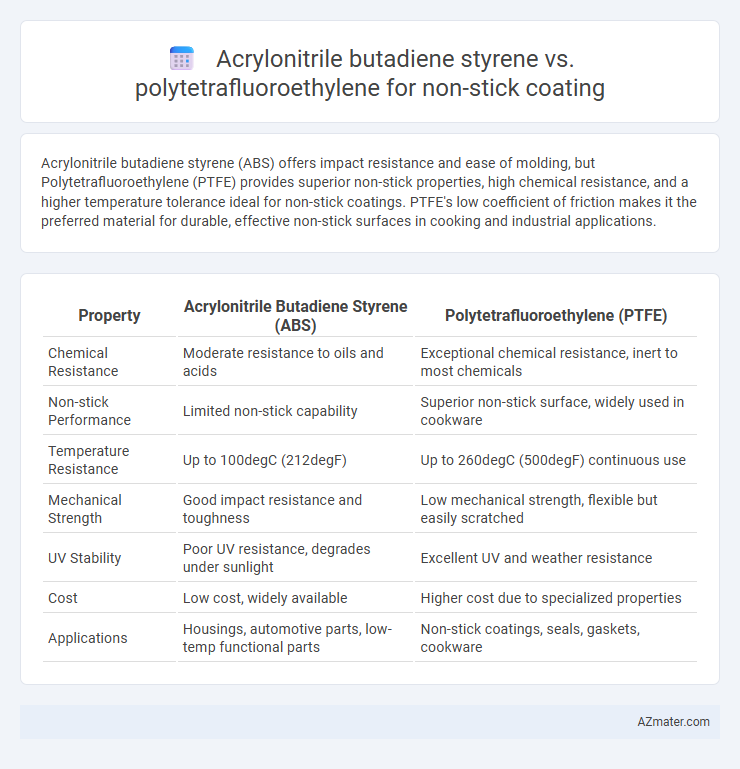
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers impact resistance and ease of molding, but Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) provides superior non-stick properties, high chemical resistance, and a higher temperature tolerance ideal for non-stick coatings. PTFE's low coefficient of friction makes it the preferred material for durable, effective non-stick surfaces in cooking and industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance to oils and acids | Exceptional chemical resistance, inert to most chemicals |
| Non-stick Performance | Limited non-stick capability | Superior non-stick surface, widely used in cookware |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 100degC (212degF) | Up to 260degC (500degF) continuous use |
| Mechanical Strength | Good impact resistance and toughness | Low mechanical strength, flexible but easily scratched |
| UV Stability | Poor UV resistance, degrades under sunlight | Excellent UV and weather resistance |
| Cost | Low cost, widely available | Higher cost due to specialized properties |
| Applications | Housings, automotive parts, low-temp functional parts | Non-stick coatings, seals, gaskets, cookware |
Introduction to Non-Stick Coating Materials
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) and Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) are prominent materials in non-stick coatings, each offering unique properties tailored for industrial applications. PTFE is renowned for its exceptional non-stick capabilities, high thermal resistance up to 260degC, and chemical inertness, making it ideal for cookware and machinery exposed to corrosive substances. ABS, while less heat resistant with a maximum service temperature around 100degC, provides superior impact resistance and mechanical strength, commonly used in lower temperature non-stick applications or as a base substrate for coating systems.
Overview of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its toughness, impact resistance, and ease of fabrication, making it popular in various industrial applications. Unlike Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), ABS lacks inherent non-stick properties and requires additional coatings or treatments to enhance surface friction and chemical resistance. ABS is widely used in manufacturing automotive parts, consumer electronics, and protective housings, where durability and mechanical strength are prioritized over non-stick performance.
Overview of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer renowned for its exceptional non-stick properties, chemical resistance, and high thermal stability, making it a preferred choice for non-stick coatings in cookware and industrial applications. Unlike Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), PTFE offers superior low friction and durability at elevated temperatures up to 260degC (500degF). Its molecular structure provides excellent resistance to corrosion, wear, and moisture, enabling long-lasting non-stick performance across diverse environments.
Chemical Properties: ABS vs PTFE
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits moderate chemical resistance but is susceptible to degradation by strong acids, bases, and solvents, limiting its use in highly reactive environments. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) features exceptional chemical inertness due to its strong carbon-fluorine bonds, resisting nearly all chemicals, including acids and bases, making it ideal for non-stick coatings in aggressive conditions. PTFE's low surface energy also enhances its non-stick properties, unlike ABS, which has higher surface energy and can attract contaminants.
Thermal Resistance Comparison
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits a thermal resistance range of approximately 80-100degC, making it suitable for applications requiring moderate heat tolerance but inadequate for high-temperature non-stick coatings. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) withstands significantly higher temperatures, with a melting point around 327degC and continuous use stability up to 260degC, offering superior thermal resistance ideal for non-stick cookware and industrial coatings. The disparity in thermal resistance between ABS and PTFE underscores PTFE's dominance in non-stick applications where sustained high temperatures are essential.
Non-Stick Performance and Efficiency
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate non-stick performance but falls short compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), which delivers superior chemical inertness and extremely low surface energy, resulting in exceptional non-stick efficiency. PTFE coatings exhibit higher durability and resistance to heat and chemicals, making them ideal for prolonged use in cookware and industrial applications. ABS, while cost-effective and impact-resistant, lacks the same level of non-stick capability and thermal stability required for high-performance non-stick coatings.
Durability and Longevity in Applications
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate durability with good impact resistance but tends to degrade under prolonged high-temperature exposure, limiting its longevity in non-stick coatings. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) excels in chemical inertness and thermal stability up to 260degC, ensuring superior long-term non-stick performance and resistance to wear. PTFE's molecular structure provides exceptional low friction and high durability, making it the preferred choice for applications requiring sustained non-stick properties and extended service life.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic known for its durability but can emit toxic fumes like styrene and acrylonitrile during high-temperature processing, posing health risks if not properly ventilated. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known as Teflon, offers exceptional non-stick properties and chemical resistance but may release harmful perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) during manufacturing and thermal decomposition. From an environmental perspective, PTFE's persistence and bioaccumulation concerns contrast with ABS's higher biodegradability but production-associated volatile organic compounds (VOCs), making safety measures and lifecycle management critical for both materials.
Cost and Availability Factors
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) generally offers a significantly lower cost compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), making it more accessible for mass production of non-stick coatings. ABS is widely available due to its extensive use in consumer products, whereas PTFE availability can be more limited and subject to fluctuating prices because of its complex manufacturing process. Cost efficiency and material availability favor ABS in budget-sensitive applications, while PTFE remains preferred for high-performance coatings despite higher expenses.
Conclusion: Best Choice for Non-Stick Coatings
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) stands out as the preferred choice for non-stick coatings due to its superior chemical resistance, high thermal stability up to 260degC, and exceptional low friction properties. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) lacks the heat resistance and chemical inertness required for effective non-stick surfaces, making it unsuitable for cooking applications where durability and safety are critical. PTFE's proven performance in cookware and industrial applications underscores its dominance in non-stick coating technology.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Polytetrafluoroethylene for Non-stick coating
 azmater.com
azmater.com