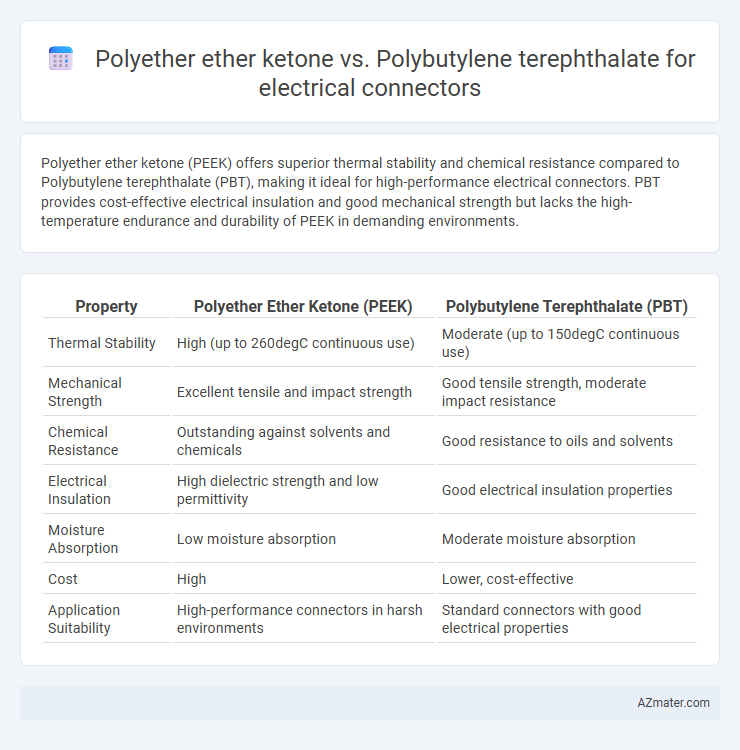
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), making it ideal for high-performance electrical connectors. PBT provides cost-effective electrical insulation and good mechanical strength but lacks the high-temperature endurance and durability of PEEK in demanding environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) | Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | High (up to 260degC continuous use) | Moderate (up to 150degC continuous use) |
| Mechanical Strength | Excellent tensile and impact strength | Good tensile strength, moderate impact resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Outstanding against solvents and chemicals | Good resistance to oils and solvents |
| Electrical Insulation | High dielectric strength and low permittivity | Good electrical insulation properties |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture absorption | Moderate moisture absorption |
| Cost | High | Lower, cost-effective |
| Application Suitability | High-performance connectors in harsh environments | Standard connectors with good electrical properties |
Introduction to Electrical Connectors: Material Selection
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) and Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) are critical thermoplastics used in electrical connectors due to their distinct performance properties. PEEK offers superior mechanical strength, high thermal stability up to 250degC, and excellent chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-demand electrical environments. PBT provides good electrical insulation, dimensional stability, and cost-effectiveness but has lower temperature resistance, typically up to 130degC, influencing material selection based on application-specific thermal and mechanical requirements.
Overview of Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK)
Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, making it ideal for electrical connectors in demanding environments. PEEK offers superior dielectric properties and maintains dimensional integrity at temperatures up to 250degC, ensuring reliable insulation and signal integrity. Compared to Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT), PEEK exhibits enhanced resistance to harsh chemicals and mechanical stress, contributing to longer connector lifespan in industrial and aerospace applications.
Overview of Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT)
Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic polyester known for its excellent electrical insulation properties, making it highly suitable for electrical connectors. It offers superior resistance to moisture, chemicals, and heat, with a continuous service temperature up to 150degC, ensuring durability in demanding electronic environments. Compared to Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK), PBT provides cost-effective performance with balanced mechanical strength and electrical stability, ideal for mass-produced electrical connector components.
Mechanical Properties Comparison: PEEK vs PBT
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) exhibits superior mechanical properties compared to polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) in electrical connector applications, offering higher tensile strength, better impact resistance, and enhanced dimensional stability under thermal stress. PEEK maintains its mechanical integrity at temperatures above 250degC, while PBT typically deforms or degrades near 150degC, limiting its use in high-temperature environments. The superior fatigue resistance and chemical stability of PEEK also contribute to its suitability for demanding, high-performance electrical connectors where durability and reliability are critical.
Electrical Insulation Performance: PEEK vs PBT
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior electrical insulation performance compared to polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) due to its high dielectric strength and low dielectric constant, making it ideal for high-voltage electrical connectors. PEEK maintains excellent insulation properties at elevated temperatures up to 250degC, whereas PBT's performance degrades above 120degC, limiting its use in harsh thermal environments. The superior moisture resistance of PEEK also ensures stable electrical characteristics in humid conditions, outperforming PBT in long-term reliability for electrical connectors.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) exhibits superior thermal stability and heat resistance compared to polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), sustaining continuous operating temperatures up to 250degC versus PBT's typical limit of 120degC. PEEK's high melting point of approximately 343degC ensures reliable electrical connector performance in harsh environments and prevents deformation under prolonged heat exposure. PBT is more susceptible to thermal degradation and dimensional changes at elevated temperatures, making PEEK the preferred choice for demanding electrical applications requiring long-term heat endurance.
Chemical Resistance and Durability
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), withstanding aggressive solvents, acids, and bases without significant degradation, making it ideal for electrical connectors in harsh chemical environments. PEEK also offers exceptional durability, maintaining mechanical strength and dimensional stability under high temperatures up to 250degC, whereas PBT performance typically degrades above 150degC. The enhanced thermal stability and resistance to hydrolysis and oxidation of PEEK ensure longer service life and reliability for electrical connectors exposed to demanding operational conditions.
Cost and Processability Considerations
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance but comes with a higher cost compared to Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), which is more budget-friendly for electrical connector manufacturing. PBT provides excellent processability with faster cycle times and lower melting temperatures, enabling efficient injection molding, while PEEK requires specialized equipment due to its higher melting point. Cost-effective PBT suits high-volume production where moderate temperature resistance is acceptable, whereas PEEK is preferred for high-performance connectors in demanding environments despite increased material and processing expenses.
Key Applications in Electrical Connectors
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-performance electrical connectors in aerospace, automotive, and industrial applications requiring durability under extreme conditions. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) provides excellent electrical insulation, dimensional stability, and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in consumer electronics, telecommunications, and household appliance connectors where moderate temperature resistance and precise molding are essential. The choice between PEEK and PBT depends on application-specific requirements such as operating temperature, mechanical stress, and exposure to harsh environments in electrical connector manufacturing.
Conclusion: Choosing Between PEEK and PBT
PEEK offers superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, making it ideal for high-performance electrical connectors in demanding environments. PBT provides cost-effective manufacturing, good electrical insulation, and adequate thermal properties for standard applications with moderate stress. Selecting between PEEK and PBT depends on balancing budget constraints with performance requirements, where PEEK suits high-reliability needs and PBT fits general-purpose uses.
Infographic: Polyether ether ketone vs Polybutylene terephthalate for Electrical connector
 azmater.com
azmater.com