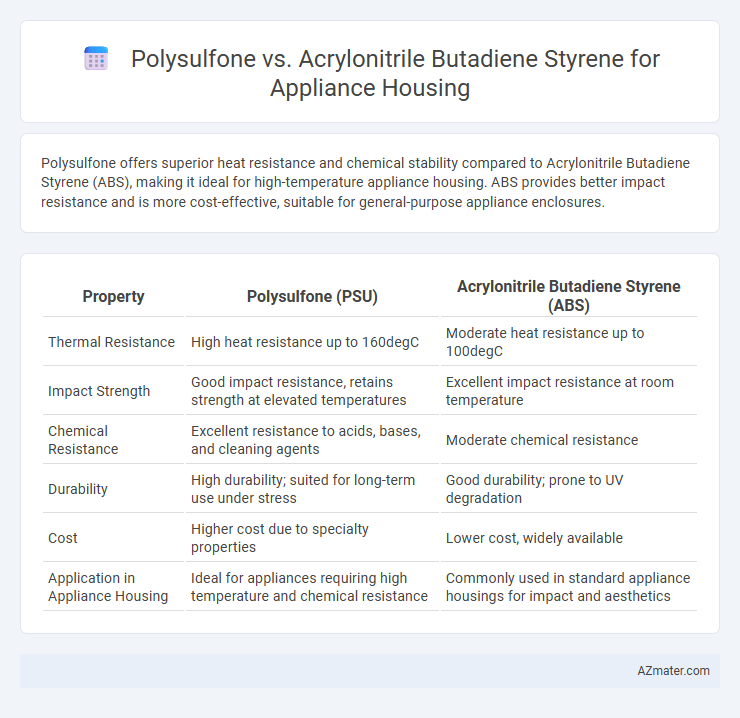
Polysulfone offers superior heat resistance and chemical stability compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), making it ideal for high-temperature appliance housing. ABS provides better impact resistance and is more cost-effective, suitable for general-purpose appliance enclosures.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfone (PSU) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | High heat resistance up to 160degC | Moderate heat resistance up to 100degC |
| Impact Strength | Good impact resistance, retains strength at elevated temperatures | Excellent impact resistance at room temperature |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to acids, bases, and cleaning agents | Moderate chemical resistance |
| Durability | High durability; suited for long-term use under stress | Good durability; prone to UV degradation |
| Cost | Higher cost due to specialty properties | Lower cost, widely available |
| Application in Appliance Housing | Ideal for appliances requiring high temperature and chemical resistance | Commonly used in standard appliance housings for impact and aesthetics |
Introduction to Appliance Housing Materials
Polysulfone offers superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), making it ideal for high-performance appliance housings exposed to heat and harsh environments. ABS is favored for its excellent impact resistance, ease of processing, and cost-effectiveness in producing durable, lightweight housings for consumer appliances. The choice between polysulfone and ABS depends on specific appliance requirements such as temperature tolerance, structural integrity, and manufacturing considerations.
Overview of Polysulfone (PSU)
Polysulfone (PSU) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and toughness, making it ideal for appliance housing. It maintains mechanical strength and dimensional stability at elevated temperatures up to 150degC, outperforming many other plastics in demanding environments. The material's inherent flame retardancy and excellent resistance to hydrolysis and oxidation ensure long-lasting durability for appliance enclosures.
Overview of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer widely used in appliance housings due to its excellent impact resistance, toughness, and ease of fabrication. ABS offers good dimensional stability and resistance to chemical corrosion, making it suitable for environments exposed to cleaning agents and moderate heat. Compared to polysulfone, ABS is more cost-effective and provides sufficient mechanical performance for most consumer appliances while allowing for vibrant color finishes.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polysulfone (PSU) exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), with a higher tensile strength typically around 70 MPa for PSU versus approximately 40 MPa for ABS. PSU also offers better impact resistance and maintains structural integrity at elevated temperatures up to 150degC, whereas ABS softens around 105degC. These properties make PSU more suitable for appliance housings requiring enhanced durability and thermal stability in demanding environments.
Thermal Resistance and Heat Stability
Polysulfone offers superior thermal resistance with continuous use temperatures up to 150degC, making it ideal for appliance housings exposed to prolonged heat. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) typically withstands temperatures up to 80-100degC, which limits its performance in high-heat environments. Polysulfone also exhibits enhanced heat stability and resists thermal degradation better than ABS, ensuring long-term durability under thermal stress.
Chemical Resistance and Durability
Polysulfone offers superior chemical resistance compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), making it ideal for appliance housings exposed to harsh cleaning agents and solvents. Its high thermal stability and resistance to hydrolysis ensure long-term durability under elevated temperatures and moist conditions, unlike ABS which tends to degrade faster when exposed to chemicals and heat. The exceptional mechanical strength of polysulfone supports enhanced impact resistance and lifespan in demanding appliance applications.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Polysulfone offers superior aesthetic appeal with its high gloss finish and excellent color retention, making it ideal for appliance housings requiring a premium look. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides greater design flexibility due to its ease of molding and capability to incorporate complex shapes and textures. Both materials support diverse design requirements, but Polysulfone excels in visual quality while ABS is favored for intricate and cost-effective manufacturing.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Polysulfone offers superior heat resistance and durability for appliance housing but comes with a higher raw material cost and more complex processing requirements compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS). ABS provides cost-effective manufacturing with easier moldability and faster cycle times, making it ideal for high-volume production where moderate thermal resistance suffices. Choosing between Polysulfone and ABS depends on balancing budget constraints against performance demands and production scalability in appliance housing applications.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polysulfone offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), making it a more durable option for appliance housings with longer service life and potentially reducing environmental waste. While ABS is widely recycled through established municipal programs, its shorter lifespan and lower heat resistance often lead to increased material turnover and environmental burden. Polysulfone's limited recyclability challenges circular economy efforts, but its extended durability may offset environmental impacts by minimizing replacement frequency.
Choosing the Right Material for Appliance Housings
Polysulfone offers superior heat resistance, chemical stability, and durability, making it ideal for high-temperature appliance housings exposed to harsh environments. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides excellent impact resistance, ease of molding, and cost-effectiveness, which suits appliances requiring toughness and aesthetic versatility. Selecting the right material depends on appliance operating conditions, with polysulfone preferred for thermal and chemical resilience, while ABS suits lightweight, cost-sensitive applications.
Infographic: Polysulfone vs Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene for Appliance Housing
 azmater.com
azmater.com