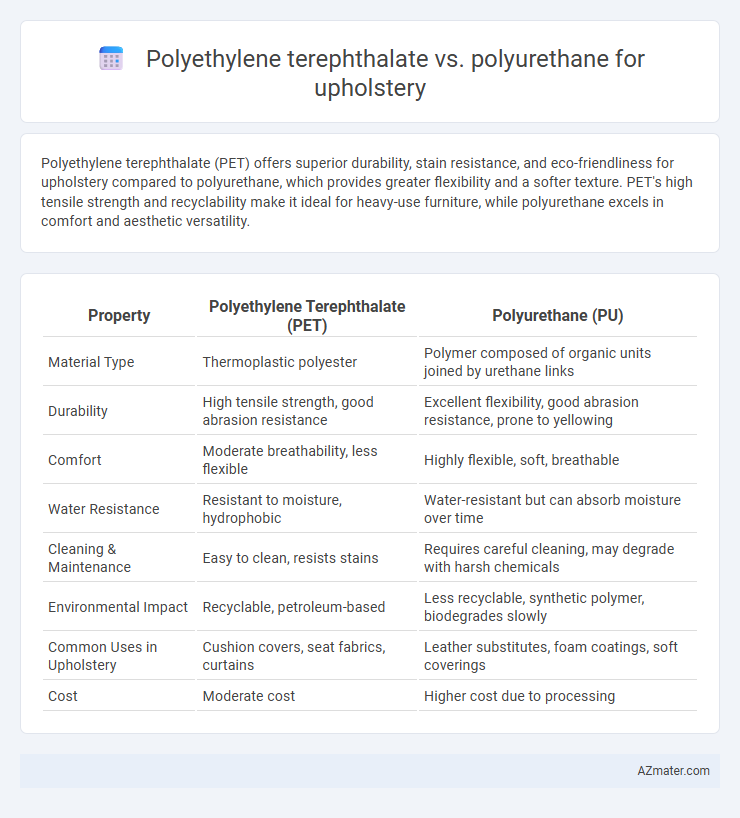
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior durability, stain resistance, and eco-friendliness for upholstery compared to polyurethane, which provides greater flexibility and a softer texture. PET's high tensile strength and recyclability make it ideal for heavy-use furniture, while polyurethane excels in comfort and aesthetic versatility.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) | Polyurethane (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polyester | Polymer composed of organic units joined by urethane links |
| Durability | High tensile strength, good abrasion resistance | Excellent flexibility, good abrasion resistance, prone to yellowing |
| Comfort | Moderate breathability, less flexible | Highly flexible, soft, breathable |
| Water Resistance | Resistant to moisture, hydrophobic | Water-resistant but can absorb moisture over time |
| Cleaning & Maintenance | Easy to clean, resists stains | Requires careful cleaning, may degrade with harsh chemicals |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, petroleum-based | Less recyclable, synthetic polymer, biodegrades slowly |
| Common Uses in Upholstery | Cushion covers, seat fabrics, curtains | Leather substitutes, foam coatings, soft coverings |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Higher cost due to processing |
Introduction to Polyethylene Terephthalate and Polyurethane
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a widely used polyester polymer known for its durability, resistance to moisture, and recyclability, making it a popular choice in upholstery fabrics. Polyurethane (PU) is a versatile synthetic polymer characterized by its flexibility, elasticity, and abrasion resistance, often utilized in upholstery for its leather-like appearance and comfort. Both materials offer distinct advantages in upholstery, with PET excelling in strength and environmental benefits, while PU provides superior softness and versatility in design.
Composition and Material Properties
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a thermoplastic polymer primarily composed of repeating units of ethylene terephthalate, known for its high tensile strength, chemical resistance, and excellent moisture barrier properties, making it suitable for durable and water-resistant upholstery applications. Polyurethane (PU) is a polymer composed of organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links, characterized by its elasticity, flexibility, and superior abrasion resistance, providing a soft and comfortable feel ideal for upholstery. The choice between PET and PU hinges on the need for rigidity and moisture resistance with PET or the demand for elasticity and cushioning inherent in PU materials.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers exceptional durability and high wear resistance due to its strong molecular structure and resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for heavy-use upholstery. Polyurethane (PU) provides superior flexibility and a soft touch but tends to degrade faster under constant friction and exposure to UV light, resulting in reduced wear resistance over time. For long-lasting upholstery in high-traffic areas, PET outperforms polyurethane by maintaining structural integrity and surface appearance for extended periods.
Comfort and Aesthetics
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) upholstery offers durability and a smooth, sleek appearance with good resistance to stains and fading, making it ideal for modern, minimalist aesthetics. Polyurethane (PU) provides a softer, more flexible texture that enhances comfort with its leather-like feel, appealing to those seeking a luxurious and cozy seating experience. While PET excels in maintaining shape and longevity, PU's versatility in color and finish delivers a more visually warm and inviting look.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers significant environmental benefits due to its recyclability and lower carbon footprint compared to polyurethane (PU), which is derived from fossil fuels and involves more toxic chemical processes. PET's ability to be recycled into new fibers reduces landfill waste, enhancing sustainability in upholstery applications. Conversely, polyurethane degradation releases harmful substances that challenge waste management and environmental safety.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) upholstery is highly resistant to stains and moisture, making it easy to clean with mild soap and water, requiring minimal maintenance. Polyurethane (PU) upholstery demands more frequent cleaning to prevent surface wear and may require specialized cleaners to maintain its appearance and prevent cracking. Both materials offer durability, but PET's superior resistance to dirt and ease of maintenance makes it ideal for high-use environments.
Cost Comparison
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) typically offers a more cost-effective solution for upholstery due to its widespread availability and efficient production processes compared to polyurethane. Polyurethane, known for its superior flexibility and cushioning, generally comes at a higher price point influenced by its complex manufacturing and enhanced durability features. Budget-conscious projects often favor PET, while applications requiring premium comfort and longevity may justify polyurethane's additional cost.
Common Applications in Upholstery
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is commonly used in upholstery for its durability, resistance to wrinkles, and ability to hold color, making it ideal for residential furniture and commercial seating where longevity and easy maintenance are critical. Polyurethane, on the other hand, is favored for its flexible texture and cushioning properties, often employed in automotive seats, office chairs, and high-end furniture that require comfort combined with wear resistance. Both materials offer distinct benefits, with PET excelling in structural fabric applications and polyurethane serving as a versatile foam or coating component in upholstery.
Health and Safety Considerations
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is widely regarded as a safer option for upholstery due to its non-toxic, hypoallergenic properties and resistance to mold and mildew, reducing indoor air quality risks. Polyurethane foam, while offering superior cushioning, can off-gas volatile organic compounds (VOCs) such as isocyanates, which may cause respiratory irritation and allergic reactions, posing health concerns in enclosed spaces. Choosing PET for upholstery minimizes exposure to harmful chemicals, making it a preferred material for health-conscious environments and individuals sensitive to airborne pollutants.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Upholstery
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers durability, stain resistance, and recyclability, making it ideal for eco-conscious upholstery projects. Polyurethane (PU) provides superior flexibility, softness, and water resistance, often chosen for premium comfort in furniture. Selecting the right upholstery material depends on balancing factors like longevity, maintenance needs, comfort level, and environmental impact.
Infographic: Polyethylene terephthalate vs Polyurethane for Upholstery
 azmater.com
azmater.com