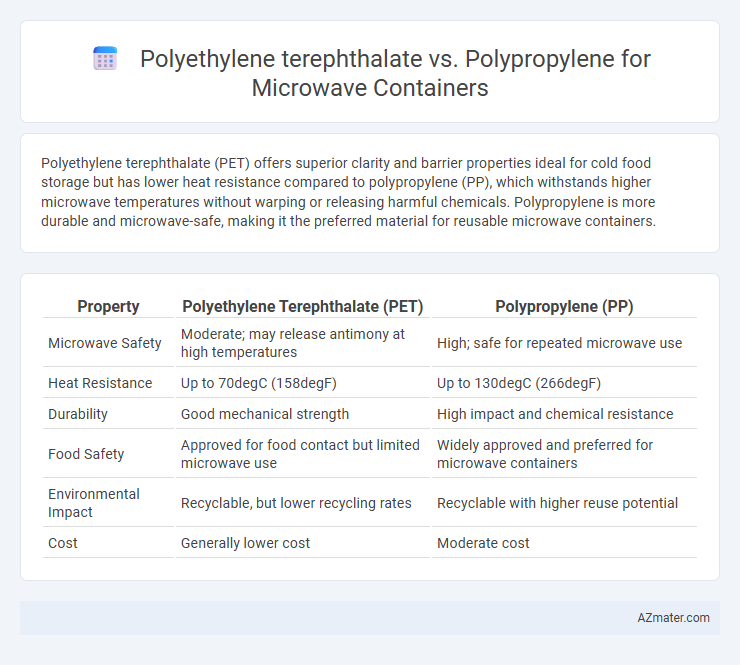
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior clarity and barrier properties ideal for cold food storage but has lower heat resistance compared to polypropylene (PP), which withstands higher microwave temperatures without warping or releasing harmful chemicals. Polypropylene is more durable and microwave-safe, making it the preferred material for reusable microwave containers.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Microwave Safety | Moderate; may release antimony at high temperatures | High; safe for repeated microwave use |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 70degC (158degF) | Up to 130degC (266degF) |
| Durability | Good mechanical strength | High impact and chemical resistance |
| Food Safety | Approved for food contact but limited microwave use | Widely approved and preferred for microwave containers |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, but lower recycling rates | Recyclable with higher reuse potential |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Moderate cost |
Overview of Microwave-Safe Plastics
Microwave-safe plastics such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polypropylene (PP) vary significantly in heat resistance and chemical leachability. Polypropylene boasts higher melting points around 160degC, making it more suitable for microwave use without deformation or release of harmful substances, whereas PET softens at lower temperatures near 260degC but is less commonly recommended for repeated microwave exposure due to potential degradation. Regulatory bodies like the FDA classify PP as microwave-safe, ensuring minimal risk in food containers, while PET is primarily used for cold or room temperature applications due to its limited thermal stability in microwaves.
What is Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)?
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) is a thermoplastic polymer widely used in packaging, including microwave containers, due to its excellent clarity, strength, and barrier properties against moisture and gases. Its high melting point and chemical resistance make PET suitable for reheating food, providing safety and durability during microwave use. Compared to polypropylene, PET offers superior transparency but generally lower heat resistance, affecting its performance in prolonged microwave exposure.
What is Polypropylene (PP)?
Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its high melting point and excellent chemical resistance, making it ideal for microwave containers. Unlike polyethylene terephthalate (PET), PP withstands repeated heating without warping or releasing harmful substances, ensuring food safety and durability. Its lightweight nature and ability to retain shape under heat make polypropylene a preferred material for microwave-safe packaging.
Heat Resistance of PET vs PP in the Microwave
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) typically withstands microwave temperatures up to 120degC, while polypropylene (PP) can endure higher temperatures, often around 140degC to 160degC, making PP more heat-resistant for microwave container applications. PET containers may deform or release harmful substances when exposed to extended microwave heating, whereas PP maintains structural integrity and safety under higher heat conditions. The superior thermal stability of PP ensures better performance and durability in microwave use compared to PET.
Chemical Stability and Food Safety Comparison
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polypropylene (PP) differ significantly in chemical stability and food safety when used for microwave containers. PP exhibits superior heat resistance and maintains chemical stability at high microwave temperatures without leaching harmful substances, making it safer for repeated microwave use. PET, while durable under normal conditions, can release antimony and other potential toxins when exposed to microwave heating, raising concerns about food safety during prolonged or high-temperature use.
Durability and Reusability Implications
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers moderate durability for microwave containers but tends to degrade faster with repeated heating cycles, limiting its long-term reusability. Polypropylene (PP) exhibits superior heat resistance and maintains structural integrity after multiple microwave uses, making it more durable and suitable for repeated applications. The chemical stability and enhanced thermal resilience of PP significantly reduce risks of warping or leaching, thereby extending the functional lifespan of microwave containers compared to PET.
Impact on Food Flavor and Quality
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior clarity and resistance to odors, minimizing the leaching of chemicals that can alter food flavor during microwave heating. Polypropylene (PP) exhibits high thermal stability and low migration rates, preserving food quality while preventing contamination from plasticizers or additives. Studies show PP containers maintain the original taste and nutritional value of microwaved food better than PET, making PP a preferred choice for microwave-safe packaging.
Environmental Considerations: Recycling PET and PP
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polypropylene (PP) both offer unique environmental advantages for microwave containers, yet PET is more widely recycled due to established global systems and a higher recycling rate exceeding 30%. Polypropylene, while less commonly recycled, provides benefits such as lower energy consumption in production and greater chemical resistance, which can extend product life and reduce waste. Effective recycling programs and innovations in sorting technology are crucial to improving the sustainability of both PET and PP microwave containers by minimizing landfill impact and enabling material recovery.
Cost and Availability for Consumers and Manufacturers
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) generally costs more than polypropylene (PP) due to its more complex manufacturing process and raw material expenses, impacting consumer prices for microwave containers. Polypropylene offers greater availability and lower production costs, making it a popular choice among manufacturers for microwave-safe containers. Both materials meet safety standards, but PP's affordability and widespread supply dominate the market in cost-sensitive applications.
Which is Better for Microwave Containers: PET or PP?
Polypropylene (PP) is generally better suited for microwave containers than Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) due to its higher heat resistance, typically withstanding temperatures up to 120degC without warping or releasing harmful chemicals. PET tends to soften at lower temperatures around 70-80degC, making it less stable for microwave use and potentially leading to leaching of antimony-based compounds. For safer and more durable microwave container performance, PP's chemical stability and ability to endure repeated heating cycles make it the preferred choice.
Infographic: Polyethylene terephthalate vs Polypropylene for Microwave Container
 azmater.com
azmater.com