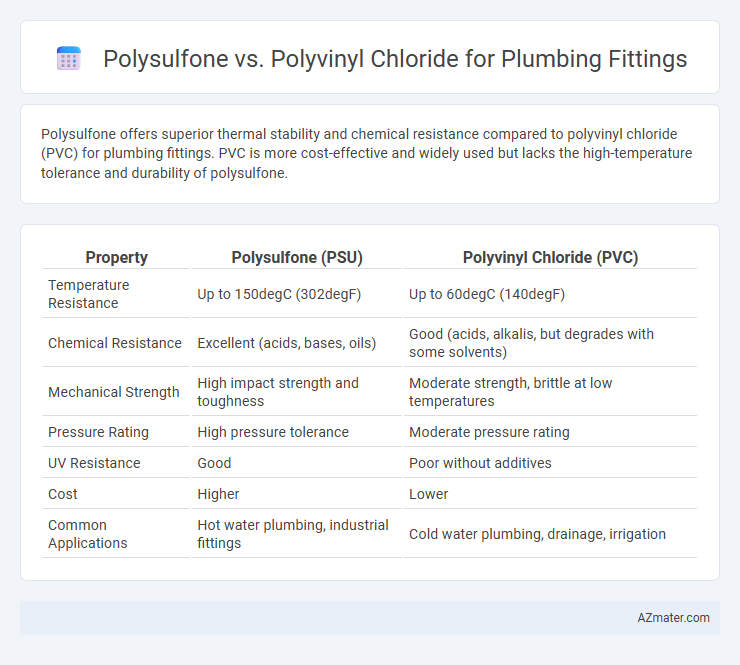
Polysulfone offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) for plumbing fittings. PVC is more cost-effective and widely used but lacks the high-temperature tolerance and durability of polysulfone.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfone (PSU) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 150degC (302degF) | Up to 60degC (140degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (acids, bases, oils) | Good (acids, alkalis, but degrades with some solvents) |
| Mechanical Strength | High impact strength and toughness | Moderate strength, brittle at low temperatures |
| Pressure Rating | High pressure tolerance | Moderate pressure rating |
| UV Resistance | Good | Poor without additives |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Common Applications | Hot water plumbing, industrial fittings | Cold water plumbing, drainage, irrigation |
Introduction to Plumbing Fitting Materials
Polysulfone and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) are widely utilized materials in plumbing fittings due to their distinct chemical and physical properties. Polysulfone offers high thermal stability and excellent chemical resistance, making it suitable for hot water applications and aggressive environments. PVC is favored for its cost-effectiveness, ease of installation, and durability in cold water systems and residential plumbing.
Overview of Polysulfone (PSU)
Polysulfone (PSU) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent chemical resistance, thermal stability up to 160degC, and superior mechanical strength, making it ideal for demanding plumbing fittings. It maintains consistent performance under repeated sterilization processes and exposure to harsh chemicals, unlike polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which can degrade under high heat or prolonged chemical exposure. PSU's inherent transparency and dimensional stability provide advantages in applications requiring visual inspection and tight tolerances in fluid transport systems.
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is a widely used thermoplastic in plumbing fittings due to its excellent chemical resistance, affordability, and ease of installation. PVC pipes offer strong durability against corrosion and are suitable for both cold and hot water applications, typically up to 140degF (60degC). Its lightweight nature and ability to be solvent-welded make PVC a preferred choice for residential and commercial plumbing systems, although it may have lower impact resistance compared to polysulfone.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Polysulfone exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), especially against hydrocarbon-based solvents and high-temperature acidic and alkaline solutions, making it ideal for industrial plumbing fittings exposed to harsh chemicals. PVC is more susceptible to degradation and embrittlement when exposed to certain solvents, chlorinated compounds, and UV radiation, limiting its application in chemically aggressive environments. The inherent thermal stability and resistance of polysulfone contribute to longer service life and reduced maintenance in chemically demanding plumbing systems.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polysulfone exhibits superior mechanical strength and temperature resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it ideal for high-pressure plumbing fittings. Its enhanced durability enables it to withstand thermal cycling and chemical exposure without degradation, ensuring long-term reliability in demanding environments. PVC, while cost-effective and corrosion-resistant, tends to be less resistant to impact and temperature fluctuations, limiting its use in heavy-duty plumbing applications.
Temperature Tolerance and Thermal Stability
Polysulfone exhibits superior temperature tolerance and thermal stability compared to polyvinyl chloride, withstanding continuous operating temperatures up to 150degC, whereas PVC typically limits performance to around 60degC. This enhanced thermal resistance makes polysulfone ideal for hot water plumbing applications where durability under heat stress is critical. In contrast, PVC's lower heat tolerance restricts its use to cold water systems or environments with limited thermal exposure.
Ease of Installation and Fabrication
Polysulfone offers superior ease of installation for plumbing fittings due to its high thermal stability and chemical resistance, allowing for reliable solvent welding and hot-melt adhesion without deformation. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is widely used for plumbing because of its affordability and straightforward solvent cement joining methods, though it is less resistant to high temperatures and certain chemicals compared to polysulfone. Fabrication of polysulfone components requires specialized equipment and expertise due to higher processing temperatures, whereas PVC fittings benefit from simpler molding and cutting techniques suitable for on-site adjustments.
Cost Analysis: PSU vs PVC
Polysulfone (PSU) plumbing fittings typically incur higher initial costs compared to Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) due to PSU's superior thermal resistance and chemical stability. PVC remains a cost-effective choice for general plumbing applications, with material expenses significantly lower and manufacturing processes well-established. Long-term cost analysis also favors PSU in high-temperature or corrosive environments, where reduced maintenance and replacement needs offset the upfront investment.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Polysulfone exhibits superior environmental sustainability compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) due to its enhanced chemical resistance, thermal stability, and potential for recycling, reducing degradation and harmful emissions over time. PVC plumbing fittings release toxic dioxins during manufacturing and incineration, posing significant environmental and health risks, while polysulfone's production involves fewer hazardous chemicals and lower volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. The biocompatibility and resistance to leaching of polysulfone ensure safer water quality in plumbing systems, contrasting with PVC's potential release of harmful additives such as phthalates and chlorine-based compounds.
Best Applications: Choosing the Right Material
Polysulfone offers superior heat resistance and chemical stability, making it ideal for hot water and industrial plumbing applications requiring long-term durability. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is cost-effective and highly resistant to corrosion, suited for cold water systems and non-pressurized drainage. Selecting the right material depends on temperature requirements, chemical exposure, and budget constraints, with polysulfone preferred for demanding environments and PVC for standard residential plumbing.
Infographic: Polysulfone vs Polyvinyl Chloride for Plumbing Fitting
 azmater.com
azmater.com