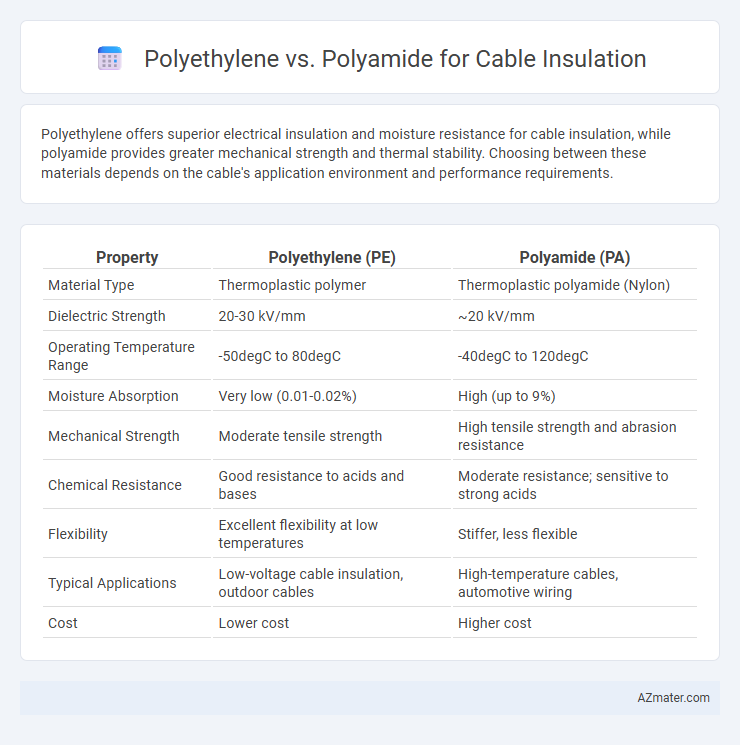
Polyethylene offers superior electrical insulation and moisture resistance for cable insulation, while polyamide provides greater mechanical strength and thermal stability. Choosing between these materials depends on the cable's application environment and performance requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene (PE) | Polyamide (PA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermoplastic polyamide (Nylon) |
| Dielectric Strength | 20-30 kV/mm | ~20 kV/mm |
| Operating Temperature Range | -50degC to 80degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Moisture Absorption | Very low (0.01-0.02%) | High (up to 9%) |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength and abrasion resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and bases | Moderate resistance; sensitive to strong acids |
| Flexibility | Excellent flexibility at low temperatures | Stiffer, less flexible |
| Typical Applications | Low-voltage cable insulation, outdoor cables | High-temperature cables, automotive wiring |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Cable Insulation Materials
Polyethylene and polyamide are two widely used materials for cable insulation, each offering distinct properties suited for various electrical applications. Polyethylene is valued for its excellent electrical insulation, moisture resistance, and low dielectric constant, making it ideal for high-frequency signal cables. Polyamide, known for its superior mechanical strength, thermal resistance, and abrasion resistance, is often chosen for cables exposed to harsh environmental conditions and mechanical stress.
Overview of Polyethylene (PE) in Cable Insulation
Polyethylene (PE) is widely used for cable insulation due to its excellent electrical insulation properties, high dielectric strength, and low moisture absorption. Its chemical resistance and flexibility make it suitable for both indoor and outdoor cable applications, ensuring long-term durability and protection against environmental factors. PE's low dielectric constant minimizes signal loss, making it ideal for high-frequency and telecom cables.
Overview of Polyamide (PA) in Cable Insulation
Polyamide (PA), commonly known as nylon, offers excellent mechanical strength, abrasion resistance, and thermal stability, making it a reliable choice for cable insulation in harsh environments. Its superior resistance to chemicals, moisture, and heat extends the durability and performance of cables used in automotive, industrial, and telecommunications applications. Polyamide's inherent flexibility and high dielectric strength ensure efficient electrical insulation while maintaining resilience against physical stresses.
Key Physical Properties: Polyethylene vs Polyamide
Polyethylene exhibits excellent electrical insulation properties, low moisture absorption, and superior chemical resistance, making it ideal for cable insulation in harsh environments. Polyamide offers higher mechanical strength, better thermal resistance up to 150degC, and greater abrasion resistance, suitable for applications requiring durability under stress. The choice between polyethylene and polyamide depends on balancing flexibility, temperature tolerance, and environmental exposure specific to the cable's operational demands.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Polyethylene (PE) offers excellent thermal stability with a maximum continuous operating temperature around 90degC, making it suitable for standard cable insulation applications. Polyamide (nylon), however, exhibits superior thermal performance, withstanding temperatures up to 150degC, which enhances cable durability in high-heat environments. The higher melting point and thermal resistance of polyamide contribute to improved safety and longevity in demanding electrical installations.
Electrical Insulation Capabilities
Polyethylene offers excellent electrical insulation due to its low dielectric constant and high resistivity, making it ideal for high-voltage cable applications. Polyamide provides good mechanical strength and thermal resistance but generally has higher dielectric losses compared to polyethylene. For optimal electrical insulation performance, polyethylene is preferred in environments requiring superior dielectric properties and minimal signal attenuation.
Chemical and Environmental Resistance
Polyethylene exhibits superior chemical resistance against acids, bases, and solvents, making it highly suitable for cable insulation in harsh chemical environments. Polyamide (nylon) offers excellent resistance to abrasion and mechanical stress but is more susceptible to hydrolysis and degradation when exposed to moisture and certain chemicals. Polyethylene's low water absorption and strong environmental resistance ensure longer cable lifespan in outdoor and wet conditions compared to polyamide.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility Analysis
Polyethylene offers excellent flexibility and moderate mechanical strength, making it suitable for applications requiring bendability and resistance to impact. Polyamide provides superior mechanical strength and abrasion resistance combined with good flexibility, ideal for demanding environments with mechanical stress. The choice between polyethylene and polyamide for cable insulation depends on balancing flexibility needs against mechanical durability requirements in the intended use case.
Cost and Availability Factors
Polyethylene offers a cost-effective solution for cable insulation due to its widespread availability and lower raw material expenses compared to polyamide. Polyamide materials, while providing superior mechanical and thermal properties, tend to have higher production costs and less consistent market availability. Choosing polyethylene can significantly reduce initial investment and ease procurement challenges in large-scale cable manufacturing projects.
Application Suitability: Choosing the Right Material
Polyethylene offers excellent electrical insulation properties and moisture resistance, making it ideal for outdoor and underground cable applications where environmental durability is crucial. Polyamide, known for its superior mechanical strength and thermal resistance, suits cables exposed to higher temperatures and mechanical stress, such as in automotive and industrial environments. Selecting the right material depends on specific use-case requirements like temperature range, environmental exposure, and mechanical demands to ensure optimal cable performance and longevity.
Infographic: Polyethylene vs Polyamide for Cable Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com