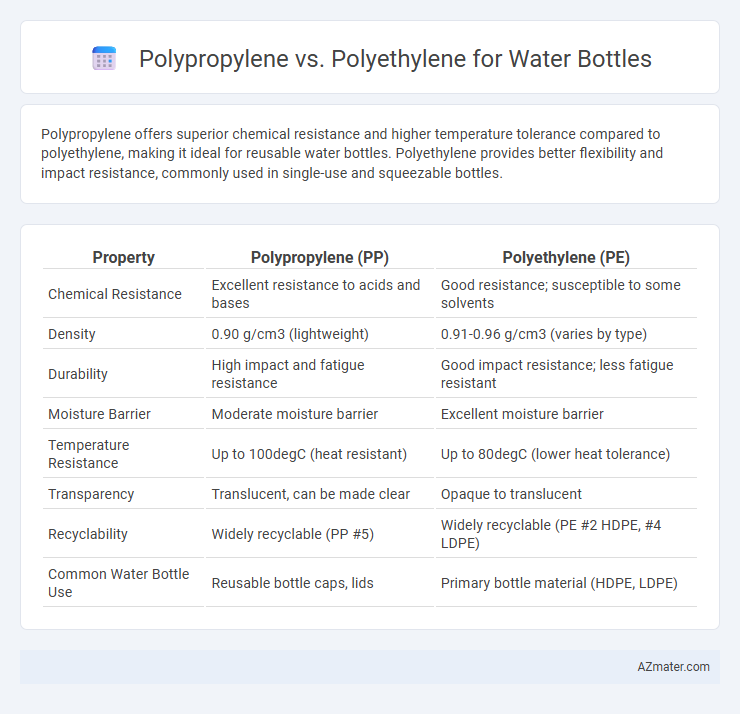
Polypropylene offers superior chemical resistance and higher temperature tolerance compared to polyethylene, making it ideal for reusable water bottles. Polyethylene provides better flexibility and impact resistance, commonly used in single-use and squeezable bottles.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polypropylene (PP) | Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to acids and bases | Good resistance; susceptible to some solvents |
| Density | 0.90 g/cm3 (lightweight) | 0.91-0.96 g/cm3 (varies by type) |
| Durability | High impact and fatigue resistance | Good impact resistance; less fatigue resistant |
| Moisture Barrier | Moderate moisture barrier | Excellent moisture barrier |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 100degC (heat resistant) | Up to 80degC (lower heat tolerance) |
| Transparency | Translucent, can be made clear | Opaque to translucent |
| Recyclability | Widely recyclable (PP #5) | Widely recyclable (PE #2 HDPE, #4 LDPE) |
| Common Water Bottle Use | Reusable bottle caps, lids | Primary bottle material (HDPE, LDPE) |
Introduction to Polypropylene and Polyethylene
Polypropylene (PP) and Polyethylene (PE) are two of the most commonly used polymers in water bottle manufacturing, each offering unique properties suited for specific applications. Polypropylene is known for its high melting point, rigidity, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for reusable bottles requiring durability and heat resistance. Polyethylene, available in high-density (HDPE) and low-density (LDPE) forms, provides excellent impact resistance, flexibility, and is widely used for single-use or squeeze bottles due to its lightweight and cost-effectiveness.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic polymer composed of repeating propylene monomers with a semi-crystalline structure, providing higher rigidity and heat resistance compared to polyethylene (PE). Polyethylene, primarily composed of ethylene monomers, features varying densities such as HDPE or LDPE, offering greater flexibility and impact resistance due to its simpler linear or branched chain structure. The differing chemical compositions influence barrier properties, with PP exhibiting a higher melting point around 160degC and better chemical resistance, while PE's lower melting point (typically 115-135degC) enhances its suitability for containers requiring toughness and moisture barrier performance.
Manufacturing Processes
Polypropylene (PP) manufacturing for water bottles involves injection molding and extrusion blow molding, offering high thermal resistance and durability. Polyethylene (PE), especially high-density polyethylene (HDPE), is commonly produced through blow molding, providing excellent chemical resistance and flexibility. The choice between PP and PE depends on the specific molding techniques and performance requirements in water bottle production.
Durability and Strength
Polypropylene offers higher tensile strength and better resistance to fatigue, making it ideal for reusable water bottles that require long-term durability. Polyethylene, particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE), provides excellent impact resistance and chemical stability but is generally less rigid than polypropylene. The choice between polypropylene and polyethylene hinges on balancing the need for structural strength with flexibility and impact absorption in water bottle applications.
Safety and Food Grade Certifications
Polypropylene (PP) and polyethylene (PE) are both widely used for water bottles due to their safety and compliance with food-grade certifications such as FDA and EFSA. Polypropylene offers higher heat resistance and is less prone to chemical leaching, making it ideal for reusable water bottles requiring sterilization. Polyethylene, especially high-density polyethylene (HDPE), provides excellent chemical resistance and durability but typically has a lower heat tolerance compared to polypropylene.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polypropylene (PP) and Polyethylene (PE) are popular materials for water bottles with distinct environmental impacts and recyclability profiles. Polyethylene, especially HDPE, is widely recycled with robust infrastructure, resulting in lower environmental footprints due to efficient reuse and energy recovery systems. Polypropylene, while more resistant to heat and chemicals, faces recycling challenges due to less developed collection streams and lower recycling rates, although innovations in polymer sorting are improving its sustainability.
Taste and Odor Retention
Polypropylene (PP) water bottles exhibit superior taste and odor retention compared to polyethylene (PE) due to their lower permeability to aromatic compounds and better chemical resistance. Polypropylene's molecular structure minimizes the absorption of external odors and prevents leaching of plastic taste into the water, maintaining purity over extended storage. In contrast, polyethylene, especially low-density variants, tends to absorb and transfer odors more readily, which can compromise the water's flavor profile.
Temperature Resistance
Polypropylene (PP) offers higher temperature resistance compared to Polyethylene (PE), typically withstanding temperatures up to 100-120degC, making it suitable for hot-fill water bottles. Polyethylene, especially High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE), usually resists temperatures up to around 80-90degC, limiting its application for hot liquids. The superior thermal stability of polypropylene ensures better durability and shape retention under heat stress in water bottle manufacturing.
Cost and Market Availability
Polypropylene water bottles generally offer a lower cost compared to polyethylene options, making them more attractive for budget-conscious manufacturers. Polyethylene, especially high-density polyethylene (HDPE), has wider market availability due to its extensive use in packaging and its strong chemical resistance. The choice between polypropylene and polyethylene ultimately depends on specific cost constraints and desired material performance in water bottle production.
Best Choice for Water Bottles
Polypropylene offers higher heat resistance and durability, making it ideal for reusable water bottles exposed to temperature variations and repeated washing. Polyethylene, especially high-density polyethylene (HDPE), provides excellent chemical resistance and flexibility, suitable for single-use or lightweight bottles. For long-term use and safe water storage, polypropylene is generally the best choice due to its combination of strength, safety, and recyclability.
Infographic: Polypropylene vs Polyethylene for Water Bottle
 azmater.com
azmater.com