Conductive polymers offer superior electrical conductivity and flexibility for smart shoe sole applications, while Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) provides excellent cushioning, lightweight durability, and shock absorption. EVA is widely preferred in athletic footwear for comfort, whereas conductive polymers enable integrated electronic functionalities like pressure sensing and heat regulation.
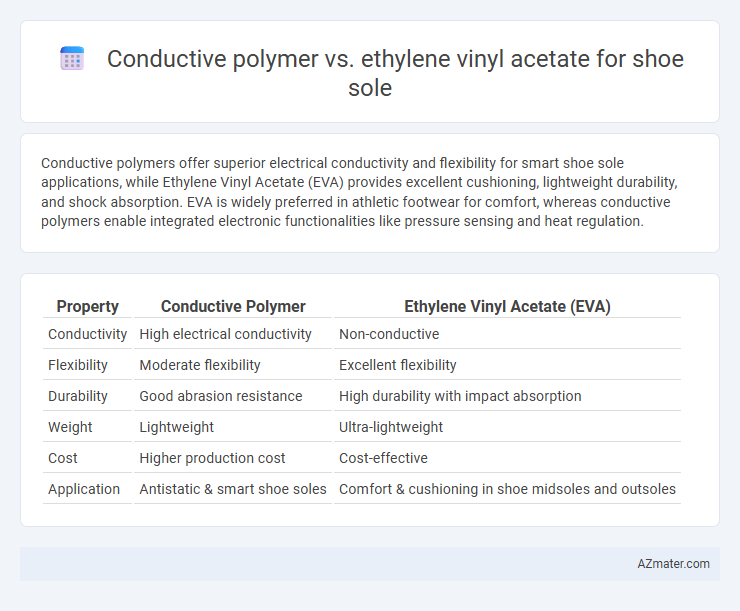
Table of Comparison
| Property | Conductive Polymer | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | High electrical conductivity | Non-conductive |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | Excellent flexibility |
| Durability | Good abrasion resistance | High durability with impact absorption |
| Weight | Lightweight | Ultra-lightweight |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Cost-effective |
| Application | Antistatic & smart shoe soles | Comfort & cushioning in shoe midsoles and outsoles |
Introduction to Innovative Shoe Sole Materials
Conductive polymers offer lightweight, flexible, and electrically conductive properties ideal for smart shoe soles integrating sensors and wearable technology. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) is favored for its excellent cushioning, shock absorption, and durability in traditional athletic and casual footwear. Innovations in shoe sole materials increasingly combine EVA's comfort with conductive polymers' technological functionalities to enhance performance and user experience.
Overview of Conductive Polymers in Footwear
Conductive polymers in footwear are advanced materials designed to dissipate static electricity, enhance comfort, and provide durability compared to traditional ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA). These polymers offer superior electrical conductivity, flexibility, and resistance to wear, making them ideal for antistatic and performance shoe soles. EVA, while lightweight and cushioning, lacks the intrinsic conductive properties found in conductive polymers, positioning the latter as a preferred choice for specialized footwear applications.
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA): Industry Standard for Shoe Soles
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) is the industry standard for shoe soles due to its excellent combination of lightweight, flexibility, and shock absorption properties, which enhance comfort and durability. Unlike conductive polymers, EVA provides superior cushioning and resistance to environmental factors such as UV radiation and water, making it ideal for athletic and casual footwear. Its cost-effective production and recyclability further solidify EVA's dominance in the footwear industry, especially for midsoles and outsoles.
Mechanical Properties: Conductive Polymer vs EVA
Conductive polymers demonstrate superior wear resistance and tensile strength compared to Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA), making them more durable for shoe soles under high-stress conditions. EVA offers excellent flexibility and shock absorption but tends to degrade faster under repetitive mechanical stress due to lower tear resistance. The mechanical properties of conductive polymers also include greater elasticity retention and improved impact resilience, which enhance overall shoe sole performance in demanding environments.
Comfort and Cushioning Comparison
Conductive polymers in shoe soles offer enhanced flexibility and breathability while providing moderate cushioning, making them suitable for lightweight footwear focused on comfort. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) is widely recognized for superior shock absorption and resilient cushioning, ensuring excellent comfort during prolonged wear by effectively reducing foot fatigue. EVA's lightweight and durable properties generally outperform conductive polymers in cushioning, making it the preferred choice for high-impact activities and all-day support.
Electrical Properties and Potential Applications
Conductive polymers exhibit excellent electrical conductivity and flexibility, making them ideal for smart shoe soles integrated with sensors or heating elements, whereas ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior cushioning and shock absorption but lacks electrical conductivity. The conductive polymer's ability to transmit electrical signals supports applications in wearable electronics and health monitoring systems embedded in footwear. EVA remains the preferred material for traditional sole cushioning, while conductive polymers enable advanced functionalities in e-textiles and responsive footwear technologies.
Durability and Longevity
Conductive polymers in shoe soles offer enhanced durability through their resistance to wear and tear, maintaining electrical conductivity over extended use. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) provides excellent longevity due to its lightweight, flexible nature and superior cushioning properties that resist compression set and material degradation. Comparing both, conductive polymers excel in applications requiring electrical functionality and abrasion resistance, while EVA emphasizes long-term comfort and impact absorption in footwear soles.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Conductive polymers in shoe soles offer enhanced recyclability and reduced reliance on non-renewable resources compared to Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA), which is petroleum-based and contributes to microplastic pollution. EVA soles pose challenges in biodegradability and generate significant carbon emissions during production, whereas conductive polymers often incorporate bio-based or recycled materials, lowering overall environmental footprint. The shift to conductive polymers supports circular economy principles by enabling efficient material recovery and reducing landfill waste in footwear manufacturing.
Cost Analysis for Manufacturers
Conductive polymers typically incur higher production costs compared to ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) due to complex synthesis and specialized raw materials, impacting manufacturers' budgets significantly. EVA offers cost-effective advantages with lower material and processing expenses, making it a preferred choice for large-scale shoe sole production. Manufacturers must balance the higher initial investment of conductive polymers against EVA's economic efficiency when prioritizing cost optimization.
Future Trends in Shoe Sole Material Technology
Conductive polymers in shoe soles enhance wearable technology by enabling integrated sensors and energy harvesting, promoting smart footwear innovations. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) remains dominant for lightweight cushioning but faces competition from bio-based and recyclable variants that meet sustainability goals. Future trends emphasize multifunctional soles combining conductivity for electronics with eco-friendly materials, driving advancements in performance and environmental impact.
Infographic: Conductive polymer vs Ethylene vinyl acetate for Shoe sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com