elasticity and softness of EVA, resulting in a firmer sole material. The choice between EVA and polyethylene for footwear soles depends on desired attributes: EVA excels in comfort and flexibility, while polyethylene provides enhanced wear resistance and structural support.
Comfort and Cushioning Comparison
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) provides superior cushioning and shock absorption in footwear soles due to its lightweight, flexible foam structure, enhancing overall comfort during prolonged wear. Polyethylene soles, while durable and resistant to abrasion, tend to be stiffer and less effective in energy return, which can reduce comfort in comparison to EVA. EVA's closed-cell foam construction also offers better cushioning by effectively distributing pressure across the foot, making it the preferred material for comfort-focused footwear designs.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior cushioning and flexibility but exhibits lower durability and wear resistance compared to polyethylene (PE) in footwear soles. Polyethylene, particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE), provides enhanced abrasion resistance and longer lifespan under repetitive stress, making it more suitable for rugged and high-impact applications. EVA's softness may lead to faster compression set and surface wear, whereas polyethylene maintains structural integrity for extended periods in demanding environments.
Flexibility and Lightweight Characteristics
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility compared to polyethylene, making it ideal for footwear soles requiring enhanced cushioning and shock absorption. EVA's lightweight nature contributes to overall comfort and agility, outperforming the denser polyethylene, which tends to be stiffer and heavier. This combination of flexibility and low weight makes EVA a preferred material for athletic and casual shoe soles.
Shock Absorption Performance
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior shock absorption for footwear soles due to its lightweight, flexible, and cushioning properties, effectively reducing impact forces during movement. Polyethylene (PE) soles are typically denser and less resilient, resulting in lower energy return and diminished shock absorption performance compared to EVA. The closed-cell structure of EVA enhances impact attenuation, making it a preferred choice for athletic and comfort footwear applications requiring high shock absorption.
Slip Resistance and Traction
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) outperforms polyethylene in footwear sole applications due to its superior slip resistance and traction properties, attributed to its softer, more flexible nature that enhances grip on various surfaces. EVA's ability to absorb shock and provide cushioning improves overall stability, reducing the risk of slips and falls. Polyethylene soles, while durable and stiff, often lack sufficient friction and flexibility, making them less effective in preventing slips compared to EVA-based soles.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers cost-effective cushioning with low raw material expenses and energy-efficient manufacturing processes, making it a preferred choice for lightweight footwear soles. Polyethylene (PE), while generally cheaper per unit, requires higher processing temperatures and more complex molding techniques, increasing manufacturing costs and cycle times. Balancing EVA's flexible manufacturing advantages against PE's material cost savings is crucial for optimizing production budgets in footwear sole applications.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility and cushioning compared to polyethylene (PE), but it is less biodegradable and more challenging to recycle, leading to higher environmental concerns in footwear sole applications. Polyethylene, particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE), is more recyclable and has a lower carbon footprint during production, making it a greener choice for sustainable footwear manufacturing. Manufacturers aiming to reduce ecological impact often prefer polyethylene soles for their better end-of-life recyclability and reduced reliance on fossil fuel resources.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Best Sole Material
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior cushioning, lightweight comfort, and excellent shock absorption, making it ideal for athletic and casual footwear soles. Polyethylene (PE) provides enhanced durability, rigidity, and resistance to chemicals, suited for work boots and heavy-duty shoes. Choosing the best sole material depends on prioritizing comfort and flexibility with EVA or opting for toughness and longevity with Polyethylene.
Infographic: Ethylene vinyl acetate vs Polyethylene for Footwear Sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com