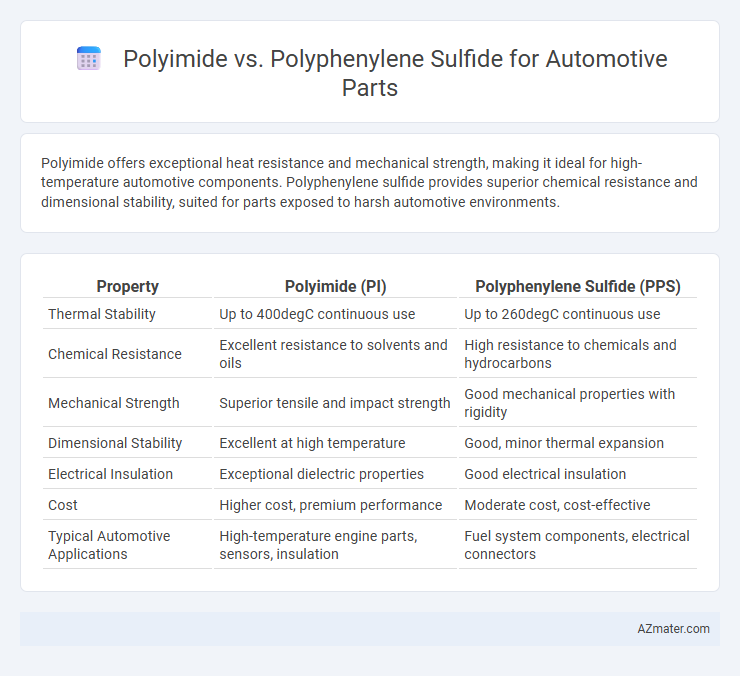
Polyimide offers exceptional heat resistance and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-temperature automotive components. Polyphenylene sulfide provides superior chemical resistance and dimensional stability, suited for parts exposed to harsh automotive environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyimide (PI) | Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | Up to 400degC continuous use | Up to 260degC continuous use |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to solvents and oils | High resistance to chemicals and hydrocarbons |
| Mechanical Strength | Superior tensile and impact strength | Good mechanical properties with rigidity |
| Dimensional Stability | Excellent at high temperature | Good, minor thermal expansion |
| Electrical Insulation | Exceptional dielectric properties | Good electrical insulation |
| Cost | Higher cost, premium performance | Moderate cost, cost-effective |
| Typical Automotive Applications | High-temperature engine parts, sensors, insulation | Fuel system components, electrical connectors |
Introduction to High-Performance Polymers in Automotive Applications
High-performance polymers such as polyimide and polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) are increasingly utilized in automotive parts due to their exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength. Polyimide offers superior heat resistance exceeding 400degC, making it ideal for under-the-hood components exposed to extreme temperatures. PPS provides a balance of dimensional stability and corrosion resistance, enhancing the durability and performance of automotive fuel system parts and electrical connectors.
Overview of Polyimide: Properties and Uses
Polyimide is a high-performance polymer distinguished by exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for demanding automotive applications. Its excellent dielectric properties and ability to maintain structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 300degC enable use in engine components, electrical insulation, and under-the-hood parts. Polyimide's versatility also supports lightweight design initiatives and enhances durability in harsh automotive environments.
Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS): Key Features and Applications
Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) is highly valued in automotive parts manufacturing due to its exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, enabling it to withstand harsh under-the-hood environments. Its low moisture absorption and excellent dimensional stability make PPS ideal for precision components such as fuel system parts, electrical connectors, and sensor housings. Compared to polyimide, PPS offers a cost-effective solution with easier processing while maintaining superior performance in high-temperature and chemically aggressive automotive applications.
Thermal Stability: Polyimide vs Polyphenylene Sulfide
Polyimide exhibits superior thermal stability with continuous use temperatures up to 400degC, making it ideal for high-heat automotive environments such as engine components and under-hood applications. Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) maintains thermal stability up to approximately 260degC, offering excellent resistance to heat but with lower continuous service temperatures compared to polyimide. The higher decomposition temperature and excellent thermal oxidative resistance of polyimide make it preferable over PPS where extreme thermal durability is critical in automotive parts.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Polyimide demonstrates superior mechanical strength with high tensile and flexural strength, making it ideal for automotive parts subjected to intense stress and thermal cycling. Polyphenylene Sulfide offers excellent chemical resistance and dimensional stability but generally exhibits lower impact resistance and mechanical toughness compared to Polyimide. The enhanced durability of Polyimide under high temperatures up to 400degC favors its use in critical automotive components exposed to severe operating conditions.
Chemical Resistance: Evaluating Polyimide and PPS
Polyimide exhibits exceptional chemical resistance against a wide range of solvents, fuels, and lubricants commonly encountered in automotive environments, maintaining stability at high temperatures up to 400degC. Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) offers superior resistance to acids, bases, and oxidative chemicals while retaining good mechanical properties at elevated temperatures around 260degC. When selecting materials for automotive parts, Polyimide is preferred for extreme thermal and chemical conditions, whereas PPS balances cost-effectiveness with strong resistance to aggressive automotive fluids.
Processing and Manufacturability for Automotive Parts
Polyimide offers excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance but requires high-temperature processing methods such as compression molding or extrusion at temperatures typically above 300degC, which can increase production complexity and cost for automotive parts. Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) provides easier manufacturability due to its ability to be processed through conventional injection molding at lower temperatures around 280degC, enabling faster cycle times and cost-effective mass production. The choice between polyimide and PPS depends on specific automotive application requirements, balancing the need for superior performance against processing efficiency and manufacturability constraints.
Cost Analysis: Polyimide vs PPS in Automotive Manufacturing
Polyimide exhibits superior thermal stability and mechanical strength compared to polyphenylene sulfide (PPS), but its higher raw material and processing costs impact overall automotive manufacturing budgets. PPS offers cost efficiency due to lower material expenses and easier moldability, making it preferable for high-volume automotive parts production. Manufacturers must balance performance requirements with budget constraints when selecting polyimide or PPS for automotive components.
Typical Automotive Components Using Polyimide and PPS
Polyimide is commonly used in automotive applications such as flexible wiring insulation, high-temperature gaskets, and sensor components due to its exceptional thermal stability and dielectric properties. Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) is favored for fuel system parts, electrical connectors, and under-the-hood components because of its chemical resistance and dimensional stability under heat. Both polymers are integral to automotive part manufacturing where high-performance materials are required to withstand extreme operating conditions.
Final Considerations: Choosing the Right Polymer for Automotive Applications
Polyimide offers exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature automotive components exposed to harsh environments. Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) provides excellent dimensional stability and solvent resistance, suitable for parts requiring mechanical strength and chemical durability at moderate temperatures. Selecting the right polymer depends on specific application demands: Polyimide excels in extreme conditions, whereas PPS delivers cost-effective performance in less severe automotive settings.
Infographic: Polyimide vs Polyphenylene Sulfide for Automotive Part
 azmater.com
azmater.com