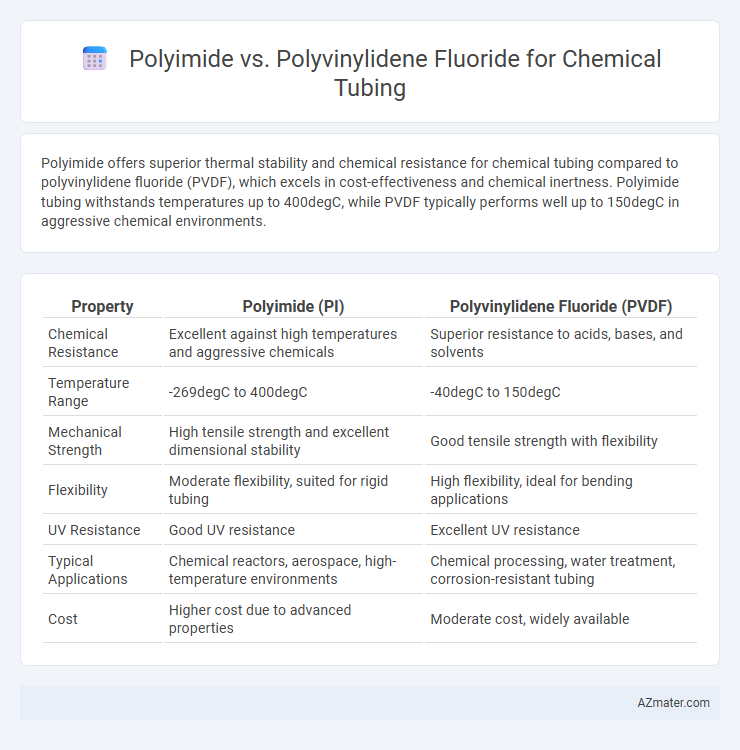
Polyimide offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance for chemical tubing compared to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), which excels in cost-effectiveness and chemical inertness. Polyimide tubing withstands temperatures up to 400degC, while PVDF typically performs well up to 150degC in aggressive chemical environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyimide (PI) | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against high temperatures and aggressive chemicals | Superior resistance to acids, bases, and solvents |
| Temperature Range | -269degC to 400degC | -40degC to 150degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and excellent dimensional stability | Good tensile strength with flexibility |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility, suited for rigid tubing | High flexibility, ideal for bending applications |
| UV Resistance | Good UV resistance | Excellent UV resistance |
| Typical Applications | Chemical reactors, aerospace, high-temperature environments | Chemical processing, water treatment, corrosion-resistant tubing |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Moderate cost, widely available |
Introduction to Chemical Tubing Materials
Polyimide and polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) are widely used materials for chemical tubing due to their excellent chemical resistance and thermal stability. Polyimide tubing performs well in extreme temperatures up to 400degC and offers superior mechanical strength, making it suitable for harsh chemical environments. PVDF tubing is highly resistant to a broad range of acids, bases, and solvents, with excellent abrasion resistance and flexibility, ideal for applications requiring durability and corrosion resistance.
Overview of Polyimide (PI)
Polyimide (PI) is a high-performance polymer known for its exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for use in chemical tubing exposed to harsh environments. Its robust molecular structure enables it to withstand temperatures up to 400degC while resisting a wide range of solvents, acids, and bases without degradation. These properties position polyimide tubing as a superior choice for applications requiring durability and long-lasting performance in aggressive chemical processing.
Overview of Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF)
Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) is a highly stable fluoropolymer known for its excellent chemical resistance and mechanical strength in chemical tubing applications. It offers superior resistance to acids, bases, and solvents, making it ideal for transporting aggressive chemicals in industrial environments. PVDF tubing also provides high thermal stability up to 150degC and maintains low permeability, ensuring long-term durability and contamination-free fluid handling.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Polyimide exhibits superior chemical resistance to a broad spectrum of solvents, acids, and bases, maintaining structural integrity in highly corrosive environments, which makes it ideal for aggressive chemical tubing applications. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers excellent resistance to acids, bases, and hydrocarbons but tends to have lower thermal stability and may degrade in strong oxidizing agents compared to polyimide. For chemical tubing requiring long-term durability against harsh chemicals and extreme temperatures, polyimide generally outperforms PVDF in chemical resistance and performance.
Temperature and Thermal Stability
Polyimide offers superior thermal stability with continuous operating temperatures up to 260degC, making it ideal for extreme heat applications in chemical tubing. In contrast, Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) maintains stability only up to around 150degC, limiting its use in high-temperature environments. The advanced thermal resistance of polyimide ensures long-term durability and performance under aggressive thermal cycling, whereas PVDF excels in chemical resistance but falls short in thermal endurance.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Polyimide tubing offers superior mechanical strength, high tensile modulus, and excellent thermal stability, making it ideal for high-stress chemical applications requiring long-term durability. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) tubing provides outstanding chemical resistance and flexibility but exhibits lower mechanical strength and thermal tolerance compared to polyimide. The choice between polyimide and PVDF depends on the balance needed between mechanical robustness and chemical resilience in specific industrial environments.
Flexibility and Processability
Polyimide offers superior flexibility with high thermal stability, making it ideal for chemical tubing applications requiring repeated bending and resistance to harsh chemicals. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) provides excellent chemical resistance and ease of processing, especially in extrusion and molding techniques, but has lower flexibility compared to polyimide. The choice depends on balancing the need for durability under dynamic stress and manufacturing efficiency in chemical environments.
Cost and Availability
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) tubing generally offers a lower initial cost compared to polyimide tubing, making it a more budget-friendly option for many chemical transfer applications. PVDF is widely available from multiple suppliers due to its extensive use in industrial and chemical processing sectors, ensuring easier procurement and faster delivery times. Polyimide tubing, while more expensive and less commonly stocked, provides exceptional thermal and chemical resistance, but its limited availability can result in longer lead times and higher overall project costs.
Common Applications in Chemical Tubing
Polyimide tubing is widely used in high-temperature chemical processing and semiconductor manufacturing due to its exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) tubing excels in applications requiring superior chemical inertness and abrasion resistance, such as pharmaceutical production and corrosive fluid transfer. Both materials are chosen for chemical tubing in environments demanding durable, non-reactive, and high-performance polymer solutions.
Choosing the Right Material: PI vs. PVDF
Polyimide (PI) offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature and aggressive chemical environments in tubing applications. Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) provides excellent chemical resistance and abrasion properties, with better flexibility and cost-effectiveness for less demanding conditions. Selecting between PI and PVDF depends on the specific chemical exposure, temperature requirements, and mechanical stresses encountered in the tubing system.
Infographic: Polyimide vs Polyvinylidene Fluoride for Chemical Tubing
 azmater.com
azmater.com