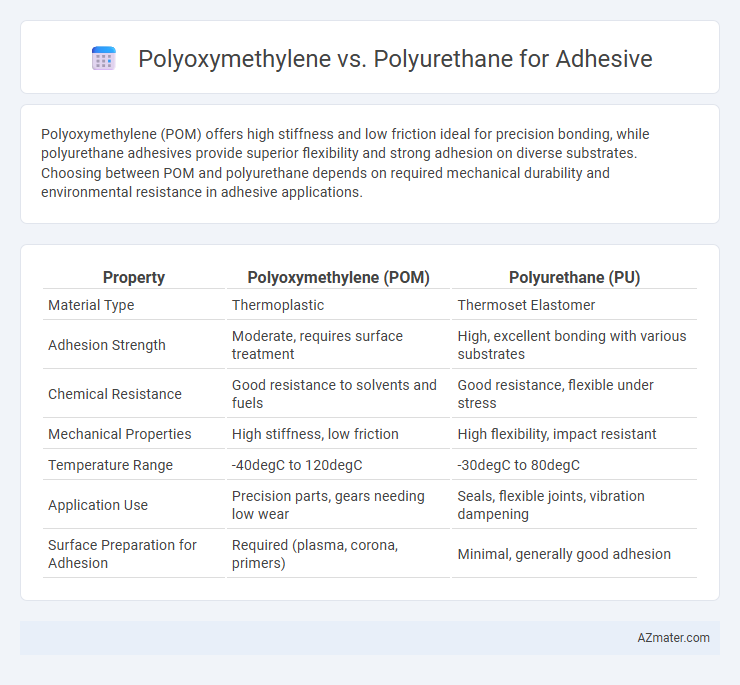
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers high stiffness and low friction ideal for precision bonding, while polyurethane adhesives provide superior flexibility and strong adhesion on diverse substrates. Choosing between POM and polyurethane depends on required mechanical durability and environmental resistance in adhesive applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyoxymethylene (POM) | Polyurethane (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic | Thermoset Elastomer |
| Adhesion Strength | Moderate, requires surface treatment | High, excellent bonding with various substrates |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to solvents and fuels | Good resistance, flexible under stress |
| Mechanical Properties | High stiffness, low friction | High flexibility, impact resistant |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -30degC to 80degC |
| Application Use | Precision parts, gears needing low wear | Seals, flexible joints, vibration dampening |
| Surface Preparation for Adhesion | Required (plasma, corona, primers) | Minimal, generally good adhesion |
Introduction to Polyoxymethylene and Polyurethane
Polyoxymethylene (POM) is a high-performance engineering thermoplastic known for its excellent mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and low friction properties, widely used in precision adhesive applications requiring durability and dimensional stability. Polyurethane (PU) is a versatile polymer characterized by its superior flexibility, strong adhesion to various substrates, and excellent abrasion resistance, making it ideal for adhesives needing elasticity and impact resistance. Comparing POM and PU in adhesive contexts highlights POM's rigidity and chemical inertness versus PU's elasticity and bonding versatility.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Polyoxymethylene (POM) features a repeating -CH2-O- backbone, providing high crystallinity and rigidity due to strong acetal linkages, which leads to excellent dimensional stability and chemical resistance in adhesive applications. Polyurethane (PU) consists of urethane groups (-NH-CO-O-) formed by reacting isocyanates with polyols, offering versatile mechanical properties, flexibility, and strong adhesion through hydrogen bonding and cross-linking in the polymer network. The chemical structure of POM favors rigid, stable bonding surfaces, while PU's segmented chains enable adaptable, durable adhesive layers suitable for diverse substrates.
Physical Properties Overview
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers high stiffness, low friction, and excellent dimensional stability, making it ideal for precision adhesive applications requiring durability under mechanical stress. Polyurethane adhesives provide superior flexibility, impact resistance, and strong bonding to diverse substrates, especially in dynamic environments. Comparing thermal resistance, POM withstands higher temperatures, whereas polyurethane excels in elasticity and resilience, influencing their selection based on application-specific physical demands.
Adhesion Performance Evaluation
Polyoxymethylene (POM) exhibits strong mechanical strength but often presents challenges for adhesion due to its low surface energy, requiring surface treatments like plasma or corona to improve bonding. In contrast, polyurethane (PU) adhesives demonstrate superior adhesion performance on various substrates, attributed to their inherent flexibility and chemical compatibility with polar and non-polar surfaces. Evaluation methods such as lap shear and peel tests consistently show polyurethane adhesives achieving higher bond strength and durability compared to untreated or treated polyoxymethylene substrates.
Bonding Strength Analysis
Polyoxymethylene (POM) exhibits moderate bonding strength with adhesives due to its low surface energy and chemical resistance, often requiring surface treatments for improved adhesion. Polyurethane adhesives provide superior bonding strength on POM surfaces by chemically interacting with treated substrates, offering flexibility and durability in bonded joints. Comparative analysis indicates polyurethane adhesives outperform standard adhesives on POM, enhancing overall bond integrity in demanding applications.
Compatibility with Adhesive Types
Polyoxymethylene (POM) exhibits limited compatibility with standard adhesives due to its low surface energy and chemical resistance, requiring specialized primers or surface treatments to achieve effective bonding. Polyurethane adhesives show superior compatibility with POM after surface modification and are preferred for flexibility and strong adhesion. Conversely, polyurethane substrates inherently bond well with a wide range of polyurethane-based adhesives, offering enhanced durability and resistance to environmental factors without extensive surface preparation.
Durability and Longevity in Adhesive Applications
Polyoxymethylene (POM) exhibits exceptional durability in adhesive applications due to its high tensile strength, resistance to abrasion, and excellent dimensional stability under mechanical stress. Polyurethane adhesives outperform in longevity, offering superior flexibility and resistance to environmental factors such as moisture, UV radiation, and temperature fluctuations, which ensures prolonged bond integrity. When selecting between POM and polyurethane for adhesives, consider POM for high-load bearing joints requiring stiffness, while polyurethane is preferable for applications demanding elasticity and long-term resilience against environmental degradation.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
Polyoxymethylene (POM) adhesives exhibit exceptional resistance to solvents, oils, and moisture, making them ideal for applications in harsh chemical environments. Polyurethane adhesives offer superior flexibility and excellent resistance to UV radiation, abrasion, and temperature variations, ensuring durability in outdoor and fluctuating conditions. When selecting between the two, POM adhesives are preferred for chemical resilience, while polyurethane adhesives excel in dynamic environmental exposure.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Polyoxymethylene (POM) adhesives offer moderate cost and are widely available due to their common use in engineering plastics, making them suitable for budget-conscious applications requiring precision bonding. Polyurethane adhesives tend to be higher in cost but provide greater flexibility and durability, often justifying the investment in high-performance or specialized settings. Availability of polyurethane is generally robust in industrial and consumer markets, but pricing fluctuations can occur based on raw material supply and formulation complexity.
Summary: Choosing Between Polyoxymethylene and Polyurethane for Adhesives
Polyoxymethylene offers high mechanical strength, excellent dimensional stability, and chemical resistance, making it suitable for structural adhesive applications requiring durability. Polyurethane adhesives provide superior flexibility, strong bonding to diverse substrates, and enhanced impact resistance, ideal for dynamic or flexible joints. Selecting between Polyoxymethylene and Polyurethane depends on the application's mechanical stress, environmental exposure, and required bonding flexibility.
Infographic: Polyoxymethylene vs Polyurethane for Adhesive
 azmater.com
azmater.com