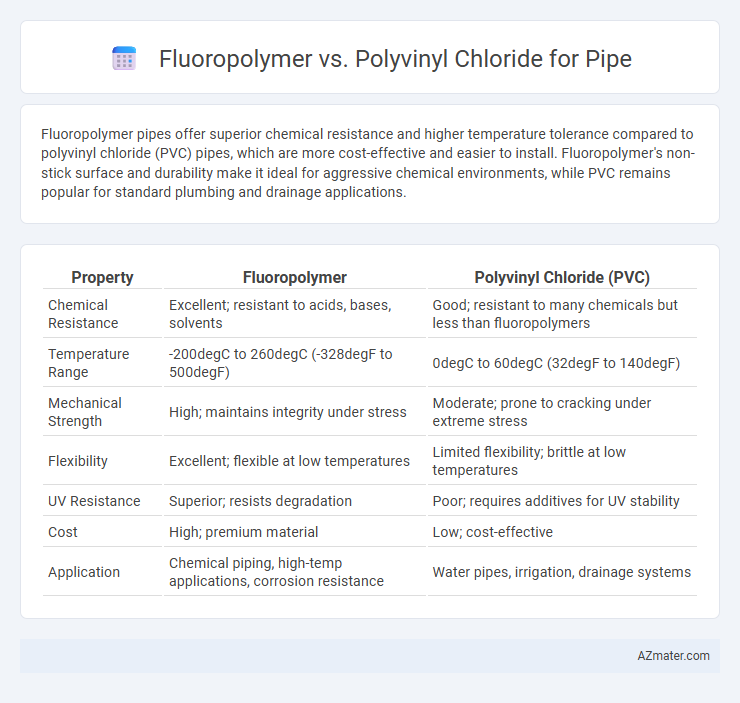
Fluoropolymer pipes offer superior chemical resistance and higher temperature tolerance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes, which are more cost-effective and easier to install. Fluoropolymer's non-stick surface and durability make it ideal for aggressive chemical environments, while PVC remains popular for standard plumbing and drainage applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fluoropolymer | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent; resistant to acids, bases, solvents | Good; resistant to many chemicals but less than fluoropolymers |
| Temperature Range | -200degC to 260degC (-328degF to 500degF) | 0degC to 60degC (32degF to 140degF) |
| Mechanical Strength | High; maintains integrity under stress | Moderate; prone to cracking under extreme stress |
| Flexibility | Excellent; flexible at low temperatures | Limited flexibility; brittle at low temperatures |
| UV Resistance | Superior; resists degradation | Poor; requires additives for UV stability |
| Cost | High; premium material | Low; cost-effective |
| Application | Chemical piping, high-temp applications, corrosion resistance | Water pipes, irrigation, drainage systems |
Introduction to Fluoropolymer and Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Fluoropolymer pipes are known for their exceptional chemical resistance, high thermal stability, and low friction properties, making them ideal for harsh industrial environments. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) pipes offer cost-effective durability, excellent corrosion resistance, and ease of installation, widely used in residential and plumbing applications. Both materials serve distinct roles in piping systems, with fluoropolymers excelling in high-performance, chemically aggressive settings, while PVC remains popular for general-purpose water and waste transport.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Fluoropolymers, such as PTFE, consist of carbon-fluorine bonds that provide exceptional chemical resistance and thermal stability due to the strong electronegativity of fluorine atoms. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is composed of repeating vinyl chloride monomers with chlorine atoms bonded to carbon, offering good mechanical strength and chemical resistance but lower thermal stability compared to fluoropolymers. The difference in chemical structure between fluoropolymers and PVC leads to variations in pipe durability, chemical inertness, and suitability for high-temperature or aggressive chemical environments.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Fluoropolymer pipes exhibit superior chemical resistance, higher temperature tolerance up to 260degC, and excellent flexibility compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes, which typically withstand temperatures only up to 60degC and exhibit lower impact resistance. The tensile strength of fluoropolymers ranges between 20-40 MPa, surpassing PVC's range of 40-55 MPa, but fluoropolymers maintain mechanical integrity under more extreme environments thanks to their exceptional corrosion and UV resistance. PVC pipes offer higher stiffness and dimensional stability, making them suitable for rigid installations, while fluoropolymers are preferred in applications demanding durability, dynamic stress resistance, and longevity under severe chemical exposure.
Corrosion and Chemical Resistance
Fluoropolymer pipes offer superior corrosion and chemical resistance compared to Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), making them ideal for handling aggressive chemicals and highly acidic or alkaline environments. Unlike PVC, which can degrade or become brittle when exposed to strong solvents and high temperatures, fluoropolymers maintain structural integrity and resist chemical attack over prolonged exposure. This enhanced durability ensures longer service life and reduced maintenance costs in industrial piping systems requiring exceptional chemical resilience.
Temperature and Pressure Tolerance
Fluoropolymer pipes exhibit superior temperature tolerance, withstanding continuous operating temperatures up to 260degC (500degF), compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes, which typically max out at around 60degC (140degF). In terms of pressure tolerance, fluoropolymer pipes maintain structural integrity under high-pressure conditions, often exceeding 1500 psi, whereas PVC pipes are generally rated for pressures up to 450 psi at ambient temperatures. The combination of high thermal resistance and enhanced pressure durability makes fluoropolymer an optimal choice for demanding industrial applications involving extreme environments.
Longevity and Durability in Piping Systems
Fluoropolymer pipes exhibit exceptional longevity and chemical resistance, maintaining structural integrity in extreme temperatures and aggressive environments for decades longer than polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes. PVC pipes, while cost-effective and resistant to corrosion, tend to degrade faster under UV exposure and high-pressure conditions, limiting their durability compared to fluoropolymers. The superior abrasion resistance and low permeability of fluoropolymers make them ideal for critical, long-term piping applications in chemical processing and harsh industrial settings.
Ease of Installation and Fabrication
Fluoropolymer pipes offer superior ease of installation and fabrication due to their flexibility, chemical resistance, and ability to withstand high temperatures without deformation. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes are easier to cut, join, and glue, making them cost-effective for straightforward applications but less adaptable to complex shapes or harsh chemical environments. Fluoropolymers provide enhanced performance in demanding installations requiring precision and durability, while PVC suits standard plumbing needs with quicker assembly.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Fluoropolymer pipes typically exhibit higher upfront costs compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes due to advanced material properties and manufacturing complexity. PVC pipes offer significant economic advantages in large-scale applications because of lower raw material expenses and widespread availability. Long-term cost analysis must factor in fluoropolymer's superior chemical resistance and durability, which can reduce maintenance and replacement expenses over the pipe's lifespan.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Fluoropolymer pipes, known for their chemical resistance and long lifespan, generate fewer replacement needs, reducing waste compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes, which often contain additives like phthalates that pose environmental risks during production and disposal. Fluoropolymers are generally more recyclable and have lower greenhouse gas emissions throughout their lifecycle, enhancing sustainability in industrial applications. PVC production relies heavily on chlorine and releases dioxins, contributing to environmental pollution, whereas fluoropolymer manufacturing involves more controlled processes that mitigate toxic byproducts.
Applications and Industry Preferences
Fluoropolymer pipes, known for exceptional chemical resistance and high-temperature tolerance, dominate industries such as chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and semiconductor manufacturing where purity and durability are critical. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes are widely preferred in construction, agriculture, and water distribution due to their cost-effectiveness, ease of installation, and resistance to corrosion from mild chemicals. Industry preferences lean towards fluoropolymers for high-performance applications requiring long-term stability, while PVC remains the go-to for general-purpose piping solutions driven by budget and standard duty requirements.
Infographic: Fluoropolymer vs Polyvinyl Chloride for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com