Polypropylene offers superior moisture resistance and higher tensile strength, making it ideal for durable packaging films, while Polyethylene Terephthalate provides excellent clarity, gas barrier properties, and thermal stability, preferred for food and beverage packaging. Selecting based on performance needs optimizes package protection and shelf life.
Table of Comparison
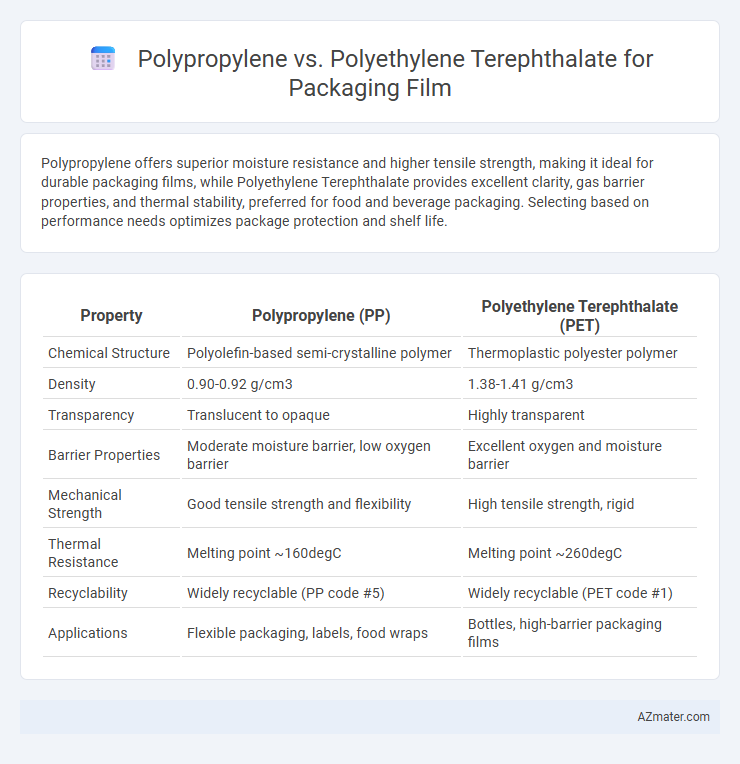
| Property | Polypropylene (PP) | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Polyolefin-based semi-crystalline polymer | Thermoplastic polyester polymer |
| Density | 0.90-0.92 g/cm3 | 1.38-1.41 g/cm3 |
| Transparency | Translucent to opaque | Highly transparent |
| Barrier Properties | Moderate moisture barrier, low oxygen barrier | Excellent oxygen and moisture barrier |
| Mechanical Strength | Good tensile strength and flexibility | High tensile strength, rigid |
| Thermal Resistance | Melting point ~160degC | Melting point ~260degC |
| Recyclability | Widely recyclable (PP code #5) | Widely recyclable (PET code #1) |
| Applications | Flexible packaging, labels, food wraps | Bottles, high-barrier packaging films |
Introduction to Polypropylene and Polyethylene Terephthalate
Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic polymer widely used in packaging films due to its excellent clarity, high tensile strength, and resistance to moisture and chemicals. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a durable polyester known for its superior gas barrier properties, dimensional stability, and recyclability, making it ideal for food and beverage packaging. Both polymers offer distinct advantages that influence their selection based on packaging requirements such as flexibility, transparency, and barrier performance.
Chemical Structure and Properties Comparison
Polypropylene (PP) features a hydrocarbon-based polymer chain with methyl side groups, granting it a semi-crystalline structure that provides excellent clarity, high tensile strength, and resistance to moisture and chemicals, ideal for flexible packaging films. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) consists of repeating ester groups in its aromatic polyester chain, contributing to its high tensile strength, superior gas barrier properties, and thermal stability, making it suitable for preserving food freshness and extending shelf life. The distinct chemical structure differences between PP and PET influence their mechanical properties and barrier performance, with PP offering better moisture resistance and PET providing enhanced oxygen barrier and thermal resistance for packaging applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polypropylene (PP) offers superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET), making it ideal for flexible packaging films requiring high mechanical durability. PET exhibits excellent dimensional stability and resistance to stretching under load, which enhances its longevity in packaging applications exposed to varying environmental conditions. The combination of PP's toughness and PET's rigidity allows manufacturers to select materials based on specific performance needs in packaging film durability and mechanical strength.
Barrier Properties: Moisture, Gas, and Aroma
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) exhibits superior barrier properties compared to Polypropylene (PP), offering enhanced resistance to moisture, oxygen, and aroma penetration, which is crucial for preserving product freshness and extending shelf life. Polypropylene provides moderate moisture barrier performance but is less effective against gases such as oxygen and aromatic compounds, making it less suitable for packaging sensitive food and beverages. PET's high crystallinity and molecular structure contribute to its low permeability rates, making it the preferred choice for high-barrier packaging applications requiring stringent protection against environmental contaminants.
Optical Clarity and Aesthetic Appeal
Polypropylene (PP) offers excellent optical clarity with its high gloss and transparency, making it ideal for packaging films that require superior visual appeal. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) boasts outstanding dimensional stability and clarity but tends to have a slightly lower gloss compared to PP, providing a sleek and professional look. In packaging applications, PP is preferred for vibrant, eye-catching displays, while PET is favored for high-end products where durability and a premium aesthetic are critical.
Temperature Resistance and Suitability for Food Packaging
Polypropylene (PP) offers superior temperature resistance with a melting point around 160degC, making it ideal for packaging applications requiring heat sterilization or microwave use, whereas Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) has a melting point near 250degC but lower heat deflection temperature, limiting its use in high-heat environments. PP's excellent moisture and chemical resistance combined with good clarity enhances its suitability for food packaging, providing effective barrier properties and maintaining product freshness. PET excels in oxygen barrier performance and mechanical strength, favoring applications like carbonated beverage bottles, but its temperature resistance is generally lower than PP for direct food contact under heat.
Processability and Manufacturing Considerations
Polypropylene (PP) offers superior processability in packaging film applications due to its low melting point and high melt flow rate, enabling faster extrusion and thermoforming cycles compared to Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET). PET requires higher processing temperatures and more precise crystallization control, resulting in longer cycle times but provides enhanced gas barrier properties and mechanical strength. Manufacturing considerations include equipment compatibility, with PP favoring simpler machinery and lower energy consumption, while PET demands advanced drying systems and temperature controls to prevent hydrolytic degradation.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polypropylene (PP) packaging film demonstrates lower carbon emissions during production compared to Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET), contributing to a reduced environmental footprint. PP offers enhanced recyclability through widespread mechanical recycling streams, whereas PET recycling is more energy-intensive, relying heavily on advanced processes like chemical recycling to maintain material quality. The biodegradability of PP is limited, similar to PET, but PP's lighter weight results in less transportation-related emissions, making it a favorable option for eco-conscious packaging solutions.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Polypropylene (PP) generally offers a lower cost per kilogram compared to Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) in packaging film applications, making PP more attractive for cost-sensitive markets. PET provides superior barrier properties and mechanical strength, which often justifies its higher price in premium or specialty packaging sectors. Both materials exhibit wide market availability, but PP's manufacturing process tends to be more flexible and energy-efficient, contributing to its broader adoption in diverse packaging formats.
Choosing the Right Material for Specific Packaging Applications
Polypropylene (PP) offers excellent clarity, high tensile strength, and moisture resistance, making it ideal for food packaging requiring durability and barrier properties against moisture. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) provides superior gas barrier capabilities and thermal stability, which are crucial for packaging carbonated beverages and products requiring extended shelf life. Selecting between PP and PET depends on factors like product sensitivity, required barrier performance, and cost efficiency in specific packaging applications.
Infographic: Polypropylene vs Polyethylene Terephthalate for Packaging Film
 azmater.com
azmater.com