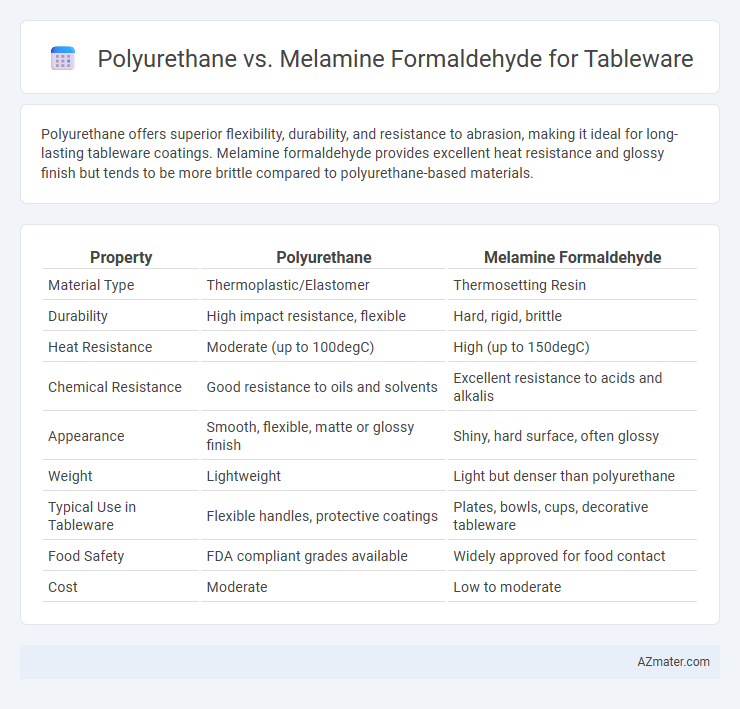
Polyurethane offers superior flexibility, durability, and resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for long-lasting tableware coatings. Melamine formaldehyde provides excellent heat resistance and glossy finish but tends to be more brittle compared to polyurethane-based materials.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane | Melamine Formaldehyde |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic/Elastomer | Thermosetting Resin |
| Durability | High impact resistance, flexible | Hard, rigid, brittle |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate (up to 100degC) | High (up to 150degC) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and solvents | Excellent resistance to acids and alkalis |
| Appearance | Smooth, flexible, matte or glossy finish | Shiny, hard surface, often glossy |
| Weight | Lightweight | Light but denser than polyurethane |
| Typical Use in Tableware | Flexible handles, protective coatings | Plates, bowls, cups, decorative tableware |
| Food Safety | FDA compliant grades available | Widely approved for food contact |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to moderate |
Introduction: Comparing Polyurethane and Melamine Formaldehyde Tableware
Polyurethane tableware offers exceptional durability and flexibility, making it resistant to impact and temperature variations, ideal for everyday use. Melamine formaldehyde tableware is renowned for its lightweight, heat-resistant properties, and vibrant color retention, commonly used in casual dining settings. Both materials provide non-porous surfaces that prevent bacterial growth, ensuring hygienic and long-lasting tableware options.
Chemical Composition of Polyurethane and Melamine Formaldehyde
Polyurethane is a polymer composed of organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links, formed through the reaction of diisocyanates with polyols, providing flexibility and durability in tableware coatings. Melamine formaldehyde is a thermosetting resin synthesized from melamine and formaldehyde, resulting in a hard, heat-resistant surface ideal for tableware that requires scratch and stain resistance. The chemical composition differences significantly affect the material properties, with polyurethane offering elasticity and melamine formaldehyde delivering rigidity and chemical resistance.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Polyurethane tableware is produced through a chemical reaction between polyols and isocyanates, resulting in a durable, flexible polymer that can be molded or cast into various shapes. Melamine formaldehyde is synthesized by combining melamine and formaldehyde under heat and pressure, creating a hard, thermosetting resin ideal for rigid, heat-resistant tableware. The polyurethane process emphasizes versatility and elasticity, while melamine formaldehyde manufacturing focuses on rigid, heat-stable products with a glossy finish.
Durability and Strength Analysis
Polyurethane tableware offers superior impact resistance and flexibility, making it highly durable against cracks and chips compared to melamine formaldehyde. Melamine formaldehyde, while providing excellent hardness and scratch resistance, tends to be more brittle and prone to shattering under high stress or impact. For long-lasting tableware requiring both strength and resilience, polyurethane typically outperforms melamine formaldehyde in durability metrics.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Stability
Polyurethane offers moderate heat resistance suitable for everyday tableware but can degrade at temperatures above 120degC, limiting its thermal stability. Melamine formaldehyde excels with high heat resistance up to 160degC and superior thermal stability, making it ideal for hot dishware and microwave-safe products. The chemical cross-linking in melamine formaldehyde provides durable heat resistance, preventing warping or discoloration better than polyurethane.
Safety, Food Contact, and Regulatory Compliance
Polyurethane and melamine formaldehyde differ significantly in safety and regulatory compliance for tableware. Polyurethane is generally considered safe for food contact when formulated without harmful additives, but it lacks widespread regulatory approvals compared to melamine formaldehyde, which is extensively tested and approved by agencies like the FDA for food contact surfaces. Melamine formaldehyde offers high durability and heat resistance but may pose risks of formaldehyde migration if improperly manufactured, making food safety certification critical for consumer use.
Design Versatility and Aesthetic Options
Polyurethane offers exceptional design versatility and a wide range of aesthetic options for tableware due to its ability to be molded into intricate shapes and finished with various textures, colors, and gloss levels. Melamine formaldehyde provides durable, vibrant, and smooth surfaces but is generally limited to more traditional, rigid designs with fewer texture variations. Choosing polyurethane supports innovative, customizable tableware designs that cater to contemporary aesthetic trends, while melamine formaldehyde suits classic, consistent patterns with reliable surface quality.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyurethane tableware typically involves petrochemical-based materials that contribute to higher carbon footprints and limited biodegradability, posing challenges for sustainability. Melamine formaldehyde, while durable and resistant to heat, is derived from formaldehyde and melamine chemicals that can release hazardous emissions during manufacturing and disposal, raising environmental concerns. Sustainable alternatives prioritize bio-based resins and recyclable options to minimize ecological damage compared to traditional polyurethane and melamine formaldehyde formulations.
Cost Considerations for Tableware Production
Polyurethane offers moderate raw material costs with high durability, reducing long-term replacement expenses in tableware production, whereas melamine formaldehyde presents a lower upfront cost but may incur higher brittleness-related breakage costs. The manufacturing process for melamine formaldehyde is generally less expensive and faster, benefiting high-volume, cost-sensitive tableware production. Balancing initial material expenses with product longevity and breakage rates is essential for optimizing overall cost-efficiency in tableware manufacturing.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Tableware
Polyurethane offers exceptional durability and flexibility, making it ideal for tableware requiring impact resistance and long-lasting performance, while melamine formaldehyde provides a hard, scratch-resistant surface perfect for everyday use with elegant finishes. The choice depends on the intended use: polyurethane suits high-traffic environments needing resilience, whereas melamine formaldehyde excels in casual dining settings due to its lightweight and aesthetic properties. Understanding these material characteristics ensures selecting tableware that balances durability, appearance, and functionality.
Infographic: Polyurethane vs Melamine formaldehyde for Tableware
 azmater.com
azmater.com