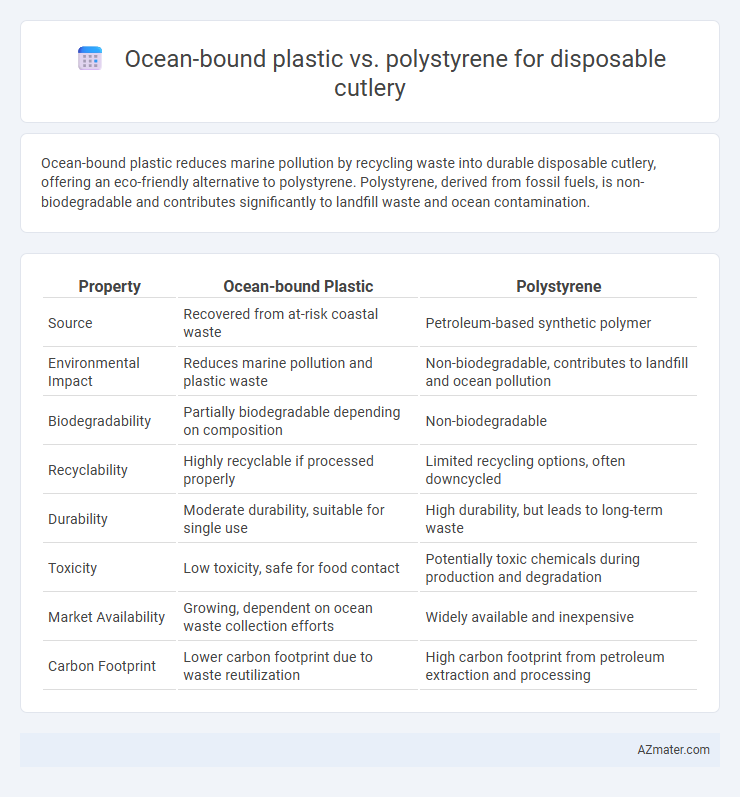
Ocean-bound plastic reduces marine pollution by recycling waste into durable disposable cutlery, offering an eco-friendly alternative to polystyrene. Polystyrene, derived from fossil fuels, is non-biodegradable and contributes significantly to landfill waste and ocean contamination.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ocean-bound Plastic | Polystyrene |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Recovered from at-risk coastal waste | Petroleum-based synthetic polymer |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces marine pollution and plastic waste | Non-biodegradable, contributes to landfill and ocean pollution |
| Biodegradability | Partially biodegradable depending on composition | Non-biodegradable |
| Recyclability | Highly recyclable if processed properly | Limited recycling options, often downcycled |
| Durability | Moderate durability, suitable for single use | High durability, but leads to long-term waste |
| Toxicity | Low toxicity, safe for food contact | Potentially toxic chemicals during production and degradation |
| Market Availability | Growing, dependent on ocean waste collection efforts | Widely available and inexpensive |
| Carbon Footprint | Lower carbon footprint due to waste reutilization | High carbon footprint from petroleum extraction and processing |
Introduction to Disposable Cutlery Materials
Disposable cutlery is commonly made from materials such as polystyrene and increasingly from ocean-bound plastics, which are repurposed waste collected near coastlines. Polystyrene is a lightweight, cost-effective plastic used widely for disposable forks, spoons, and knives but is non-biodegradable and contributes significantly to landfill pollution. Ocean-bound plastic offers an eco-friendly alternative by reducing marine litter and promoting plastic waste recovery while maintaining functional durability for single-use utensils.
What is Ocean-Bound Plastic?
Ocean-bound plastic refers to plastic waste collected within 50 kilometers of coastlines that is at high risk of entering marine environments, often gathered before reaching the ocean. This material is increasingly used to produce eco-friendly disposable cutlery, offering a sustainable alternative to conventional polystyrene, which is non-biodegradable and contributes to long-term pollution. Utilizing ocean-bound plastic reduces marine debris and promotes circular economy practices in single-use utensil manufacturing.
Understanding Polystyrene in Disposable Cutlery
Polystyrene, a petroleum-based plastic commonly used for disposable cutlery, is lightweight but notoriously difficult to recycle, often contributing to environmental pollution. Unlike ocean-bound plastic, which diverts waste from marine environments by repurposing collected debris, polystyrene fragments easily, leading to microplastic contamination in oceans. Understanding the chemical stability and low biodegradability of polystyrene highlights the urgent need for eco-friendly alternatives in disposable cutlery manufacturing.
Environmental Impact: Ocean-Bound Plastic vs Polystyrene
Ocean-bound plastic disposable cutlery significantly reduces marine pollution by diverting plastic waste from oceans and coastlines, promoting circular economy practices. Polystyrene cutlery, on the other hand, poses severe environmental hazards due to its non-biodegradable nature and tendency to fragment into microplastics, which harm marine life and ecosystems. Using ocean-bound plastic supports sustainable waste management and lowers the carbon footprint compared to the production and disposal impacts of polystyrene.
Decomposition Rates in Marine and Landfill Environments
Ocean-bound plastic cutlery decomposes significantly faster than polystyrene in both marine and landfill environments, often breaking down within 1 to 3 years compared to polystyrene's persistence for over 500 years. Polystyrene's dense molecular structure resists microbial activity, leading to prolonged environmental pollution and accumulation in oceans and landfills. Marine degradation rates for ocean-bound plastics are accelerated by exposure to UV light and saltwater, making them a more sustainable option for disposable cutlery in terms of reducing long-term ecological impact.
Manufacturing Processes and Resource Use
Ocean-bound plastic for disposable cutlery is manufactured using recycled plastic waste collected near coastlines, reducing reliance on virgin materials and lowering carbon emissions associated with plastic production. Polystyrene cutlery is produced from petroleum-based raw materials through polymerization, involving energy-intensive processes and significant fossil fuel consumption. The use of ocean-bound plastic supports circular economy principles by repurposing existing waste, whereas polystyrene production contributes to resource depletion and environmental pollution due to its non-biodegradable nature.
Health and Safety Considerations
Ocean-bound plastic cutlery reduces environmental toxicity by repurposing waste with fewer chemical additives compared to polystyrene, which can leach harmful styrene and toxic additives during use. Polystyrene disposable cutlery poses health risks such as potential endocrine disruption and respiratory issues from exposure to styrene vapors, especially when heated or in contact with hot foods. Ocean-bound plastic alternatives generally offer safer usage by minimizing direct exposure to hazardous chemicals commonly associated with polystyrene, making them more favorable for consumer health and safety.
Cost Comparison: Ocean-Bound Plastic vs Polystyrene
Ocean-bound plastic disposable cutlery typically costs 20-30% more than traditional polystyrene due to the sourcing and recycling processes involved. Polystyrene remains cheaper because of low production costs and widespread manufacturing infrastructure. However, ocean-bound plastic offers long-term environmental savings by reducing marine pollution and supporting circular economy initiatives.
Consumer Perception and Market Trends
Ocean-bound plastic disposable cutlery gains consumer favor due to its eco-friendly image and growing awareness of marine pollution, driving demand in sustainable product markets. Polystyrene cutlery faces declining market share as consumers increasingly associate it with environmental harm and non-biodegradability. Trends indicate a shift towards biodegradable and recycled materials, with ocean-bound plastic positioned as a preferred alternative in green consumer segments.
Future Outlook and Sustainable Alternatives
Ocean-bound plastic offers a promising sustainable alternative to polystyrene for disposable cutlery by significantly reducing marine pollution and lowering carbon footprints during production. Innovations in biodegradable polymers and advances in recycling technologies aim to enhance the durability and environmental compatibility of ocean-bound plastic cutlery. Future outlooks emphasize increased adoption of circular economy principles and regulatory support to phase out polystyrene waste and promote eco-friendly materials in the foodservice industry.
Infographic: Ocean-bound plastic vs Polystyrene for Disposable cutlery
 azmater.com
azmater.com