Polyimide offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for reusable water bottles exposed to extreme temperatures. Polypropylene is lightweight and cost-effective but less durable and heat-resistant than polyimide, which ensures longer lifespan and safety in reusable bottle applications.
Table of Comparison
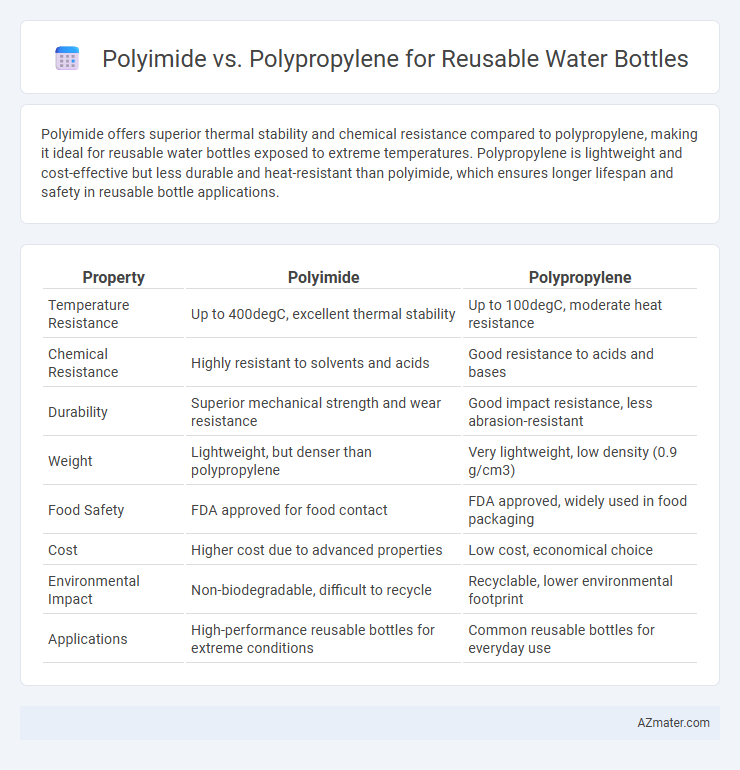
| Property | Polyimide | Polypropylene |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 400degC, excellent thermal stability | Up to 100degC, moderate heat resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Highly resistant to solvents and acids | Good resistance to acids and bases |
| Durability | Superior mechanical strength and wear resistance | Good impact resistance, less abrasion-resistant |
| Weight | Lightweight, but denser than polypropylene | Very lightweight, low density (0.9 g/cm3) |
| Food Safety | FDA approved for food contact | FDA approved, widely used in food packaging |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Low cost, economical choice |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, difficult to recycle | Recyclable, lower environmental footprint |
| Applications | High-performance reusable bottles for extreme conditions | Common reusable bottles for everyday use |
Introduction to Polyimide and Polypropylene
Polyimide is a high-performance polymer known for its exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for reusable water bottles that require durability under extreme conditions. Polypropylene, a widely used thermoplastic polymer, offers excellent chemical resistance, lightweight properties, and low moisture absorption, making it cost-effective and safe for everyday use in water bottles. Comparing both materials, polyimide provides superior heat resistance and longevity, while polypropylene is favored for its affordability and ease of manufacturing.
Material Properties Overview
Polyimide offers exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for reusable water bottles needing durability under extreme conditions. Polypropylene is lightweight, cost-effective, and resistant to moisture and fatigue but has lower heat resistance and mechanical strength compared to polyimide. The choice depends on required performance; polyimide suits high-end, long-lasting bottles, while polypropylene is preferred for everyday, budget-friendly options.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Polyimide offers superior durability and strength compared to polypropylene, making it highly resistant to thermal degradation, impact, and chemical wear in reusable water bottles. Polypropylene provides good strength and flexibility but tends to degrade faster under UV exposure and high temperatures, reducing long-term durability. Polyimide's enhanced mechanical properties and thermal stability ensure longer-lasting performance in demanding environments.
Heat Resistance and Temperature Tolerance
Polyimide outperforms polypropylene in heat resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 400degC compared to polypropylene's limit of around 100degC, making it ideal for reusable water bottles exposed to hot liquids. Its superior thermal stability prevents deformation and chemical leaching under high temperatures, ensuring safety and durability. Polypropylene, while more cost-effective and lightweight, is better suited for cold or room temperature use due to its lower temperature tolerance and risk of warping when exposed to heat.
Chemical Resistance of Each Material
Polyimide exhibits superior chemical resistance, maintaining stability and integrity when exposed to strong acids, bases, and solvents, making it ideal for reusable water bottles used in harsh environments. Polypropylene offers good chemical resistance against many common substances but can degrade over time when exposed to strong acids or organic solvents. For long-term durability and resistance to aggressive chemicals, polyimide is the preferred material due to its robust molecular structure and exceptional inertness.
Safety and Toxicity Concerns
Polyimide offers exceptional chemical resistance and thermal stability, making it a safe choice for reusable water bottles with minimal risk of leaching harmful substances. Polypropylene, commonly used in food containers, is BPA-free and generally considered non-toxic, but it can degrade over time with repeated use and exposure to heat, potentially releasing microplastics. Evaluating safety and toxicity, polyimide provides superior durability and stability, reducing concerns about chemical migration, while polypropylene remains a cost-effective option with acceptable safety when used properly.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyimide offers excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it durable for reusable water bottles but is less commonly recycled due to complex processing requirements and limited recycling infrastructure. Polypropylene is widely used for water bottles because it is lightweight, affordable, and highly recyclable through established municipal systems, contributing to lower environmental impact through easier reuse and recycling. Choosing polypropylene enhances environmental sustainability by enabling efficient recycling and reducing landfill waste compared to polyimide's limited recyclability and higher production energy demands.
Taste and Odor Retention
Polyimide exhibits superior resistance to odor and taste retention compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for reusable water bottles where maintaining beverage purity is crucial. Polyimide's dense molecular structure minimizes chemical leaching and prevents flavor absorption, ensuring beverages taste fresh over time. In contrast, polypropylene often absorbs and retains residual flavors, which can negatively impact the taste of water after repeated use.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Polyimide offers superior heat resistance and chemical stability but comes at a significantly higher manufacturing cost compared to polypropylene, which is more affordable and easier to process through injection molding. Polypropylene's lightweight and flexible nature reduces production time and material expenses, making it a cost-effective choice for mass-produced reusable water bottles. However, polyimide's enhanced durability may justify its premium price for applications requiring extreme temperature tolerance and long-term chemical resistance.
Which Material is Better for Reusable Water Bottles?
Polyimide offers superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and durability, making it ideal for high-performance reusable water bottles that can withstand extreme temperatures and repeated use. Polypropylene is lightweight, cost-effective, and resistant to moisture, but it lacks the high heat resistance and toughness of polyimide, which can limit its lifespan in demanding conditions. For reusable water bottles, polyimide is better suited for long-term durability and performance, whereas polypropylene is more suitable for budget-friendly, everyday use.
Infographic: Polyimide vs Polypropylene for Reusable Water Bottle
 azmater.com
azmater.com