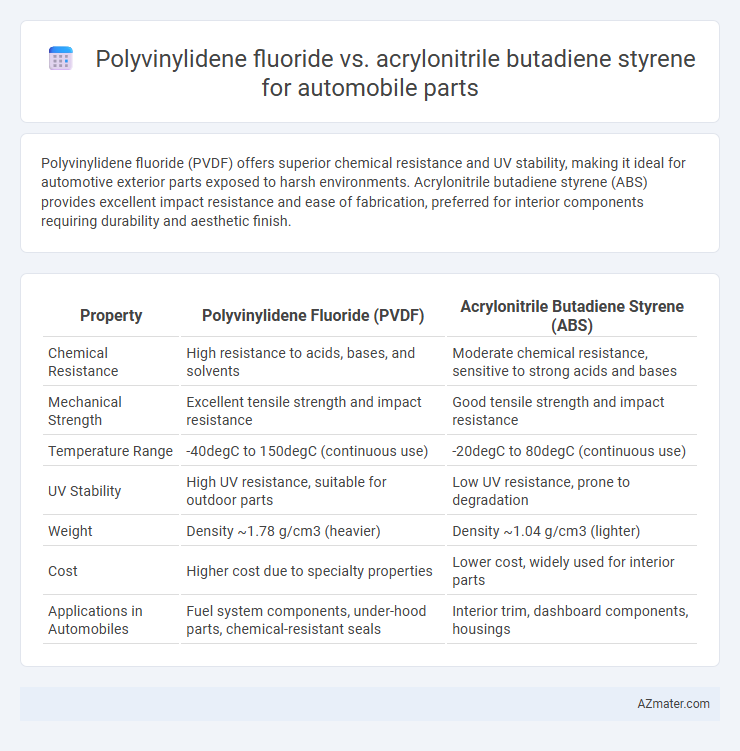
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and UV stability, making it ideal for automotive exterior parts exposed to harsh environments. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides excellent impact resistance and ease of fabrication, preferred for interior components requiring durability and aesthetic finish.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to acids, bases, and solvents | Moderate chemical resistance, sensitive to strong acids and bases |
| Mechanical Strength | Excellent tensile strength and impact resistance | Good tensile strength and impact resistance |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC (continuous use) | -20degC to 80degC (continuous use) |
| UV Stability | High UV resistance, suitable for outdoor parts | Low UV resistance, prone to degradation |
| Weight | Density ~1.78 g/cm3 (heavier) | Density ~1.04 g/cm3 (lighter) |
| Cost | Higher cost due to specialty properties | Lower cost, widely used for interior parts |
| Applications in Automobiles | Fuel system components, under-hood parts, chemical-resistant seals | Interior trim, dashboard components, housings |
Introduction: Choosing the Right Polymer for Automotive Parts
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers exceptional chemical resistance, UV stability, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for under-the-hood and exterior automotive parts exposed to harsh environments. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides excellent impact resistance, ease of processing, and cost-effectiveness, suitable for interior components and trim pieces requiring durability and aesthetic appeal. Selecting between PVDF and ABS depends on specific application demands such as chemical exposure, thermal conditions, and mechanical stress in automotive manufacturing.
Overview of Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF)
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent chemical resistance, UV stability, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for demanding automotive applications such as fuel system components and exterior trims. PVDF exhibits superior resistance to hydrocarbons and solvents compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), which offers good impact resistance and ease of processing but lower chemical and thermal stability. The unique balance of durability and resistance allows PVDF to withstand harsh environmental conditions in automobiles, extending part lifespan and maintaining structural integrity.
Overview of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer widely used in automobile parts due to its excellent impact resistance, toughness, and ease of manufacturing through injection molding. ABS offers superior dimensional stability and resistance to heat and chemicals compared to many other plastics, making it suitable for interior components, trim, and protective covers. Its lightweight nature and cost-effectiveness contribute to enhanced vehicle performance and reduced production expenses.
Mechanical Properties: PVDF vs ABS
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior chemical resistance, high tensile strength (around 34 MPa), and excellent impact resistance compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), which typically shows tensile strength of 40 MPa but lower chemical resistance. PVDF offers higher thermal stability with a melting point near 177degC, making it suitable for under-the-hood automotive parts exposed to harsh environments, whereas ABS has a lower heat deflection temperature around 100degC. The flexibility and abrasion resistance of PVDF outperform ABS, enhancing durability and lifespan in mechanically demanding automobile components.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Stability
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance against acids, bases, and solvents, making it ideal for automotive parts exposed to harsh fluids and chemicals. In comparison, Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits moderate chemical resistance but is more susceptible to degradation from solvents and UV exposure. PVDF also provides enhanced environmental stability with excellent resistance to UV radiation and high temperatures, while ABS tends to degrade faster under prolonged environmental stress, impacting its durability in automotive applications.
Thermal Performance and Temperature Tolerance
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior thermal performance with a continuous operating temperature up to 150degC, making it ideal for under-the-hood automobile parts exposed to high heat. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) has a lower temperature tolerance, typically up to 80degC, which limits its use to interior components or areas with minimal thermal exposure. The chemical resistance and thermal stability of PVDF provide enhanced durability compared to ABS when subjected to fluctuating automotive engine temperatures.
Processing and Manufacturability in Automotive Applications
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and high thermal stability, enabling precise molding processes such as injection molding and extrusion suitable for demanding automotive parts. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides excellent impact resistance and ease of processing, making it ideal for large-scale production with fast cycle times and good dimensional stability. PVDF's processing requires higher temperatures and controlled conditions, while ABS allows for more cost-effective manufacturability and efficient prototyping in automotive applications.
Cost Comparison: PVDF Versus ABS
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) commands a higher price point compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) due to its superior chemical resistance and durability in harsh automotive environments. ABS remains more cost-effective for large-scale production of automobile parts, offering adequate mechanical strength and ease of processing with lower raw material and manufacturing expenses. Cost implications of selecting PVDF over ABS must consider long-term performance benefits against initial budget constraints in automotive manufacturing.
Typical Automotive Applications: PVDF and ABS Use Cases
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is commonly used in automotive fuel system components, wiring insulation, and corrosion-resistant coatings due to its excellent chemical resistance and thermal stability. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is widely applied in interior parts, instrument panels, and bumper covers because of its impact resistance and ease of molding. PVDF's durability under harsh conditions contrasts with ABS's strength in aesthetic and structural applications within the automotive industry.
Conclusion: Which Polymer Suits Your Automotive Needs?
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance, UV stability, and thermal performance, making it ideal for under-the-hood and exterior automotive components exposed to harsh environments. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides excellent impact resistance, ease of molding, and cost-effectiveness, suitable for interior trims and structural parts where durability and aesthetic finish are key. Selecting between PVDF and ABS depends on the specific automotive application requirements, prioritizing chemical/temperature resistance for PVDF and toughness with affordability for ABS.
Infographic: Polyvinylidene fluoride vs Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene for Automobile part
 azmater.com
azmater.com