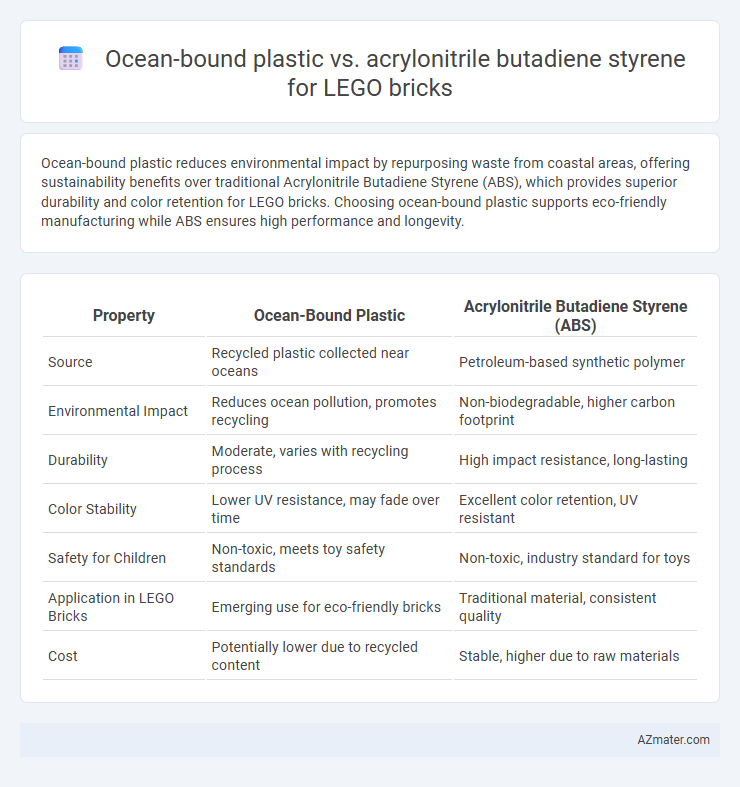
Ocean-bound plastic reduces environmental impact by repurposing waste from coastal areas, offering sustainability benefits over traditional Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), which provides superior durability and color retention for LEGO bricks. Choosing ocean-bound plastic supports eco-friendly manufacturing while ABS ensures high performance and longevity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ocean-Bound Plastic | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Recycled plastic collected near oceans | Petroleum-based synthetic polymer |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces ocean pollution, promotes recycling | Non-biodegradable, higher carbon footprint |
| Durability | Moderate, varies with recycling process | High impact resistance, long-lasting |
| Color Stability | Lower UV resistance, may fade over time | Excellent color retention, UV resistant |
| Safety for Children | Non-toxic, meets toy safety standards | Non-toxic, industry standard for toys |
| Application in LEGO Bricks | Emerging use for eco-friendly bricks | Traditional material, consistent quality |
| Cost | Potentially lower due to recycled content | Stable, higher due to raw materials |
Introduction: The Urgency of Sustainable LEGO Bricks
Ocean-bound plastic offers a crucial sustainable alternative to traditional materials like Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) in LEGO bricks by reducing plastic pollution threatening marine ecosystems. ABS, while durable and vibrant, is derived from non-renewable fossil fuels and contributes significantly to environmental degradation. Integrating ocean-bound plastic into LEGO production addresses urgent ecological concerns by repurposing waste and fostering circular economy practices.
What Is Ocean-Bound Plastic?
Ocean-bound plastic refers to waste plastics collected within 50 kilometers of coastlines, preventing them from entering marine environments and contributing to ocean pollution. LEGO incorporates ocean-bound plastic derived from discarded fishing nets, ropes, and other plastic debris to create sustainable bricks, reducing environmental impact. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), a durable petroleum-based plastic, has traditionally been used for LEGO bricks due to its strength and resilience but poses challenges in terms of recyclability and environmental footprint.
Understanding Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a durable thermoplastic polymer widely used in manufacturing LEGO bricks due to its strength, impact resistance, and high-quality finish. Unlike ocean-bound plastic, which is derived from waste materials collected near coastlines, ABS is synthesized from petrochemical components, ensuring consistent material properties and precise molding capabilities essential for intricate LEGO designs. ABS's excellent heat resistance and color retention make it the preferred choice for maintaining LEGO bricks' long-lasting performance and vibrant appearance.
Environmental Impact: Ocean-Bound Plastic vs ABS
Ocean-bound plastic significantly reduces environmental pollution by diverting waste from marine ecosystems, lowering plastic leakage into oceans, and promoting circular economy principles. In contrast, Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), a petroleum-derived plastic, contributes to higher carbon emissions and non-biodegradable waste accumulation during production and disposal. LEGO's initiative to replace ABS with ocean-bound plastic in bricks helps decrease fossil fuel dependence and mitigates ocean pollution, enhancing overall environmental sustainability.
Material Properties and Durability Comparison
Ocean-bound plastic exhibits moderate durability and sustainability benefits in LEGO bricks but lacks the mechanical strength and heat resistance of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS). ABS offers superior impact resistance, rigidity, and long-term color retention, making it ideal for precise and durable LEGO components. While ocean-bound plastic supports environmental goals by reducing marine pollution, ABS remains the standard for performance-critical LEGO bricks due to its superior material properties.
Manufacturing Challenges and Solutions
Ocean-bound plastic presents significant manufacturing challenges for LEGO bricks, including inconsistent raw material quality and contamination risks that affect moldability and product durability. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior structural integrity and color stability but relies heavily on fossil fuels, raising sustainability concerns. To address these issues, LEGO invests in advanced sorting technologies and innovative polymer blends to enhance the performance of recycled ocean-bound plastics while maintaining the high-quality standards of ABS bricks.
Recycling and End-of-Life Considerations
Ocean-bound plastic offers a sustainable alternative for LEGO bricks by reducing marine pollution while promoting a circular economy through material recovery and reuse. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), the traditional material, poses recycling challenges due to its complex polymer structure, often leading to downcycling or incineration at end-of-life. Advancing recycling technologies and adopting ocean-bound plastics enhance resource efficiency and minimize environmental impact across LEGO brick life cycles.
Consumer Perception and Brand Responsibility
Ocean-bound plastic used in LEGO bricks highlights the brand's commitment to environmental sustainability, resonating strongly with eco-conscious consumers seeking responsible product choices. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), known for durability and vibrant color retention, remains preferred for traditional LEGO bricks, ensuring high-quality play experiences but raising concerns over plastic waste. Emphasizing ocean-bound plastic integration enhances LEGO's brand responsibility narrative, fostering positive consumer perception toward reducing marine pollution while maintaining product performance.
Innovations in LEGO’s Sustainability Journey
LEGO's sustainability journey highlights innovations such as replacing traditional Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) with ocean-bound plastic in select bricks, reducing environmental impact. Ocean-bound plastic, sourced from coastal areas vulnerable to pollution, promotes circular economy principles by preventing marine debris. This shift exemplifies LEGO's commitment to eco-friendly materials while maintaining the durability and quality associated with ABS plastic bricks.
Future Prospects: Which Material Leads LEGO’s Green Revolution?
Ocean-bound plastic, sourced from waste collected near coastlines, offers LEGO a sustainable pathway by significantly reducing marine pollution and promoting circular economy principles. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), while durable and ideal for LEGO brick performance, relies on fossil fuels and poses challenges for biodegradability and recycling. Future prospects favor ocean-bound plastic as LEGO intensifies efforts toward eco-friendly innovation, expanding green materials usage and advancing carbon footprint reduction in production processes.
Infographic: Ocean-bound plastic vs Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene for LEGO brick
 azmater.com
azmater.com