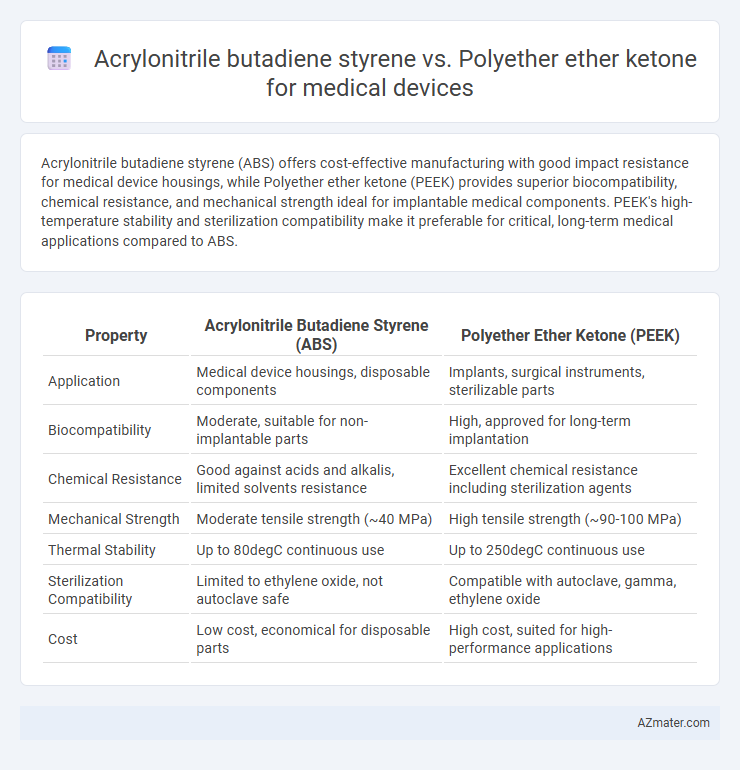
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers cost-effective manufacturing with good impact resistance for medical device housings, while Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) provides superior biocompatibility, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength ideal for implantable medical components. PEEK's high-temperature stability and sterilization compatibility make it preferable for critical, long-term medical applications compared to ABS.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) |
|---|---|---|
| Application | Medical device housings, disposable components | Implants, surgical instruments, sterilizable parts |
| Biocompatibility | Moderate, suitable for non-implantable parts | High, approved for long-term implantation |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against acids and alkalis, limited solvents resistance | Excellent chemical resistance including sterilization agents |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate tensile strength (~40 MPa) | High tensile strength (~90-100 MPa) |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 80degC continuous use | Up to 250degC continuous use |
| Sterilization Compatibility | Limited to ethylene oxide, not autoclave safe | Compatible with autoclave, gamma, ethylene oxide |
| Cost | Low cost, economical for disposable parts | High cost, suited for high-performance applications |
Introduction to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) and Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its impact resistance, ease of processing, and cost-effectiveness in medical device manufacturing. Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) offers superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and biocompatibility, making it suitable for high-performance medical implants and surgical instruments. ABS is typically used for external components and prototypes, while PEEK is preferred for load-bearing applications requiring sterilization and long-term durability.
Material Properties: ABS vs PEEK
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance, good machinability, and cost-effectiveness but has limited chemical resistance and lower temperature tolerance compared to Polyether ether ketone (PEEK). PEEK exhibits superior mechanical strength, exceptional biocompatibility, and high resistance to sterilization processes, making it ideal for implantable or long-term medical devices. The high melting point and chemical inertness of PEEK significantly outperform ABS in demanding medical environments requiring durability and repeated sterilization cycles.
Biocompatibility and Safety in Medical Applications
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers good mechanical strength and ease of fabrication but has limited biocompatibility and may release toxic compounds under sterilization, restricting its use in long-term medical devices. Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) exhibits exceptional biocompatibility, chemical resistance, and stability under sterilization processes, making it highly suitable for implantable medical devices and instruments requiring prolonged in vivo contact. The superior bio-inert nature and FDA approval of PEEK for medical applications significantly outweigh ABS in terms of patient safety and regulatory compliance.
Sterilization Compatibility: ABS Compared to PEEK
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits limited sterilization compatibility, as it can degrade or deform under common sterilization methods like autoclaving and gamma radiation, which restricts its use in reusable medical devices. Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) demonstrates exceptional resistance to high-temperature steam sterilization, gamma radiation, and ethylene oxide, maintaining structural integrity and biocompatibility, making it ideal for demanding medical applications. The chemical stability and thermal endurance of PEEK significantly outperform ABS in sterilization protocols, ensuring device reliability and patient safety.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate mechanical strength and impact resistance, making it suitable for non-implantable medical devices that require durability and ease of fabrication. Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) exhibits superior mechanical strength, high tensile properties, and exceptional fatigue resistance, ideal for demanding implantable medical applications requiring long-term durability. PEEK's chemical resistance and biocompatibility provide enhanced performance over ABS in sterilization cycles and harsh physiological environments.
Chemical Resistance in Medical Environments
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits moderate chemical resistance suitable for short-term exposure to common disinfectants but may degrade when exposed to strong solvents or sterilization chemicals frequently used in medical environments. Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers exceptional chemical resistance, withstanding aggressive sterilization agents such as autoclaves, gamma radiation, and ethylene oxide without compromising structural integrity. The superior chemical resistance of PEEK makes it a preferred material for long-term use in demanding medical device applications where exposure to harsh chemicals is routine.
Cost Efficiency and Production Feasibility
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior cost efficiency and ease of production compared to Polyether ether ketone (PEEK), making it a popular choice for medical devices requiring rapid manufacturing and lower expenses. ABS features excellent moldability and shorter cycle times, significantly reducing production costs, whereas PEEK's high-performance thermal resistance and chemical stability come with substantially higher material and machining expenses. For applications prioritizing budget and scalable fabrication, ABS provides a more economically feasible solution without compromising essential mechanical properties.
Applications of ABS and PEEK in Medical Devices
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is widely used in medical devices for its excellent impact resistance and ease of sterilization, making it ideal for housings and external parts of diagnostic equipment and surgical instruments. Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior chemical resistance, biocompatibility, and mechanical strength, which is essential for implantable devices such as spinal cages, orthopedic fixation devices, and dental implants. The choice between ABS and PEEK depends on the specific application requirements, with ABS suited for non-implantable, cost-effective components and PEEK preferred for long-term, high-performance implants.
Regulatory Compliance and Certifications
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) differ significantly in regulatory compliance and certifications for medical device applications. ABS typically meets basic ISO 10993 biocompatibility standards and FDA 21 CFR 177.1640 for indirect food contact, but its use is limited in sterilizable or implantable devices due to lower chemical and temperature resistance. PEEK complies with stringent FDA and USP Class VI certifications, supports multiple sterilization methods like autoclaving and gamma radiation, and demonstrates high biocompatibility, making it the preferred choice for implantable medical devices requiring long-term stability and regulatory adherence.
Choosing the Right Material: ABS or PEEK for Medical Devices
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers cost-effective manufacturing and ease of processing, making it suitable for non-implantable medical device housings and prototypes due to its moderate chemical resistance and impact strength. Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) provides superior biocompatibility, chemical resistance, and sterilization tolerance, ideal for implantable devices and components exposed to harsh environments. Selecting ABS or PEEK depends on the specific application requirements, balancing factors like mechanical performance, sterilization methods, biocompatibility, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Polyether ether ketone for Medical device
 azmater.com
azmater.com