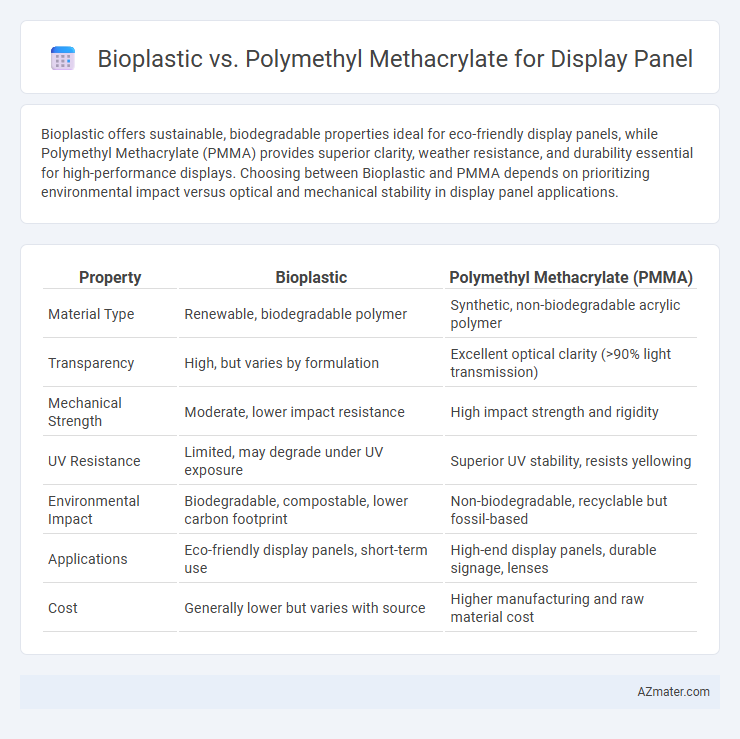
Bioplastic offers sustainable, biodegradable properties ideal for eco-friendly display panels, while Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) provides superior clarity, weather resistance, and durability essential for high-performance displays. Choosing between Bioplastic and PMMA depends on prioritizing environmental impact versus optical and mechanical stability in display panel applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bioplastic | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Renewable, biodegradable polymer | Synthetic, non-biodegradable acrylic polymer |
| Transparency | High, but varies by formulation | Excellent optical clarity (>90% light transmission) |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate, lower impact resistance | High impact strength and rigidity |
| UV Resistance | Limited, may degrade under UV exposure | Superior UV stability, resists yellowing |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, compostable, lower carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, recyclable but fossil-based |
| Applications | Eco-friendly display panels, short-term use | High-end display panels, durable signage, lenses |
| Cost | Generally lower but varies with source | Higher manufacturing and raw material cost |
Introduction to Display Panel Materials
Display panels utilize materials such as bioplastics and polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) to balance transparency, durability, and environmental impact. Bioplastics offer renewable sources and biodegradability, making them attractive for sustainable display applications. PMMA provides superior optical clarity, weather resistance, and mechanical strength, commonly used in high-performance display screens.
Overview of Bioplastics
Bioplastics are derived from renewable biomass sources such as corn starch, sugarcane, and cellulose, offering an eco-friendly alternative to conventional plastics like polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA). These materials exhibit biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint, making them suitable for sustainable display panel applications where environmental impact is a concern. Bioplastics also provide flexibility in processing and design, though their mechanical properties and durability may differ from those of PMMA, which is known for superior clarity and strength.
Understanding Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA), a synthetic polymer known for its superior optical clarity and UV resistance, is widely used in display panels due to its high scratch resistance and excellent light transmission, typically around 92%. Unlike bioplastics, PMMA offers greater durability and dimensional stability, making it ideal for long-lasting display applications in consumer electronics and automotive industries. Its superior weatherability and ease of fabrication also contribute to its preference over bioplastics in high-performance transparent panel solutions.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Bioplastic exhibits superior flexibility and impact resistance compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), making it more suitable for applications requiring durability under stress. PMMA offers higher tensile strength and excellent optical clarity, which is essential for display panels demanding sharp image quality. The choice between bioplastic and PMMA hinges on balancing mechanical toughness with optical performance in display panel manufacturing.
Optical Performance and Clarity
Bioplastics and polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) differ significantly in optical performance and clarity when used for display panels. PMMA exhibits exceptional transparency with light transmittance rates above 92%, offering superior clarity and resistance to yellowing, making it ideal for high-definition displays. In contrast, bioplastics typically show lower optical purity and higher haze levels, which may result in reduced sharpness and color fidelity in display applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bioplastics offer a lower carbon footprint and biodegradability compared to Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA), which is derived from non-renewable petroleum resources and is not biodegradable. The production of bioplastics typically involves renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane, contributing to reduced greenhouse gas emissions and enhanced sustainability. Conversely, PMMA's durability and recyclability are limited, resulting in longer-term environmental persistence and greater landfill accumulation.
Cost Analysis and Economic Feasibility
Bioplastic offers a sustainable alternative to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) for display panels, but its production costs remain higher due to raw material sourcing and lower economies of scale. PMMA benefits from established manufacturing processes and widespread availability, resulting in lower unit costs and higher economic feasibility for large-scale applications. Despite bioplastic's environmental advantages, its cost structure currently limits competitive pricing, impacting widespread adoption in display panel markets.
Durability and Lifespan in Display Applications
Bioplastics used in display panels offer eco-friendly alternatives with moderate durability but generally have shorter lifespans compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA). PMMA exhibits superior resistance to UV radiation, scratches, and impact, making it ideal for long-lasting display applications requiring clarity and strength. The inherent biodegradability of bioplastics often limits their lifespan under prolonged exposure to environmental stressors, whereas PMMA's robust molecular structure ensures extended durability.
Processing and Manufacturability
Bioplastics offer eco-friendly alternatives with lower processing temperatures and biodegradability, but often pose challenges in moldability and long-term durability compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA). PMMA exhibits excellent machinability, high optical clarity, and superior resistance to UV degradation, making it highly suitable for precision display panel manufacturing through injection molding and extrusion. The manufacturability of PMMA outperforms bioplastics in maintaining dimensional stability and ease of large-scale production for high-quality, transparent display components.
Future Trends and Innovations
Future trends in display panels emphasize sustainability, driving the adoption of bioplastics due to their biodegradability and reduced environmental impact compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA). Innovations in bioplastic formulations aim to enhance optical clarity, durability, and UV resistance to match or exceed the performance standards of PMMA. Research into bio-based composites and nanotechnology integration promises to revolutionize display panel materials, offering lightweight, flexible, and eco-friendly alternatives with improved mechanical and thermal properties.
Infographic: Bioplastic vs Polymethyl Methacrylate for Display Panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com