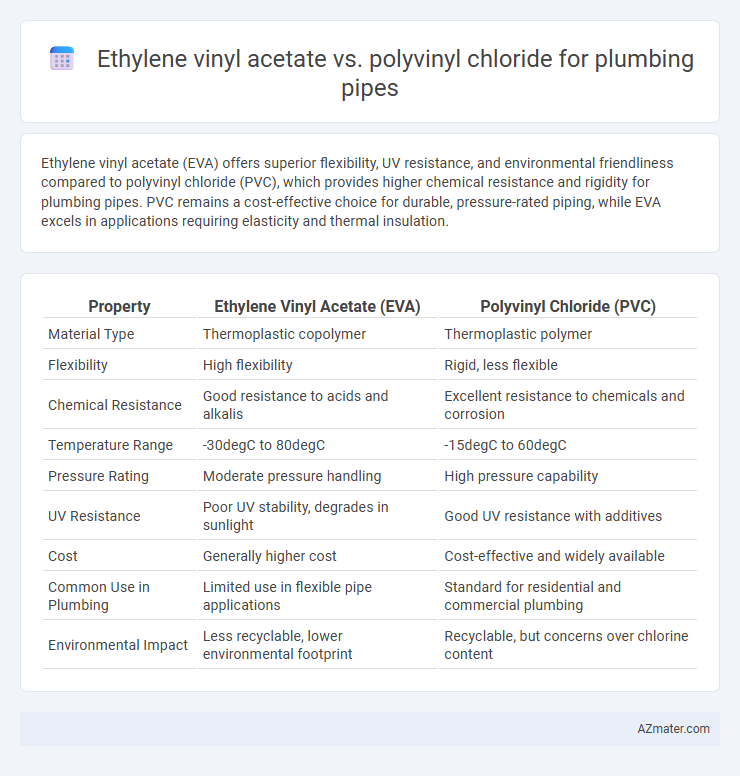
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility, UV resistance, and environmental friendliness compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which provides higher chemical resistance and rigidity for plumbing pipes. PVC remains a cost-effective choice for durable, pressure-rated piping, while EVA excels in applications requiring elasticity and thermal insulation.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic copolymer | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Flexibility | High flexibility | Rigid, less flexible |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and alkalis | Excellent resistance to chemicals and corrosion |
| Temperature Range | -30degC to 80degC | -15degC to 60degC |
| Pressure Rating | Moderate pressure handling | High pressure capability |
| UV Resistance | Poor UV stability, degrades in sunlight | Good UV resistance with additives |
| Cost | Generally higher cost | Cost-effective and widely available |
| Common Use in Plumbing | Limited use in flexible pipe applications | Standard for residential and commercial plumbing |
| Environmental Impact | Less recyclable, lower environmental footprint | Recyclable, but concerns over chlorine content |
Introduction to EVA and PVC Plumbing Pipes
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) plumbing pipes offer excellent flexibility, chemical resistance, and durability, making them suitable for various residential and commercial plumbing applications. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes are widely used for their affordability, rigidity, and high resistance to corrosion and chemical degradation, especially in cold water supply systems. Both EVA and PVC materials provide reliable solutions, with EVA favored for flexibility and thermal resistance, while PVC is preferred for cost-effectiveness and structural strength in plumbing installations.
Chemical Composition and Properties
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) features a copolymer structure of ethylene and vinyl acetate units, providing flexibility, high impact resistance, and excellent chemical resistance ideal for plumbing applications. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) consists of a polymerized vinyl chloride monomer, offering superior rigidity, chemical inertness, and strong resistance to corrosion and abrasion in pipe systems. EVA pipes excel in flexibility and low-temperature performance, while PVC pipes deliver greater strength, dimensional stability, and cost-effectiveness for plumbing installations.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) plumbing pipes exhibit superior flexibility and resistance to environmental stress cracking compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes, enhancing their durability in dynamic pressure conditions. EVA pipes demonstrate a lifespan of approximately 50 years under optimal conditions, while PVC pipes typically last between 25 to 40 years, influenced by exposure to UV light, chemicals, and temperature fluctuations. The enhanced elasticity of EVA contributes to better impact resistance and reduced brittleness over time, making it a more durable choice for plumbing applications in varying environmental conditions.
Flexibility and Installation Ease
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), allowing it to bend easily around corners without the need for additional fittings. This flexibility reduces installation time and labor costs, making EVA pipes ideal for complex plumbing layouts. PVC pipes, while rigid and durable, require precise measurements and more fittings, which can complicate and prolong the installation process.
Chemical Resistance in Plumbing Applications
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior chemical resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) in plumbing applications, particularly against acids, alkalis, and solvents commonly found in industrial and residential water systems. EVA's flexible polymer structure allows it to withstand harsh chemical exposure without degradation, while PVC can become brittle and crack when exposed to certain chemicals over time. This enhanced durability makes EVA a preferred choice for plumbing pipes in environments where chemical corrosion and long-term reliability are critical factors.
Cost Analysis: EVA vs PVC Pipes
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) pipes generally exhibit higher material costs compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes due to EVA's enhanced flexibility and chemical resistance. PVC pipes remain the more cost-effective choice for standard plumbing applications, offering lower manufacturing and installation expenses. However, EVA pipes can provide long-term savings by reducing maintenance and replacement frequency in systems exposed to extreme conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) pipes generally have a lower environmental impact than polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes due to EVA's non-toxic composition and better chemical recyclability. PVC production produces harmful dioxins and requires additives like phthalates, which pose environmental and health risks during manufacturing, use, and disposal. EVA pipes also demonstrate higher durability and flexibility, reducing material waste and extending service life, thus improving overall sustainability in plumbing applications.
Safety Considerations and Health Factors
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) pipes exhibit superior safety profiles compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes due to their lower release of harmful chemicals such as phthalates and vinyl chloride, which are known carcinogens associated with PVC. EVA's flexible and non-toxic properties reduce the risk of leaching hazardous substances into potable water, making it preferable for drinking water systems. In contrast, PVC plumbing requires careful management of additives and stabilizers to mitigate health risks linked to long-term exposure to its chemical components.
Common Plumbing Applications and Suitability
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) is prized in plumbing for its flexibility, chemical resistance, and suitability in hot and cold water systems, making it ideal for residential and commercial applications such as potable water distribution and radiant floor heating. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) excels in durability, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in drainage, waste, and vent (DWV) piping and irrigation systems. While EVA offers superior flexibility for bending and thermal expansion, PVC provides robust structural integrity for high-pressure applications and outdoor exposure.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Pipe Material
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility and chemical resistance, making it ideal for residential plumbing where durability and ease of installation are priorities. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) provides higher stiffness and excellent resistance to corrosion, preferred for commercial plumbing systems with higher pressure requirements. Selecting between EVA and PVC depends on application-specific factors like temperature tolerance, pressure demands, and environmental exposure to ensure optimal plumbing performance and longevity.
Infographic: Ethylene vinyl acetate vs Polyvinyl chloride for Plumbing Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com