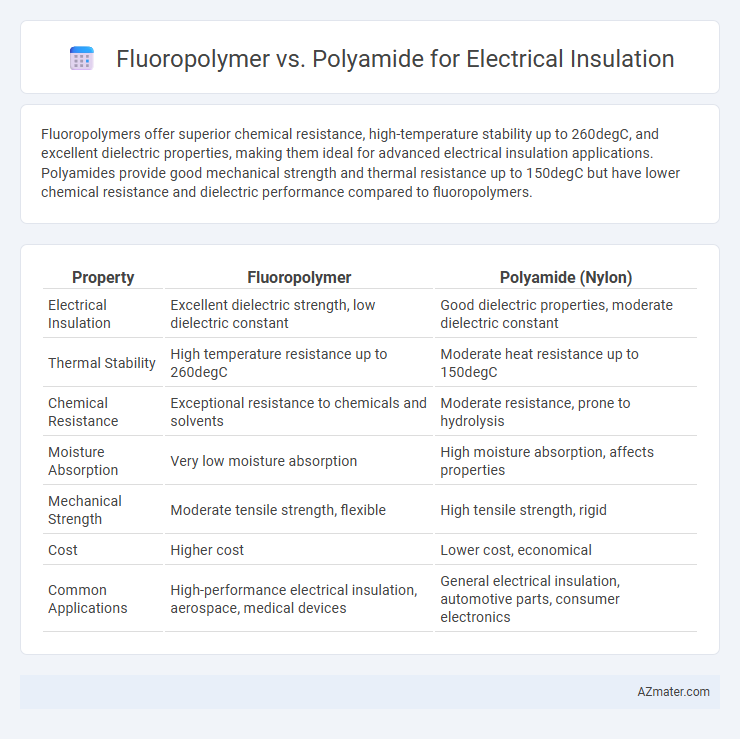
Fluoropolymers offer superior chemical resistance, high-temperature stability up to 260degC, and excellent dielectric properties, making them ideal for advanced electrical insulation applications. Polyamides provide good mechanical strength and thermal resistance up to 150degC but have lower chemical resistance and dielectric performance compared to fluoropolymers.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fluoropolymer | Polyamide (Nylon) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric strength, low dielectric constant | Good dielectric properties, moderate dielectric constant |
| Thermal Stability | High temperature resistance up to 260degC | Moderate heat resistance up to 150degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Exceptional resistance to chemicals and solvents | Moderate resistance, prone to hydrolysis |
| Moisture Absorption | Very low moisture absorption | High moisture absorption, affects properties |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate tensile strength, flexible | High tensile strength, rigid |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost, economical |
| Common Applications | High-performance electrical insulation, aerospace, medical devices | General electrical insulation, automotive parts, consumer electronics |
Introduction to Electrical Insulation Materials
Fluoropolymers and polyamides are prominent electrical insulation materials known for their distinct properties and applications. Fluoropolymers, such as PTFE, exhibit exceptional chemical resistance, high dielectric strength, and excellent thermal stability, making them ideal for harsh environments and high-frequency applications. Polyamides, including nylon variants, offer good mechanical strength and flexibility but have lower thermal and chemical resistance compared to fluoropolymers, positioning them well for moderate electrical insulation needs.
Overview of Fluoropolymers
Fluoropolymers, such as PTFE and FEP, offer exceptional electrical insulation properties due to their high dielectric strength and low dielectric constant, making them ideal for high-frequency and high-temperature applications. Their chemical inertness and resistance to moisture, UV radiation, and aggressive chemicals ensure long-term durability and reliability in harsh environments. These materials also exhibit excellent thermal stability, often operating effectively at temperatures exceeding 200degC, outperforming many polyamides in demanding electrical insulation roles.
Overview of Polyamides
Polyamides, known for their excellent mechanical strength and thermal resistance, are widely used in electrical insulation applications where durability and flexibility are critical. Their inherent moisture absorption can affect electrical properties, requiring careful consideration in high-humidity environments. Compared to fluoropolymers, polyamides offer cost-effective insulation with good dielectric performance but generally lower chemical resistance and lower temperature stability.
Key Properties of Fluoropolymers in Electrical Insulation
Fluoropolymers exhibit exceptional electrical insulation properties characterized by high dielectric strength, low dielectric constant, and outstanding chemical resistance, making them ideal for harsh environments. Their inherent thermal stability allows continuous operation at elevated temperatures up to 260degC, outperforming polyamides which typically degrade above 150degC. Superior moisture resistance and minimal surface energy prevent contamination and ensure reliable insulation performance in demanding electrical applications.
Key Properties of Polyamides in Electrical Applications
Polyamides exhibit excellent mechanical strength, high thermal stability, and good dielectric properties, making them suitable for electrical insulation applications. Their inherent resistance to abrasion, moisture absorption, and chemical exposure ensures reliable performance in harsh environments. Polyamides also provide superior toughness and dimensional stability under electrical stress compared to many fluoropolymers.
Dielectric Strength Comparison
Fluoropolymers exhibit superior dielectric strength typically ranging between 110 to 220 kV/mm, making them highly effective for high-voltage electrical insulation applications. Polyamides, with dielectric strength values generally around 20 to 40 kV/mm, offer moderate insulation performance but lower resistance to electrical stress compared to fluoropolymers. The higher dielectric strength of fluoropolymers results from their strong carbon-fluorine bonds, which provide excellent chemical stability and resistance to electrical breakdown.
Thermal Stability: Fluoropolymer vs Polyamide
Fluoropolymers exhibit superior thermal stability compared to polyamides, maintaining structural integrity and electrical insulation properties at temperatures exceeding 200degC, with some grades tolerating up to 260degC or higher. Polyamides typically withstand continuous use temperatures around 120degC to 150degC but tend to degrade and lose insulation performance when exposed to prolonged high heat or thermal cycling. This enhanced thermal endurance makes fluoropolymers the preferred choice for high-temperature electrical insulation applications in harsh environments such as aerospace and automotive industries.
Chemical Resistance in Insulation Environments
Fluoropolymer exhibits superior chemical resistance in electrical insulation environments due to its strong carbon-fluorine bonds, making it highly resistant to acids, bases, solvents, and oils. Polyamide, while offering good mechanical strength and moderate chemical resistance, tends to degrade when exposed to harsh chemicals and moisture over time. In applications where exposure to aggressive chemicals is critical, fluoropolymer insulation ensures longer service life and maintains dielectric integrity more effectively than polyamide.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Fluoropolymers typically offer superior electrical insulation properties and chemical resistance but come with higher material and processing costs compared to polyamides. Polyamides provide cost-effective manufacturing with easier processing and better mechanical strength, making them suitable for budget-sensitive applications requiring moderate electrical insulation. Choosing between the two depends on balancing the high-performance benefits of fluoropolymers against the affordability and manufacturability of polyamides.
Application Suitability: Choosing the Right Material
Fluoropolymers offer superior chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance up to 260degC, and excellent dielectric properties, making them ideal for harsh environments in aerospace and medical device insulation. Polyamides, while less heat resistant (typically up to 120degC), provide good mechanical strength and cost-effective insulation solutions suitable for automotive and consumer electronics applications. Selecting between fluoropolymer and polyamide depends on specific requirements such as operating temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical durability to ensure optimal electrical insulation performance.
Infographic: Fluoropolymer vs Polyamide for Electrical Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com