Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent clarity and UV resistance, making it ideal for food wraps that require visual appeal and light protection. Polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) excels in oxygen and moisture barrier properties, providing superior food preservation and shelf life extension.
Table of Comparison
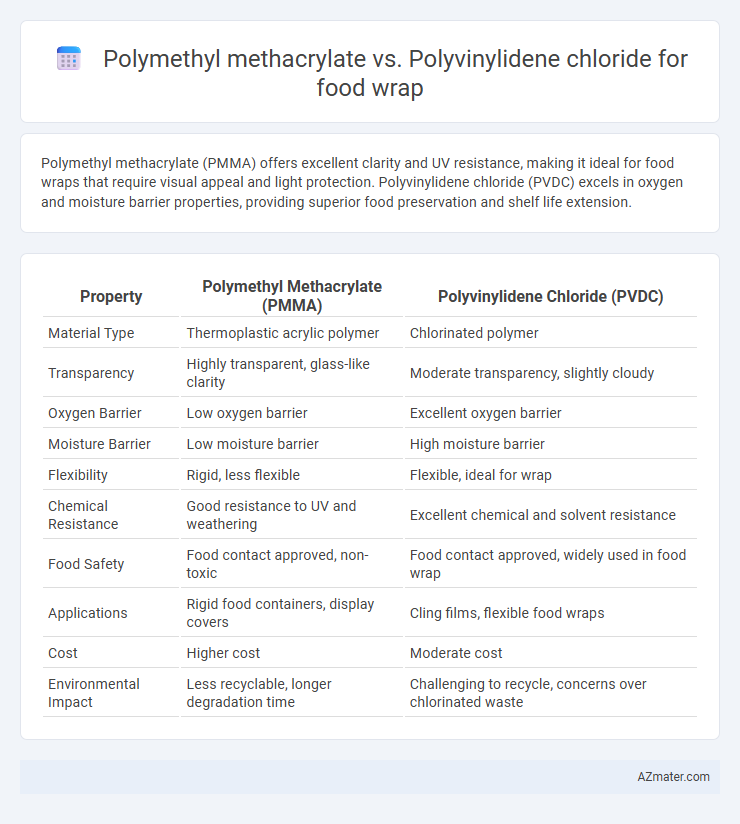
| Property | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) | Polyvinylidene Chloride (PVDC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic acrylic polymer | Chlorinated polymer |
| Transparency | Highly transparent, glass-like clarity | Moderate transparency, slightly cloudy |
| Oxygen Barrier | Low oxygen barrier | Excellent oxygen barrier |
| Moisture Barrier | Low moisture barrier | High moisture barrier |
| Flexibility | Rigid, less flexible | Flexible, ideal for wrap |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to UV and weathering | Excellent chemical and solvent resistance |
| Food Safety | Food contact approved, non-toxic | Food contact approved, widely used in food wrap |
| Applications | Rigid food containers, display covers | Cling films, flexible food wraps |
| Cost | Higher cost | Moderate cost |
| Environmental Impact | Less recyclable, longer degradation time | Challenging to recycle, concerns over chlorinated waste |
Introduction to Food Wrap Materials
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) are prominent polymers used in food wrap applications due to their distinctive barrier properties. PMMA offers excellent clarity and UV resistance, making it ideal for product visibility and protection from light-induced degradation. PVDC provides superior oxygen and moisture barrier performance, extending the shelf life of perishable foods by minimizing oxidation and moisture loss.
Overview of Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) is a transparent thermoplastic often used as a shatter-resistant alternative to glass in food wrap applications due to its excellent clarity and durability. PMMA offers superior UV resistance and chemical stability compared to Polyvinylidene Chloride (PVDC), making it suitable for preserving food freshness while maintaining product visibility. Its non-toxic and recyclable nature enhances its appeal for sustainable food packaging solutions.
Overview of Polyvinylidene Chloride (PVDC)
Polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) is a high-performance polymer known for its excellent barrier properties against moisture, oxygen, and aroma, making it ideal for food wrap applications. PVDC films provide superior preservation of food freshness and shelf life compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), due to their low permeability and chemical resistance. Its versatility and durability make PVDC a preferred choice in packaging foods that require extended protection from environmental factors.
Barrier Properties: PMMA vs PVDC
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent clarity and moderate barrier properties against oxygen and moisture, making it suitable for applications requiring transparency but less critical barrier performance. Polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) provides superior barrier properties, particularly against oxygen, moisture, and aroma, ensuring longer shelf life and preservation of food quality. The choice between PMMA and PVDC for food wrap primarily depends on the balance between required barrier effectiveness and visual clarity, with PVDC favored for high barrier needs and PMMA for aesthetic packaging.
Flexibility and Strength Comparison
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent rigidity and clarity but lacks the flexibility required for tight food wrapping, making it more prone to cracking under stress. Polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) demonstrates superior flexibility and strength, providing a durable, stretchable barrier that conforms closely to food surfaces without tearing. PVDC's enhanced tensile strength and elongation properties make it a preferred choice for food wrap applications needing secure, flexible packaging.
Food Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent clarity and is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) for food contact applications, complying with FDA regulations for food wraps. Polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) provides superior barrier properties against moisture, oxygen, and contaminants, meeting stringent food safety standards and FDA approvals for packaging sensitive food products. Both materials ensure regulatory compliance but differ in barrier performance and transparency, influencing their selection based on specific food safety requirements.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is a transparent thermoplastic known for its durability and recyclability but is derived from non-renewable petroleum resources, resulting in a moderate environmental footprint. Polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC), commonly used in food wrap for its excellent barrier properties, poses significant environmental challenges due to its chlorine content, which complicates recycling and leads to hazardous byproducts during incineration. From a sustainability perspective, PMMA offers better recyclability and lower toxic emissions, while PVDC's environmental impact is heightened by its persistence and difficult disposal, making PMMA a more eco-friendly choice for food packaging.
Cost and Commercial Availability
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers moderate cost and widespread commercial availability as a food wrap material, favored for its clarity and durability. Polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) typically presents higher material and processing costs but excels in barrier properties against gases and moisture, making it suitable for specialized or premium food packaging. Commercial availability for PVDC is more limited, often reserved for applications requiring superior preservation performance despite cost considerations.
Typical Applications in Food Packaging
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is commonly used in food packaging for its clarity, rigidity, and excellent barrier properties against oxygen, making it ideal for display windows and protective covers in bakery and confectionery packaging. Polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) is favored for its superior moisture, oxygen, and aroma barrier capabilities, making it suitable for preserving freshness in packaging for meats, cheese, and other perishable food products. Both materials contribute to extending shelf life and ensuring product safety but are selected based on specific barrier needs and packaging design requirements.
Choosing the Right Material for Food Wrap
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior clarity and UV resistance, making it ideal for showcasing food products while maintaining protection against light degradation. Polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) provides exceptional barrier properties against oxygen, moisture, and aromas, extending the shelf life of perishable foods effectively. Selecting the right material for food wrap depends on prioritizing visual appeal with PMMA or enhanced preservation performance with PVDC.
Infographic: Polymethyl methacrylate vs Polyvinylidene chloride for Food Wrap
 azmater.com
azmater.com