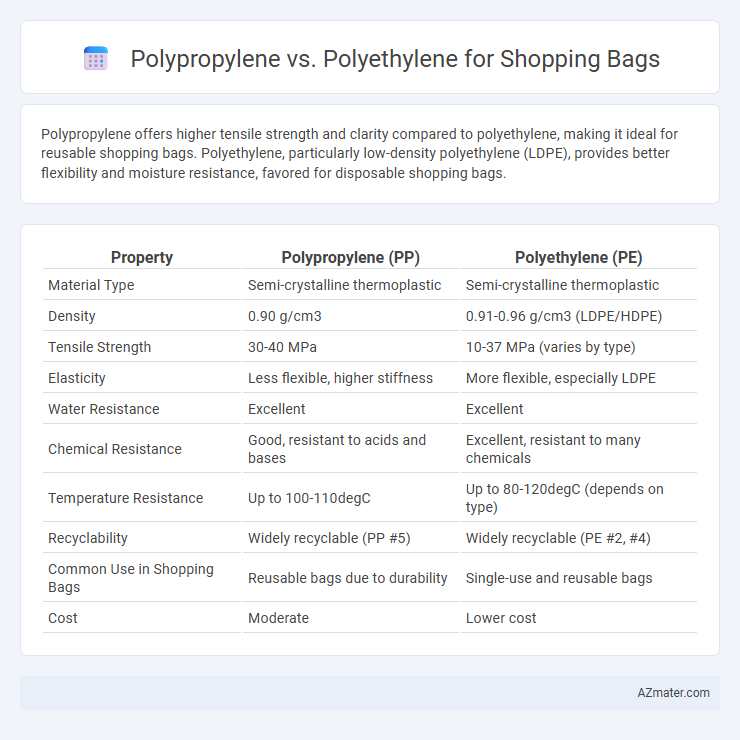
Polypropylene offers higher tensile strength and clarity compared to polyethylene, making it ideal for reusable shopping bags. Polyethylene, particularly low-density polyethylene (LDPE), provides better flexibility and moisture resistance, favored for disposable shopping bags.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polypropylene (PP) | Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Semi-crystalline thermoplastic | Semi-crystalline thermoplastic |
| Density | 0.90 g/cm3 | 0.91-0.96 g/cm3 (LDPE/HDPE) |
| Tensile Strength | 30-40 MPa | 10-37 MPa (varies by type) |
| Elasticity | Less flexible, higher stiffness | More flexible, especially LDPE |
| Water Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
| Chemical Resistance | Good, resistant to acids and bases | Excellent, resistant to many chemicals |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 100-110degC | Up to 80-120degC (depends on type) |
| Recyclability | Widely recyclable (PP #5) | Widely recyclable (PE #2, #4) |
| Common Use in Shopping Bags | Reusable bags due to durability | Single-use and reusable bags |
| Cost | Moderate | Lower cost |
Introduction to Polypropylene and Polyethylene
Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its rigidity, high melting point, and excellent chemical resistance, making it ideal for reusable shopping bags due to durability and lightweight properties. Polyethylene (PE), particularly low-density polyethylene (LDPE) and high-density polyethylene (HDPE), is widely used for single-use and reusable shopping bags because of its flexibility, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Both polymers are preferred materials in the shopping bag industry, with PP offering higher strength and HDPE providing superior stretch and tear resistance.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Polypropylene (PP) is composed of repeating propylene monomers with a methyl group attached to every other carbon atom, giving it a semi-crystalline structure that provides high tensile strength and resistance to fatigue, ideal for durable shopping bags. Polyethylene (PE), primarily made of ethylene monomers, has a simpler linear or branched hydrocarbon chain, resulting in varying densities such as low-density polyethylene (LDPE) and high-density polyethylene (HDPE), each offering different flexibility and toughness for shopping bag applications. The distinct chemical structures affect their melting points, with PP typically around 160-170degC and PE ranging from 105-135degC, influencing their heat resistance and recyclability in packaging.
Manufacturing Processes
Polypropylene shopping bags are produced using spunbond or extrusion blow molding techniques, which provide high tensile strength and durability, ideal for reusable bags. Polyethylene shopping bags, commonly made through blown film extrusion, offer flexibility and lightweight properties, making them suitable for single-use or lightweight carrier bags. Manufacturing polypropylene involves higher melting temperatures (around 160-170degC) compared to polyethylene (about 115-135degC), influencing energy consumption and process efficiency.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Polypropylene shopping bags exhibit higher tensile strength and better resistance to stress compared to polyethylene bags, making them more durable for heavy loads. Polyethylene bags, especially high-density polyethylene (HDPE), offer good flexibility but tend to tear more easily under strain. The molecular structure of polypropylene provides enhanced resistance to wear and environmental factors, resulting in longer-lasting shopping bags.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polypropylene shopping bags generate less carbon dioxide during production compared to polyethylene bags, making them a more environmentally friendly choice. Polyethylene bags, particularly single-use variants, contribute significantly to plastic pollution due to their slow biodegradation rates, whereas reusable polypropylene bags reduce waste by offering higher durability and longer product life cycles. Biodegradable options made from polyethylene blends are emerging, but neither material fully addresses marine pollution concerns, emphasizing the need for effective recycling and responsible consumer behavior.
Cost Efficiency for Retailers
Polypropylene offers better cost efficiency for retailers due to its lower production costs and higher durability compared to polyethylene, resulting in longer-lasting shopping bags that reduce replacement frequency. Polyethylene bags, while cheaper upfront, tend to tear more easily, leading to increased expenses from frequent restocking and customer complaints. Choosing polypropylene enhances overall value by balancing affordability with product longevity, optimizing retailer expenditure on shopping bags.
Reusability and Recycling Options
Polypropylene shopping bags offer higher durability and better reusability than polyethylene bags, making them ideal for multiple uses. Polyethylene bags, particularly low-density types, are more prone to tearing but are widely accepted in recycling programs due to their simpler polymer structure. Recycling of polypropylene is less common but increasing with advancements in sorting technologies, enhancing its sustainability profile for eco-conscious consumers.
Printability and Customization Features
Polypropylene offers superior printability for shopping bags due to its smooth surface, which allows for sharper and more vibrant graphics compared to polyethylene. Polyethylene bags, especially low-density types, tend to have a waxy texture that can cause ink to smear or fade, limiting customization options. Customization features on polypropylene bags include a wider range of color options and compatibility with various printing techniques like flexographic and screen printing, making them ideal for detailed branding.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Polypropylene shopping bags are favored by consumers for their durability, lightweight nature, and resistance to moisture, making them ideal for repeated use. Polyethylene bags, especially low-density variants, are preferred for their flexibility and cost-effectiveness, though concerns over environmental impact drive shifts toward biodegradable options. Market trends indicate a growing consumer demand for sustainable materials, boosting the popularity of reusable polypropylene bags while regulatory pressures reduce polyethylene bag usage in retail sectors.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Shopping Bags
Polypropylene offers superior strength, durability, and resistance to moisture, making it ideal for reusable shopping bags that require long-term use. Polyethylene, while more cost-effective and flexible, is generally suited for lightweight, disposable bags but lacks the robustness needed for heavy or repeated use. Selecting polypropylene optimizes sustainability and usability, whereas polyethylene serves budget-conscious, short-term applications effectively.
Infographic: Polypropylene vs Polyethylene for Shopping bag
 azmater.com
azmater.com