Fluoropolymer offers superior chemical resistance and high-temperature tolerance compared to Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET), which provides excellent clarity and impact resistance. Fluoropolymer bottles excel in harsh chemical environments, while PET is widely used for lightweight, transparent beverage containers.
Table of Comparison
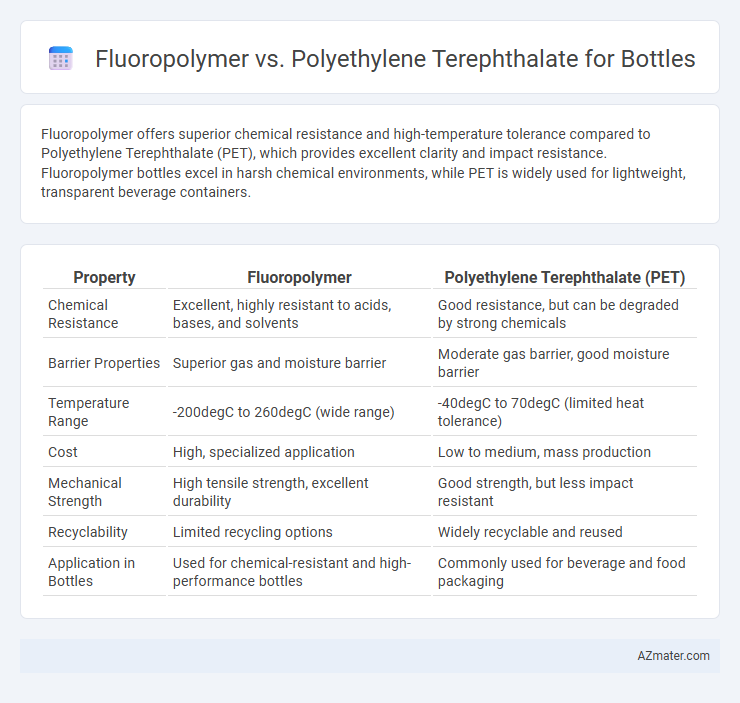
| Property | Fluoropolymer | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, highly resistant to acids, bases, and solvents | Good resistance, but can be degraded by strong chemicals |
| Barrier Properties | Superior gas and moisture barrier | Moderate gas barrier, good moisture barrier |
| Temperature Range | -200degC to 260degC (wide range) | -40degC to 70degC (limited heat tolerance) |
| Cost | High, specialized application | Low to medium, mass production |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength, excellent durability | Good strength, but less impact resistant |
| Recyclability | Limited recycling options | Widely recyclable and reused |
| Application in Bottles | Used for chemical-resistant and high-performance bottles | Commonly used for beverage and food packaging |
Introduction to Fluoropolymer and Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
Fluoropolymers are high-performance polymers known for exceptional chemical resistance, thermal stability, and low surface energy, making them ideal for specialized bottle applications requiring durability and inertness. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) is a widely used thermoplastic polyester characterized by its lightweight, clarity, and excellent barrier properties against gases and moisture, commonly used in beverage and food packaging. Both materials offer distinct advantages, with fluoropolymers suited for aggressive environmental conditions, while PET provides cost-effective, recyclable solutions for mass-market bottles.
Chemical Structure and Material Composition
Fluoropolymers feature carbon-fluorine bonds that provide exceptional chemical resistance and thermal stability, making them ideal for aggressive chemical storage in bottles. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) consists of repeating ester linkages derived from terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol, offering excellent clarity, mechanical strength, and barrier properties against oxygen and moisture. The distinct molecular architecture of fluoropolymers results in superior inertness and non-reactivity, whereas PET's semi-crystalline polyester structure balances durability with recyclability for beverage packaging applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Fluoropolymer bottles exhibit superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance compared to Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET), making them ideal for harsh environments and aggressive chemicals. PET bottles provide good durability and impact resistance but tend to degrade under UV exposure and extreme temperatures faster than fluoropolymer alternatives. The enhanced durability and low permeability of fluoropolymers extend the lifespan of containers, ensuring reliable performance in demanding applications.
Barrier Properties: Gas and Moisture Resistance
Fluoropolymers exhibit superior barrier properties against gases and moisture compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), making them ideal for applications requiring extended shelf life and high protection. The dense molecular structure of fluoropolymers significantly reduces oxygen and water vapor transmission rates, enhancing preservation of sensitive contents. PET offers good barrier performance for general packaging but falls short in extreme moisture and gas resistance, limiting its use in high-barrier requirements.
Temperature Tolerance and Thermal Stability
Fluoropolymer exhibits superior temperature tolerance compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), withstanding continuous use temperatures up to 260degC, whereas PET typically tolerates up to PET typically tolerates up to 70-80degC. The exceptional thermal stability of fluoropolymers ensures resistance to chemical degradation and thermal deformation at high temperatures, making them ideal for applications requiring sterilization or exposure to heat. PET, while widely used for beverage bottles due to its clarity and strength, shows susceptibility to thermal softening and dimensional changes under prolonged heat exposure.
Chemical Resistance and Reactivity
Fluoropolymer bottles exhibit superior chemical resistance and inertness compared to Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET), effectively withstanding aggressive solvents, acids, and bases without degradation. PET bottles, while cost-effective and clear, are prone to chemical reactivity with certain organic solvents and acidic substances, leading to potential leaching and compromised structural integrity. The low surface energy and high thermal stability of fluoropolymers make them ideal for storing highly reactive or corrosive chemicals, ensuring long-term durability and safety.
Safety, Toxicity, and Food Contact Compliance
Fluoropolymers offer excellent chemical resistance and high-temperature stability, making them highly safe and non-toxic for food contact applications, with compliance to FDA and EU food contact regulations. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) is widely approved for direct food contact due to its inert nature, low toxicity, and recyclability, meeting stringent global food safety standards. Both materials maintain strong regulatory compliance, but fluoropolymers typically provide superior barrier properties against leaching and contamination in bottle manufacturing.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Fluoropolymer bottles exhibit high chemical resistance and durability but pose significant challenges in environmental impact due to their persistence and difficulty in recycling processes, often requiring specialized facilities. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles offer greater recyclability, with widely established recycling streams resulting in reduced landfill waste and lower carbon footprint when properly processed. The environmental sustainability of PET is generally favored, given its potential for closed-loop recycling and broader infrastructure support compared to fluoropolymers.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Fluoropolymer bottles exhibit superior chemical resistance and durability but carry significantly higher production costs compared to Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET), which is widely preferred for its cost-effectiveness and extensive market availability. PET dominates the packaging industry with global production surpassing 25 million metric tons annually, offering abundant supply chains and recyclability advantages that reduce overall lifecycle expenses. Fluoropolymer usage remains niche due to limited manufacturing facilities and premium pricing, restricting its market penetration primarily to specialized industrial and pharmaceutical applications.
Best Use Cases and Industry Applications
Fluoropolymer bottles excel in chemical resistance and high-temperature durability, making them ideal for pharmaceutical and specialty chemical storage where contamination prevention is critical. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers excellent clarity, lightweight properties, and cost-effectiveness, which makes it the preferred choice for beverage packaging and everyday consumer goods. Industries requiring barrier protection against moisture and oxygen, such as food and beverage or cosmetics, typically favor PET, while high-performance applications like industrial solvents and laboratory containers rely on fluoropolymer materials.
Infographic: Fluoropolymer vs Polyethylene Terephthalate for Bottle
 azmater.com
azmater.com