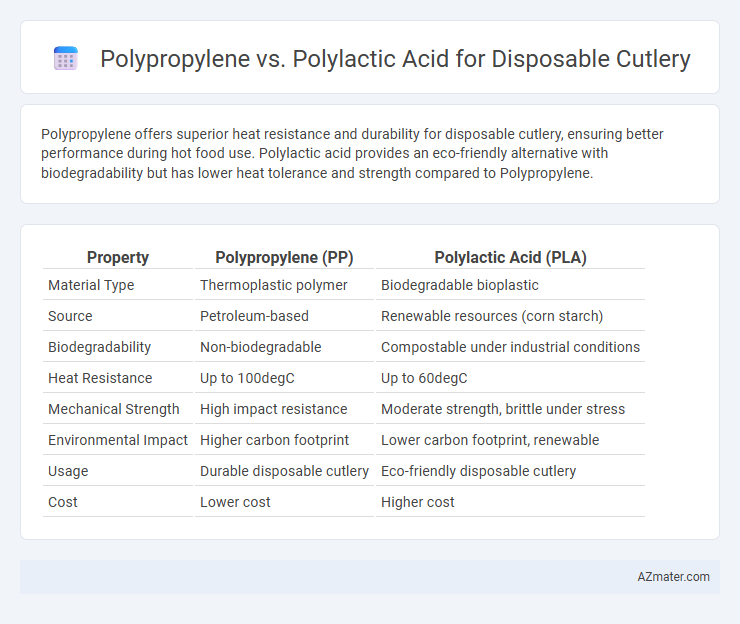
Polypropylene offers superior heat resistance and durability for disposable cutlery, ensuring better performance during hot food use. Polylactic acid provides an eco-friendly alternative with biodegradability but has lower heat tolerance and strength compared to Polypropylene.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polypropylene (PP) | Polylactic Acid (PLA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Biodegradable bioplastic |
| Source | Petroleum-based | Renewable resources (corn starch) |
| Biodegradability | Non-biodegradable | Compostable under industrial conditions |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 100degC | Up to 60degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High impact resistance | Moderate strength, brittle under stress |
| Environmental Impact | Higher carbon footprint | Lower carbon footprint, renewable |
| Usage | Durable disposable cutlery | Eco-friendly disposable cutlery |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Disposable Cutlery Materials
Polypropylene (PP) and Polylactic Acid (PLA) are prominent materials used in disposable cutlery manufacturing due to their distinct properties and environmental impacts. Polypropylene is a durable, lightweight thermoplastic known for its high melting point and resistance to chemicals, making it ideal for hot and cold food applications. Polylactic Acid, a biodegradable polymer derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offers compostability but generally has lower heat resistance compared to polypropylene.
Overview of Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene (PP) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer known for its durability, chemical resistance, and high melting point, making it ideal for disposable cutlery manufacturing. Its lightweight nature and cost-effectiveness contribute significantly to its popularity in single-use food service products. PP's resistance to grease and moisture ensures reliable performance, while its recyclability aligns with sustainable waste management practices.
Overview of Polylactic Acid (PLA)
Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane, making it an eco-friendly alternative to conventional plastics such as polypropylene. PLA offers excellent clarity, rigidity, and compostability under industrial conditions, which makes it highly suitable for disposable cutlery applications aimed at reducing plastic waste. Its lower carbon footprint and ability to break down into non-toxic components contribute significantly to sustainable product development in the foodservice industry.
Manufacturing Processes: PP vs PLA
Polypropylene (PP) disposable cutlery is produced through injection molding, a process characterized by high-temperature melting of polypropylene pellets, enabling rapid mass production with consistent structural integrity and heat resistance. Polylactic Acid (PLA) cutlery manufacturing involves injection molding as well, but requires more precise temperature control due to PLA's lower melting point and sensitivity to thermal degradation, which can affect mechanical properties and biodegradability. PP's lower production cost and thermal stability contrast with PLA's renewable origin and compostability, making the choice dependent on environmental focus and processing capabilities.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Polypropylene (PP) exhibits superior strength and durability compared to Polylactic Acid (PLA), making it a more resilient choice for disposable cutlery under heavy use. PP resists moisture and high temperatures better, preventing warping or degradation during hot food consumption, while PLA tends to soften and lose structural integrity when exposed to heat or prolonged use. The mechanical robustness and longer shelf-life of PP products contribute to a more reliable disposable cutlery option in demanding environments.
Heat Resistance and Performance
Polypropylene (PP) offers superior heat resistance up to 100-120degC, making it suitable for hot food applications, while polylactic acid (PLA) softens around 60degC and is prone to deformation under high temperatures. The performance of PP in disposable cutlery ensures rigidity and durability during use, whereas PLA, derived from renewable resources, provides eco-friendliness but compromises strength and heat tolerance. For applications demanding heat resistance and reliable structural integrity, polypropylene outperforms polylactic acid in disposable cutlery manufacturing.
Environmental Impact: Biodegradability and Compostability
Polypropylene (PP) offers durability and cost-effectiveness but is non-biodegradable, contributing to persistent plastic pollution in landfills and oceans. Polylactic Acid (PLA), derived from renewable resources such as corn starch, is both biodegradable and industrially compostable, breaking down into non-toxic components under controlled composting conditions. The environmental advantage of PLA lies in its reduced carbon footprint and ability to decompose, contrasting with the long-term ecological impact of polypropylene-based disposable cutlery.
Cost Analysis: PP vs PLA Cutlery
Polypropylene (PP) cutlery typically costs 20-40% less than Polylactic Acid (PLA) counterparts due to lower raw material and manufacturing expenses. While PP is derived from petroleum, enabling mass production economies, PLA relies on renewable resources like corn starch, driving higher pricing. Cost analysis reveals PP as a more budget-friendly option for disposable cutlery, though PLA offers environmental benefits that may justify its premium in sustainable markets.
Consumer Safety and Regulatory Considerations
Polypropylene (PP) is widely recognized for its chemical resistance and heat tolerance, making it a safe choice for disposable cutlery that meets FDA and EFSA food contact regulations. Polylactic Acid (PLA), derived from renewable resources, offers biodegradability but has limitations in heat resistance and may release lactic acid under high temperatures, necessitating strict compliance with compostability standards like EN 13432. Consumer safety assessments emphasize PP's stability in hot food applications, while PLA requires careful monitoring of degradation products and certification under regulatory frameworks to ensure non-toxicity during use.
Choosing the Right Material for Disposable Cutlery
Polypropylene offers durability, heat resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for disposable cutlery requiring strength and thermal stability during use. Polylactic Acid (PLA), derived from renewable resources like corn starch, provides biodegradability and compostability, appealing to eco-conscious consumers seeking sustainable alternatives. Selecting the right material depends on balancing environmental impact, mechanical performance, and cost, with polypropylene favored for robustness and PLA chosen for biodegradability in disposable utensils.
Infographic: Polypropylene vs Polylactic Acid for Disposable Cutlery
 azmater.com
azmater.com