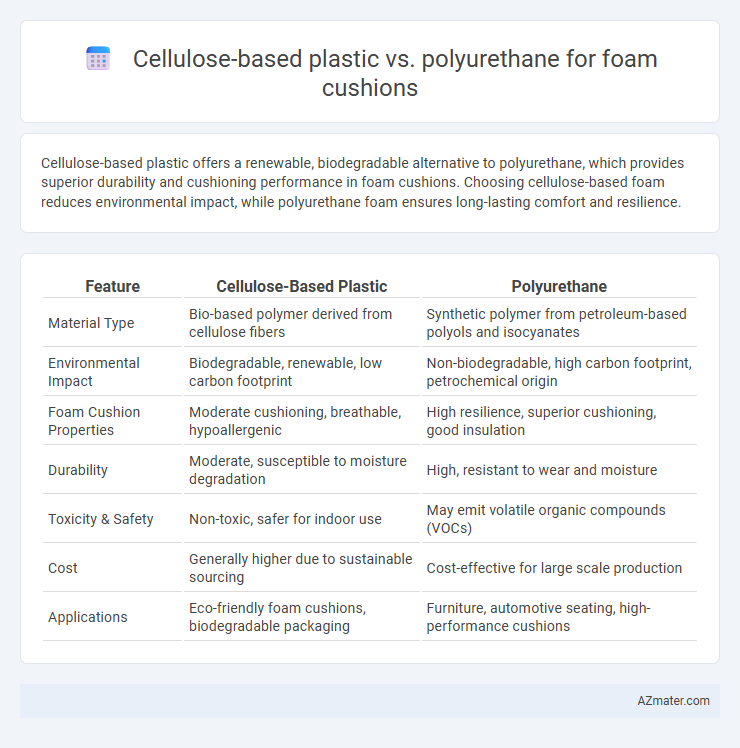
Cellulose-based plastic offers a renewable, biodegradable alternative to polyurethane, which provides superior durability and cushioning performance in foam cushions. Choosing cellulose-based foam reduces environmental impact, while polyurethane foam ensures long-lasting comfort and resilience.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cellulose-Based Plastic | Polyurethane |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Bio-based polymer derived from cellulose fibers | Synthetic polymer from petroleum-based polyols and isocyanates |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, renewable, low carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, high carbon footprint, petrochemical origin |
| Foam Cushion Properties | Moderate cushioning, breathable, hypoallergenic | High resilience, superior cushioning, good insulation |
| Durability | Moderate, susceptible to moisture degradation | High, resistant to wear and moisture |
| Toxicity & Safety | Non-toxic, safer for indoor use | May emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) |
| Cost | Generally higher due to sustainable sourcing | Cost-effective for large scale production |
| Applications | Eco-friendly foam cushions, biodegradable packaging | Furniture, automotive seating, high-performance cushions |
Introduction to Foam Cushion Materials
Cellulose-based plastics and polyurethane are widely used materials in foam cushions, each offering distinct environmental and performance benefits. Cellulose-based plastics are derived from renewable resources such as wood pulp and agricultural byproducts, providing biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint compared to petroleum-based polyurethane. Polyurethane foam cushions excel in durability, flexibility, and cushioning properties, making them a popular choice in automotive, furniture, and packaging industries.
Overview of Cellulose-Based Plastics
Cellulose-based plastics are derived from natural polymers found in plant cell walls, offering a biodegradable and renewable alternative to traditional petroleum-based foams like polyurethane. These plastics exhibit excellent breathability, moisture regulation, and resistance to microbial growth, making them suitable for eco-friendly foam cushions. Their lower environmental impact and ability to decompose naturally align with increasing demand for sustainable cushioning materials in furniture and automotive industries.
Fundamentals of Polyurethane Foam
Polyurethane foam, a versatile polymer derived from the reaction of polyols and diisocyanates, offers superior cushioning properties due to its open-cell or closed-cell structure that provides excellent resilience and support. Unlike cellulose-based plastics, polyurethane foam's customizable density and firmness make it ideal for tailored comfort and durability in foam cushions. Its widespread use in furniture, automotive, and bedding industries stems from its ability to absorb impact, resist deformation, and maintain structural integrity over prolonged use.
Production Processes Compared
Cellulose-based plastic foam cushions are produced through the chemical modification and regeneration of cellulose fibers, involving processes such as dissolution, shaping, and drying, which emphasize renewable raw materials and biodegradability. Polyurethane foam cushions are created via a polymerization reaction between polyols and isocyanates, resulting in a versatile foam with tunable density and cushioning properties through control of catalyst and blowing agents. The production of cellulose-based foams typically entails lower environmental impact due to bio-based inputs, whereas polyurethane foam manufacturing relies heavily on petrochemical feedstocks and generates more hazardous byproducts.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cellulose-based plastic foam cushions offer superior biodegradability and lower carbon footprints compared to polyurethane, which relies heavily on fossil fuels and emits toxic gases during production and disposal. The renewable nature of cellulose, derived from plant fibers, ensures sustainability through carbon sequestration and reduced landfill persistence. Polyurethane foam's resistance to degradation contributes significantly to environmental pollution and challenges in waste management.
Mechanical Properties and Performance
Cellulose-based plastic foam cushions exhibit excellent biodegradability and moderate mechanical strength, with tensile strengths typically ranging from 5 to 15 MPa and compressive strength around 100-200 kPa, making them suitable for eco-friendly applications with lightweight cushioning needs. Polyurethane foam offers superior mechanical properties, including higher tensile strength (20-40 MPa) and greater compressive resilience (up to 300 kPa), enabling enhanced durability, flexibility, and long-term performance under repeated stress. Performance-wise, polyurethane foam cushions maintain structural integrity and cushioning over prolonged use, whereas cellulose-based foams may degrade faster under mechanical loading but provide sustainable alternatives prioritizing environmental impact.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Cellulose-based plastic foam cushions typically offer a lower production cost due to the abundance and renewability of cellulose materials, making them a more economical choice for sustainable packaging and furniture applications. Polyurethane foam, while generally more expensive because of its petroleum-derived components and complex manufacturing process, provides superior durability and comfort, justifying its higher price in premium markets. Evaluating long-term costs, cellulose-based foam's biodegradability can reduce environmental disposal fees, whereas polyurethane's extended lifespan may offset its initial investment through durability and performance.
Comfort and User Experience
Cellulose-based plastic foam cushions offer superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties, enhancing overall comfort by maintaining a cooler seating surface compared to polyurethane foam. Polyurethane foam provides durable support with higher resilience and cushioning density, which can contribute to enhanced posture support but may retain more heat and moisture, potentially reducing user comfort over extended use. Users often prefer cellulose-based foam for its eco-friendly composition and natural ventilation, while polyurethane is favored for its long-lasting performance and varied firmness options.
Applications and Market Trends
Cellulose-based plastics are increasingly favored in sustainable foam cushion applications due to their biodegradability and renewable sourcing, making them ideal for eco-friendly furniture and packaging markets. Polyurethane foam cushions retain dominance in automotive, bedding, and acoustic insulation sectors because of their superior durability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Market trends indicate a rising demand for cellulose-based alternatives driven by stricter environmental regulations and consumer preference for green products, while polyurethane continues to innovate with bio-based variants to reduce its environmental footprint.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Cellulose-based plastic foam cushions offer sustainable advantages by utilizing renewable biomass, reducing reliance on petrochemicals, and enhancing biodegradability compared to traditional polyurethane foams. Innovations in nanocellulose incorporation and bio-based composite formulations are driving improvements in durability, comfort, and thermal insulation properties. Future prospects emphasize scaling eco-friendly production methods and integrating smart technologies to meet increasing consumer demand for environmentally responsible and high-performance cushioning materials.
Infographic: Cellulose-based plastic vs Polyurethane for Foam cushion
 azmater.com
azmater.com