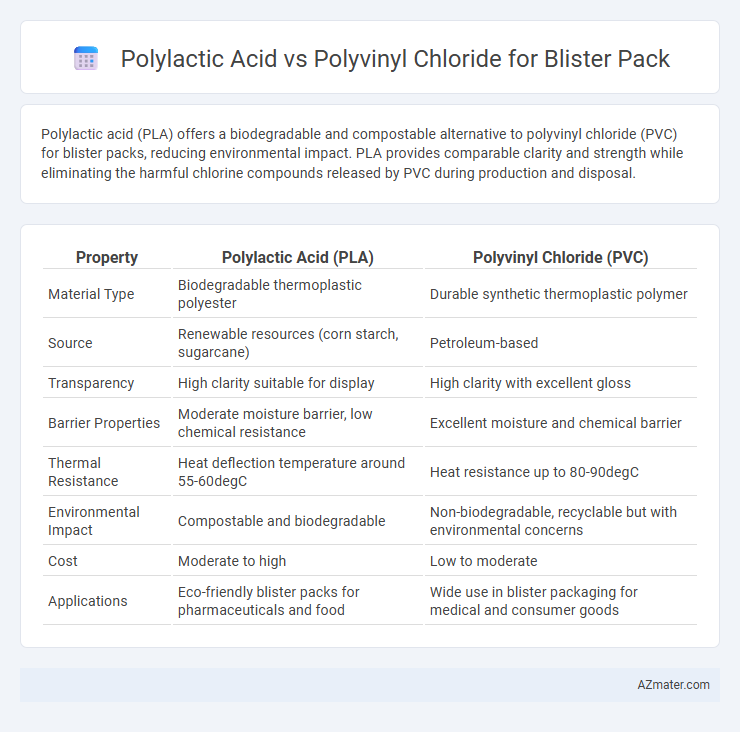
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers a biodegradable and compostable alternative to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) for blister packs, reducing environmental impact. PLA provides comparable clarity and strength while eliminating the harmful chlorine compounds released by PVC during production and disposal.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polylactic Acid (PLA) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Biodegradable thermoplastic polyester | Durable synthetic thermoplastic polymer |
| Source | Renewable resources (corn starch, sugarcane) | Petroleum-based |
| Transparency | High clarity suitable for display | High clarity with excellent gloss |
| Barrier Properties | Moderate moisture barrier, low chemical resistance | Excellent moisture and chemical barrier |
| Thermal Resistance | Heat deflection temperature around 55-60degC | Heat resistance up to 80-90degC |
| Environmental Impact | Compostable and biodegradable | Non-biodegradable, recyclable but with environmental concerns |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
| Applications | Eco-friendly blister packs for pharmaceuticals and food | Wide use in blister packaging for medical and consumer goods |
Introduction to Blister Packaging Materials
Polylactic acid (PLA) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) are prominent materials used in blister packaging due to their distinct properties and environmental impacts. PLA, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offers biodegradability and a lower carbon footprint, making it an eco-friendly option for sustainable packaging solutions. In contrast, PVC, a petroleum-based plastic, provides superior clarity, durability, and chemical resistance, but its non-biodegradable nature and potential health hazards have raised concerns in the packaging industry.
Overview of Polylactic Acid (PLA)
Polylactic acid (PLA) is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources such as corn starch and sugarcane, making it an eco-friendly alternative to traditional plastics. PLA offers excellent clarity, good mechanical strength, and compostability, which is crucial for sustainable blister packaging applications. Its lower environmental impact compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which is derived from non-renewable petroleum and poses recycling challenges, makes PLA increasingly preferred in the packaging industry.
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a widely used plastic in blister packaging due to its excellent clarity, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness. PVC offers strong barrier properties that protect pharmaceuticals from moisture and contamination, ensuring product integrity. However, concerns over environmental impact and recyclability have led to increasing interest in alternative materials like polylactic acid (PLA).
Material Properties: PLA vs PVC
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers excellent biodegradability and is derived from renewable resources, making it an eco-friendly alternative to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which is petroleum-based and non-biodegradable. PLA exhibits good transparency and stiffness but has lower thermal resistance and impact strength compared to PVC, limiting its use in high-temperature or heavy-duty applications. PVC provides superior chemical resistance, flexibility, and durability, making it a more robust choice for blister packs requiring longevity and mechanical performance.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Polylactic acid (PLA) blister packs offer a significantly lower environmental impact compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) due to their biodegradability and derivation from renewable resources like corn starch. PVC blister packs contribute to pollution through the release of toxic chlorine-based compounds during production and disposal, which pose risks to soil and water ecosystems. PLA's compostable nature reduces landfill accumulation and greenhouse gas emissions, making it a more sustainable choice for eco-friendly packaging solutions.
Performance in Blister Pack Applications
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers superior biodegradability and comparable clarity to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) in blister pack applications, making it an eco-friendlier alternative with reduced environmental impact. PVC provides excellent chemical resistance, durability, and moisture barrier properties, ensuring prolonged product shelf life and protection against contamination. Performance in packaging depends on application-specific requirements, with PLA favored for sustainable solutions and PVC preferred for high barrier and strength needs.
Cost Analysis of PLA and PVC
Polylactic acid (PLA) blister packs generally incur higher raw material costs compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), largely due to the biodegradable nature and limited large-scale production of PLA. PVC remains cost-effective because of established manufacturing processes and widespread availability, leading to lower per-unit expenses. However, long-term environmental regulations and disposal costs may affect the overall economic feasibility of PVC in blister packaging applications.
Regulatory and Safety Considerations
Polylactic acid (PLA) is favored in blister pack applications due to its biodegradable nature and compliance with stringent FDA and EU regulations on food contact materials, reducing concerns about toxic additives. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), while widely used for its durability and clarity, faces increasing regulatory scrutiny over harmful plasticizers like phthalates and chlorine-based stabilizers that pose health and environmental risks. Choosing PLA can enhance product safety and sustainability, aligning with global regulatory trends prioritizing non-toxic, eco-friendly packaging solutions.
Market Trends and Industry Adoption
Polylactic acid (PLA) is gaining traction in the blister pack market due to its biodegradable properties and growing consumer demand for sustainable packaging solutions, with global PLA market size projected to reach USD 1.9 billion by 2027. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) remains widely used for blister packs due to its durability, versatility, and cost-efficiency, holding a dominant share of over 45% in the plastic packaging market as of 2023. Industry adoption trends indicate a gradual shift towards PLA in pharmaceutical and food sectors driven by regulatory pressure and environmental concerns, while PVC maintains strong presence where performance and shelf life are prioritized.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Blister Packs
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers biodegradability and compostability, making it an eco-friendly alternative to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which is widely used but poses environmental and health concerns due to its chlorine content and difficulty in recycling. PLA is suitable for brands prioritizing sustainability and regulatory compliance in eco-conscious markets, whereas PVC remains favored for its superior durability, clarity, and cost-effectiveness in traditional packaging applications. Selecting the right material depends on balancing environmental impact, mechanical properties, and regulatory requirements specific to the intended product and market.
Infographic: Polylactic acid vs Polyvinyl chloride for Blister Pack
 azmater.com
azmater.com