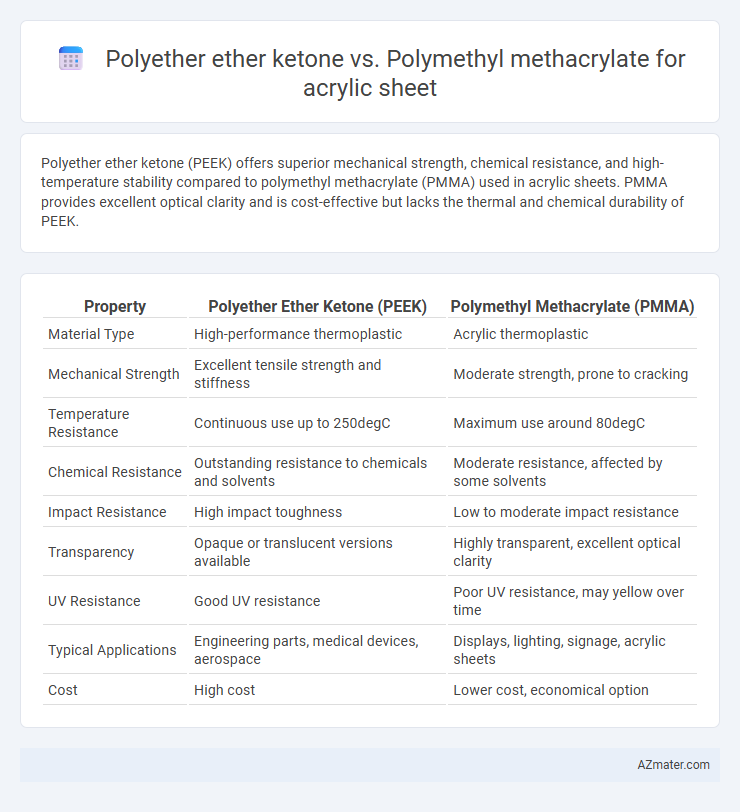
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and high-temperature stability compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) used in acrylic sheets. PMMA provides excellent optical clarity and is cost-effective but lacks the thermal and chemical durability of PEEK.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-performance thermoplastic | Acrylic thermoplastic |
| Mechanical Strength | Excellent tensile strength and stiffness | Moderate strength, prone to cracking |
| Temperature Resistance | Continuous use up to 250degC | Maximum use around 80degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Outstanding resistance to chemicals and solvents | Moderate resistance, affected by some solvents |
| Impact Resistance | High impact toughness | Low to moderate impact resistance |
| Transparency | Opaque or translucent versions available | Highly transparent, excellent optical clarity |
| UV Resistance | Good UV resistance | Poor UV resistance, may yellow over time |
| Typical Applications | Engineering parts, medical devices, aerospace | Displays, lighting, signage, acrylic sheets |
| Cost | High cost | Lower cost, economical option |
Introduction to Acrylic Sheet Materials
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) and Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) are prominent materials used in the production of acrylic sheets, each offering distinct mechanical and chemical properties. PMMA, known for its clarity, UV resistance, and ease of fabrication, serves as a widely preferred acrylic sheet material in applications demanding transparency and lightweight durability. In contrast, PEEK provides superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it suitable for high-performance engineering acrylic components requiring enhanced durability under extreme conditions.
Overview of Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK)
Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, making it suitable for demanding engineering applications. Unlike Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA), which is commonly used for transparent acrylic sheets due to its optical clarity and ease of fabrication, PEEK offers superior durability and resistance to wear, chemicals, and high temperatures. This makes PEEK ideal for specialized industrial components, although it lacks the transparency and cost-effectiveness that PMMA provides for general-purpose acrylic sheet applications.
Overview of Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) is a transparent thermoplastic commonly used as an acrylic sheet due to its high optical clarity and excellent weather resistance. It offers superior UV stability and scratch resistance compared to Polyether ether ketone (PEEK), making it ideal for applications requiring durability and light transmission. PMMA sheets provide easier fabrication and cost-effectiveness while maintaining strong impact resistance for various architectural and automotive uses.
Mechanical Properties Comparison: PEEK vs PMMA
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) exhibits superior mechanical properties compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) for acrylic sheet applications, offering higher tensile strength, greater impact resistance, and enhanced flexibility. PEEK's tensile strength ranges around 90-100 MPa, significantly outperforming PMMA's typical 70 MPa, while its elongation at break reaches up to 50%, compared to PMMA's brittle nature with less than 5% elongation. The enhanced mechanical durability of PEEK makes it suitable for demanding structural uses, whereas PMMA excels in clarity but falls short in toughness and impact resistance.
Optical Clarity and Aesthetics
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers excellent mechanical strength and chemical resistance but has lower optical clarity compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), which is renowned for its superior transparency and brilliant aesthetics. PMMA acrylic sheets provide exceptional light transmittance up to 92%, ensuring clear visibility and vibrant color rendering ideal for display and architectural applications. The high-gloss finish and UV resistance of PMMA further enhance its aesthetic appeal, making it the preferred choice for transparent and visually striking acrylic sheets.
Chemical Resistance and Durability
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) acrylic sheets, withstanding aggressive solvents, acids, and high temperatures without degradation. PMMA offers moderate chemical resistance but is prone to surface damage and discoloration when exposed to solvents like acetone and strong alkalis. In terms of durability, PEEK provides exceptional mechanical strength, impact resistance, and long-term stability under harsh environmental conditions, whereas PMMA is more susceptible to brittleness and UV-induced degradation over time.
Thermal Performance of PEEK and PMMA
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) exhibits superior thermal performance compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) in acrylic sheet applications, with a high melting point around 343degC versus PMMA's glass transition temperature near 105degC. PEEK maintains mechanical properties and dimensional stability at elevated temperatures, making it suitable for high-heat environments where PMMA tends to soften and deform. The inherent heat resistance and thermal degradation temperature of PEEK significantly outperform the thermal limits of PMMA, ensuring long-term durability under thermal stress.
Applications in Industry: PEEK vs PMMA
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior mechanical strength, thermal stability, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for aerospace, automotive, and medical implant applications where durability and performance under extreme conditions are critical. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), known as acrylic, excels in optical clarity and weather resistance, widely used in signage, lighting fixtures, and automotive glazing. PEEK's higher cost limits its use to specialized industrial components, while PMMA remains preferred for cost-effective, transparent solutions in architectural and display industries.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) is significantly more expensive than polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), with costs often several times higher due to its high-performance properties and specialized manufacturing processes. PMMA acrylic sheets offer superior availability and cost-effectiveness, making them the preferred choice for applications where budget constraints and widespread supply are critical. The extensive global supply chain for PMMA ensures consistent availability, whereas PEEK is typically reserved for niche industrial applications requiring exceptional chemical and thermal resistance.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) exhibits superior environmental resilience with high chemical stability and thermal resistance, enabling extended lifecycle and reduced waste compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), commonly used in acrylic sheets. PMMA is more readily recyclable through established mechanical recycling processes, though it requires significant energy input and can degrade in quality after multiple cycles, impacting sustainability metrics. PEEK's limited recyclability is a challenge, but ongoing advances in chemical recycling aim to improve its environmental footprint relative to traditional acrylic materials.
Infographic: Polyether ether ketone vs Polymethyl methacrylate for Acrylic sheet
 azmater.com
azmater.com