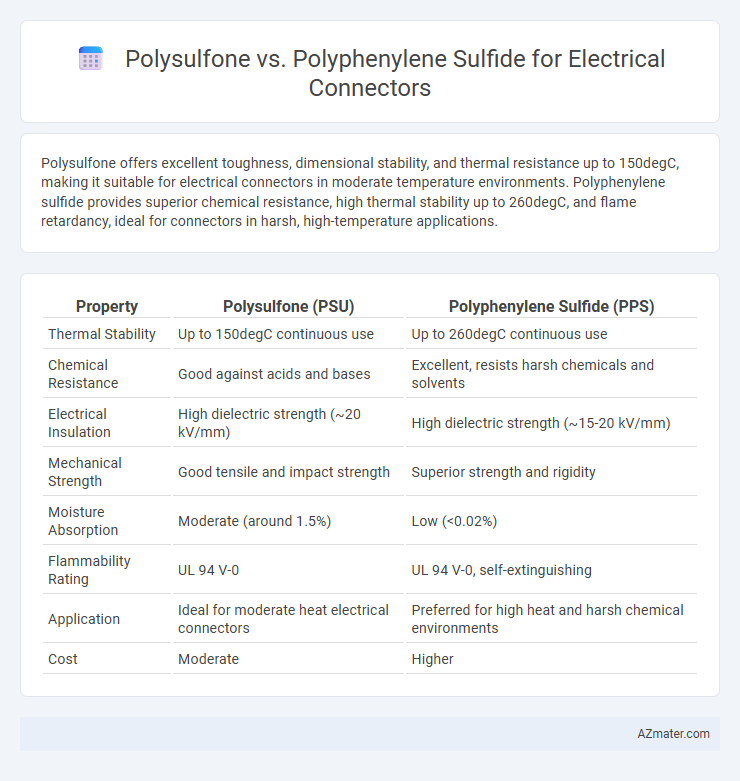
Polysulfone offers excellent toughness, dimensional stability, and thermal resistance up to 150degC, making it suitable for electrical connectors in moderate temperature environments. Polyphenylene sulfide provides superior chemical resistance, high thermal stability up to 260degC, and flame retardancy, ideal for connectors in harsh, high-temperature applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfone (PSU) | Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | Up to 150degC continuous use | Up to 260degC continuous use |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against acids and bases | Excellent, resists harsh chemicals and solvents |
| Electrical Insulation | High dielectric strength (~20 kV/mm) | High dielectric strength (~15-20 kV/mm) |
| Mechanical Strength | Good tensile and impact strength | Superior strength and rigidity |
| Moisture Absorption | Moderate (around 1.5%) | Low (<0.02%) |
| Flammability Rating | UL 94 V-0 | UL 94 V-0, self-extinguishing |
| Application | Ideal for moderate heat electrical connectors | Preferred for high heat and harsh chemical environments |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
Introduction to Polysulfone and Polyphenylene Sulfide
Polysulfone (PSU) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent thermal stability, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance, making it suitable for electrical connectors in demanding environments. Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) offers superior chemical and heat resistance along with excellent dimensional stability and low moisture absorption, ideal for connectors requiring long-term reliability. Both materials provide unique advantages in electrical connectors, with PSU excelling in toughness and clarity, while PPS is preferred for high-temperature applications and resistance to aggressive chemicals.
Overview of Electrical Connector Materials
Polysulfone (PSU) and Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) are key thermoplastic polymers used in electrical connector applications due to their excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance. Polysulfone offers high impact strength and dimensional stability up to 150degC, making it suitable for connectors in moderately high-temperature environments. Polyphenylene Sulfide provides superior thermal resistance up to 260degC, exceptional chemical resistance, and excellent electrical insulation properties, making it ideal for high-performance electrical connectors in harsh conditions.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Polysulfone (PSU) features repeating aromatic rings linked by sulfone (-SO2-) groups, providing high thermal stability and chemical resistance essential for electrical connectors. Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) consists of a backbone of alternating phenylene rings and sulfide (-S-) linkages, offering superior chemical inertness and dimensional stability under harsh environments. The sulfone groups in PSU contribute to greater toughness, while the sulfide linkages in PPS enhance resistance to solvents and high-temperature degradation, making material selection critical depending on operational conditions.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Polysulfone (PSU) offers excellent thermal stability with a continuous use temperature up to 160degC, making it suitable for electrical connectors requiring moderate heat resistance. Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) exhibits superior heat resistance, maintaining structural integrity and electrical insulation performance at temperatures exceeding 200degC, ideal for high-temperature applications. The chemical structure of PPS provides greater thermal oxidative stability and resistance to hydrolysis compared to PSU, making it a preferred choice in harsh thermal environments for electrical connectors.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Polysulfone exhibits high tensile strength and excellent impact resistance, making it suitable for electrical connectors requiring dimensional stability under mechanical stress. Polyphenylene sulfide offers superior chemical resistance and maintains mechanical integrity at high temperatures, enhancing connector durability in harsh environments. Both materials provide flame retardancy, but polyphenylene sulfide generally delivers longer service life due to its enhanced thermal and chemical resilience.
Electrical Insulation Performance
Polysulfone (PSU) offers excellent electrical insulation properties with high dielectric strength and thermal stability, making it suitable for connectors operating in moderate temperature environments up to 150degC. Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) outperforms PSU with superior insulation resistance, lower dielectric constant, and the ability to maintain electrical integrity at elevated temperatures up to 260degC, which is critical for high-performance electrical connectors exposed to harsh thermal and chemical conditions. PPS also exhibits better resistance to tracking and arc erosion, enhancing long-term reliability in demanding electrical insulation applications.
Chemical and Environmental Resistance
Polysulfone (PSU) offers excellent resistance to high temperatures and hydrolysis, making it suitable for electrical connectors exposed to water and steam environments. Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) excels in chemical resistance, particularly against acids, bases, and organic solvents, providing enhanced durability in harsh chemical conditions. PPS also demonstrates superior environmental resistance with high dimensional stability and resistance to UV radiation, making it ideal for outdoor electrical connector applications.
Manufacturability and Processing Techniques
Polysulfone (PSU) offers excellent thermal stability and dimensional stability, making it suitable for electrical connectors requiring precision molding and machining, with common processing techniques including injection molding and extrusion. Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) exhibits superior chemical resistance and higher temperature tolerance, enabling processing through injection molding and compression molding while maintaining structural integrity in harsh environments. PPS's inherent rigidity and lower melt viscosity improve manufacturability in high-volume applications compared to PSU, which may require more controlled processing conditions to prevent degradation.
Cost-Effectiveness and Market Availability
Polysulfone offers moderate cost-effectiveness with stable market availability, making it suitable for standard electrical connectors requiring good thermal and chemical resistance. Polyphenylene sulfide provides superior performance in high-temperature and chemically aggressive environments but typically comes at a higher price and with more limited market availability. Selection between these polymers depends on balancing budget constraints with performance needs in electrical connector applications.
Application Suitability and Final Recommendations
Polysulfone offers excellent thermal stability and flame resistance, making it suitable for electrical connectors in moderate temperature environments up to 150degC with a strong balance of mechanical strength and chemical resistance. Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) outperforms Polysulfone in high-temperature applications, maintaining dimensional stability and electrical insulation properties above 200degC, ideal for connectors exposed to harsh chemical and thermal conditions. For applications requiring elevated heat resistance and superior chemical durability, PPS is the recommended choice, while Polysulfone serves well in less demanding environments that benefit from cost-effectiveness and good overall performance.
Infographic: Polysulfone vs Polyphenylene sulfide for Electrical connector
 azmater.com
azmater.com