Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) ropes offer excellent abrasion resistance and weather durability, making them ideal for heavy-duty outdoor applications. Polypropylene ropes are lightweight, buoyant, and resistant to chemicals, preferred for marine and water-related uses.
Table of Comparison
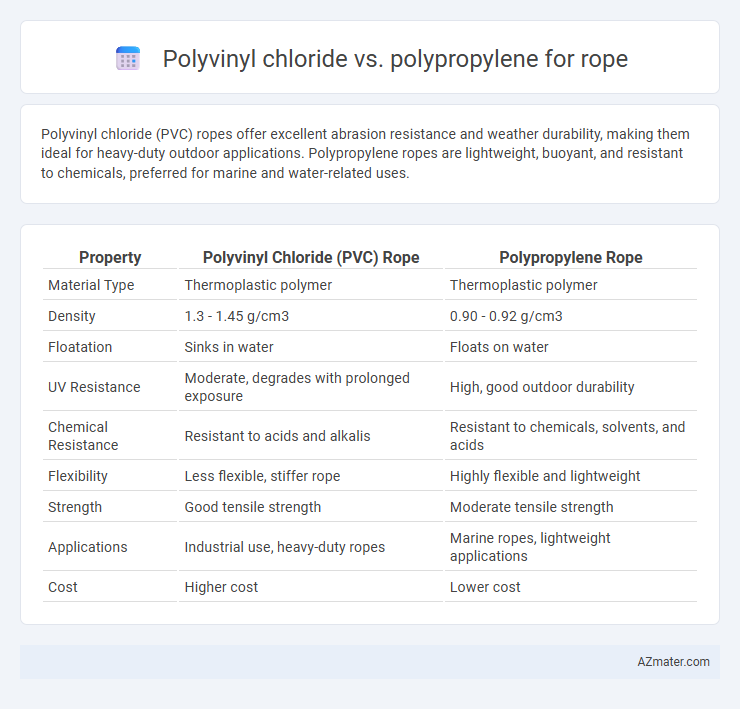
| Property | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Rope | Polypropylene Rope |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Density | 1.3 - 1.45 g/cm3 | 0.90 - 0.92 g/cm3 |
| Floatation | Sinks in water | Floats on water |
| UV Resistance | Moderate, degrades with prolonged exposure | High, good outdoor durability |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to acids and alkalis | Resistant to chemicals, solvents, and acids |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, stiffer rope | Highly flexible and lightweight |
| Strength | Good tensile strength | Moderate tensile strength |
| Applications | Industrial use, heavy-duty ropes | Marine ropes, lightweight applications |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
Introduction to Polyvinyl Chloride and Polypropylene Ropes
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) ropes are known for their durability, flexibility, and resistance to abrasion, water, and chemicals, making them suitable for marine and industrial applications. Polypropylene ropes, on the other hand, are lightweight, buoyant, and have excellent resistance to UV exposure and moisture, often used in water sports and general-purpose tasks. Both materials offer distinct advantages depending on the environmental conditions and mechanical requirements of the rope application.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a synthetic polymer composed of repeating vinyl chloride monomers, characterized by its rigid backbone with chlorine atoms providing chemical resistance and durability. Polypropylene (PP) consists of propylene monomers forming a semi-crystalline structure with a methyl group attached to every other carbon atom, resulting in high tensile strength and flexibility. The chlorine atoms in PVC contribute to its stiffness and flame resistance, whereas the hydrocarbon-based PP offers superior fatigue resistance and lower density, influencing their performance in rope applications.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) ropes offer moderate strength and high resistance to abrasion and chemical exposure but tend to be less flexible and prone to cracking over time compared to polypropylene ropes. Polypropylene ropes demonstrate superior tensile strength and excellent durability in wet environments due to their resistance to moisture absorption, UV degradation, and mildew. For heavy-duty applications requiring long-term durability and high strength, polypropylene is generally preferred, while PVC ropes are suitable for lighter, chemically resistant uses.
Flexibility and Handling Characteristics
Polypropylene ropes offer superior flexibility and lightweight handling, making them ideal for applications requiring easy knotting and quick deployment. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) ropes tend to be stiffer, providing enhanced abrasion resistance but reduced pliability compared to polypropylene. The choice between PVC and polypropylene ropes depends on the need for flexibility and ease of handling versus durability and resistance to environmental factors.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) ropes exhibit strong resistance to chemicals, UV radiation, and moisture, making them ideal for harsh outdoor environments and marine applications. Polypropylene ropes provide excellent resistance to water absorption and chemical exposure but degrade faster under prolonged UV sunlight compared to PVC. Choosing between PVC and polypropylene ropes depends on specific environmental stressors such as UV exposure intensity and chemical contact frequency.
Weight and Buoyancy Differences
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) ropes are heavier due to their higher density, typically around 1.4 g/cm3, while polypropylene (PP) ropes have a lower density of approximately 0.91 g/cm3, making them significantly lighter. The buoyancy advantage of polypropylene ropes is pronounced, as they naturally float on water, contrasting with PVC ropes that tend to sink due to their greater weight. These weight and buoyancy properties make polypropylene ideal for marine applications where floatation is critical, whereas PVC ropes are preferred when extra weight and durability are needed.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) ropes generally offer lower initial costs compared to polypropylene ropes, making them economically attractive for budget-sensitive projects. PVC ropes provide durability and resistance to abrasion, which reduces long-term replacement expenses and maintenance costs. Polypropylene, while slightly more expensive, boasts superior resistance to UV degradation and chemical exposure, potentially lowering lifecycle expenses in harsh outdoor or industrial environments.
Common Applications in Various Industries
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) ropes are widely used in marine and construction industries due to their excellent weather resistance, durability, and ability to resist abrasion and chemicals. Polypropylene ropes are commonly found in agriculture, boating, and sports applications because of their lightweight nature, buoyancy, and resistance to moisture and mildew. Both materials offer specific advantages tailored to industry needs, with PVC favored for heavy-duty, industrial tasks and polypropylene preferred for cost-effective, versatile uses.
Safety and Performance Standards
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) ropes excel in chemical resistance and UV stability, meeting ASTM D4381 safety standards for marine and industrial use, while polypropylene ropes surpass in buoyancy and flexibility but require enhanced flame retardant treatments to comply with NFPA 701 fire safety codes. Polypropylene's lightweight nature and resistance to rot and mildew improve performance in wet environments, yet PVC ropes offer superior abrasion resistance and tensile strength per ISO 2307 testing. Choosing between PVC and polypropylene ropes depends on application-specific safety criteria and performance demands, with PVC preferred for high-stress industrial tasks and polypropylene favored in recreational or buoyant applications.
Choosing the Right Rope Material for Your Needs
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) ropes offer excellent abrasion resistance and chemical stability, making them ideal for marine and industrial applications where durability against harsh conditions is critical. Polypropylene ropes are lightweight, buoyant, and resistant to moisture and mildew, favored for recreational water activities and general-purpose use. Selecting the right rope material depends on specific requirements such as load capacity, environmental exposure, and flexibility, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride vs Polypropylene for Rope
 azmater.com
azmater.com