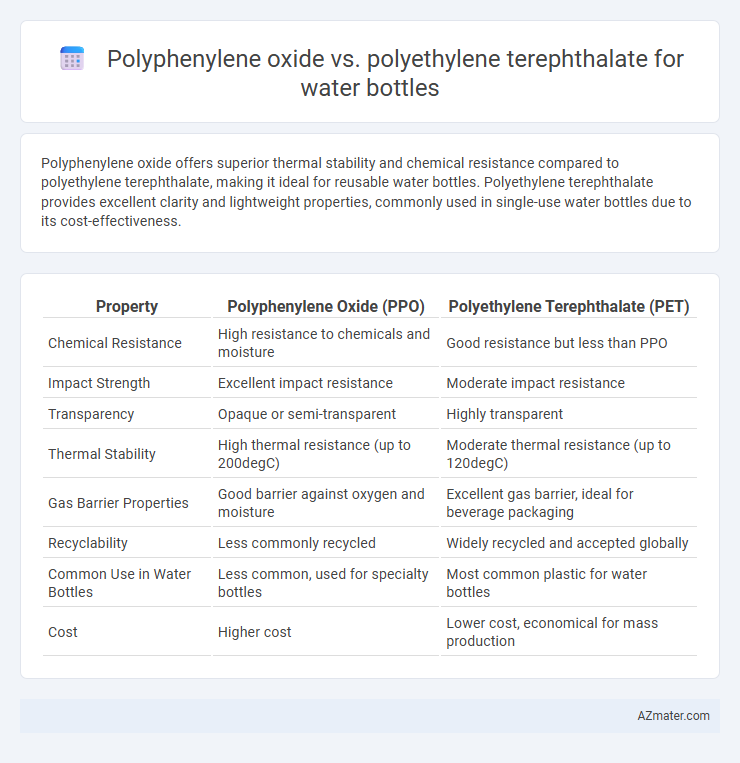
Polyphenylene oxide offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polyethylene terephthalate, making it ideal for reusable water bottles. Polyethylene terephthalate provides excellent clarity and lightweight properties, commonly used in single-use water bottles due to its cost-effectiveness.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to chemicals and moisture | Good resistance but less than PPO |
| Impact Strength | Excellent impact resistance | Moderate impact resistance |
| Transparency | Opaque or semi-transparent | Highly transparent |
| Thermal Stability | High thermal resistance (up to 200degC) | Moderate thermal resistance (up to 120degC) |
| Gas Barrier Properties | Good barrier against oxygen and moisture | Excellent gas barrier, ideal for beverage packaging |
| Recyclability | Less commonly recycled | Widely recycled and accepted globally |
| Common Use in Water Bottles | Less common, used for specialty bottles | Most common plastic for water bottles |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost, economical for mass production |
Introduction to Polyphenylene Oxide and Polyethylene Terephthalate
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability, making it suitable for reusable water bottles that require durability and longevity. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a widely used polyester resin characterized by its clarity, lightweight, and good barrier properties against moisture and gases, commonly utilized in single-use and recyclable water bottles. Both polymers offer distinct advantages depending on requirements for strength, transparency, and environmental sustainability in water bottle applications.
Chemical Structure and Properties Comparison
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) features a rigid aromatic backbone with ether linkages, providing excellent thermal stability and high dimensional accuracy, making it resistant to hydrolysis and chemical degradation in water bottle applications. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) consists of ester linkages with a semi-crystalline structure, offering good gas barrier properties and mechanical strength but lower thermal resistance compared to PPO. The superior chemical resistance and thermal stability of PPO contrast with PET's cost-effectiveness and recyclability, influencing material selection based on application requirements.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), making it more resistant to impact and deformation under stress, which enhances the durability of water bottles. PPO's inherent thermal stability and chemical resistance contribute to a longer lifespan in environments involving frequent temperature changes and exposure to various substances. PET offers good clarity and processability but generally lacks the robust toughness and long-term durability provided by PPO in demanding applications.
Thermal Stability and Temperature Resistance
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior thermal stability with a high glass transition temperature around 215degC, making it highly resistant to deformation under elevated heat conditions. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) has a lower thermal resistance, typically softening around 70-80degC, which limits its performance in hot-fill water bottle applications. The enhanced temperature resistance of PPO ensures better retention of mechanical properties and structural integrity during sterilization and high-temperature exposure compared to PET.
Water and Moisture Barrier Performance
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior water and moisture barrier performance compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET) due to its low water vapor transmission rate (WVTR) and excellent dimensional stability under humid conditions. PET, while commonly used for water bottles, has higher permeability to water vapor, which can affect shelf life and product integrity in high-moisture environments. Selecting PPO for water bottle applications enhances durability and preserves liquid quality by minimizing moisture ingress and maintaining barrier effectiveness.
Safety and Chemical Leaching Concerns
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior chemical resistance and lower risk of harmful leaching compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), making it a safer choice for water bottles. PET can release antimony and other degradation products under prolonged exposure to heat or UV light, raising potential health concerns. PPO's inherent stability ensures minimal chemical interaction with stored liquids, maintaining water purity and consumer safety.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior thermal stability and durability compared to Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), resulting in a longer lifespan for water bottles, which can reduce environmental waste. PET is widely recyclable and supported by extensive global recycling infrastructure, enabling efficient material recovery and reducing plastic pollution. However, PPO's limited recyclability and less established recycling streams contribute to a higher environmental impact over its lifecycle compared to PET.
Cost Analysis and Manufacturing Considerations
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) water bottles typically incur higher raw material costs than polyethylene terephthalate (PET), impacting overall production expenses. Manufacturing PPO requires specialized processing conditions, such as higher extrusion temperatures and equipment resistant to thermal degradation, leading to increased energy consumption and maintenance. PET benefits from established, high-volume production lines with lower cycle times, resulting in cost-efficient scalability and widespread availability in the water bottle market.
Applications in Water Bottle Production
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for reusable water bottles designed to withstand high temperatures and repeated sterilization. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is widely used for single-use water bottles due to its lightweight nature, excellent clarity, and cost-effectiveness in mass production. While PPO provides enhanced durability and resistance to cracking, PET remains preferred for disposable water bottles due to its excellent barrier properties against moisture and gases.
Conclusion: Which Polymer is Better for Water Bottles?
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), making PPO ideal for reusable water bottles subjected to high temperatures and frequent washing. PET, however, excels in cost efficiency, clarity, and recyclability, which favors single-use or disposable bottles. For sustainable, long-term use with durability, PPO is the better polymer choice, while PET remains preferred for economical and widely recyclable applications.
Infographic: Polyphenylene oxide vs Polyethylene terephthalate for Water bottle
 azmater.com
azmater.com